Configuration
Configurations ensure that the system reflects your business processes and requirements. By setting up these options correctly, you can:
Standardise data entry across teams
Control what appears on customer‑facing documents
Automate calculations such as charges or discounts
Maintain consistency across modules
Using a Configuration Screen
This is the standard layout you’ll encounter across most Configuration screens. While many of these screens are simple and straightforward, some include additional detail that can be accessed through clickable links when complex configuration is available.
Locating Configuration Modules
Each module in Latner such as Sales, Rental, Equipment, Service, Stock, Customers, Suppliers, Financials, and Security has its own Configuration menu. Within this menu, you’ll find a drop-down list of all configuration screens specific to that module.

For example:
In the Rental module, configuration screens may include settings for rental rates, packages, or setting up data relating Rental Contract / Quote changes such as Stand Downs, Cancellation.
In the Equipment module, configuration screens may include categories, fuel-types or reasons relating Equipment changes such as Transfers, Disposal, Adjustment.
Navigating through Configuration Screens
There are two types of configuration screens in the system: Basic and Detailed.
Basic Configuration Screen
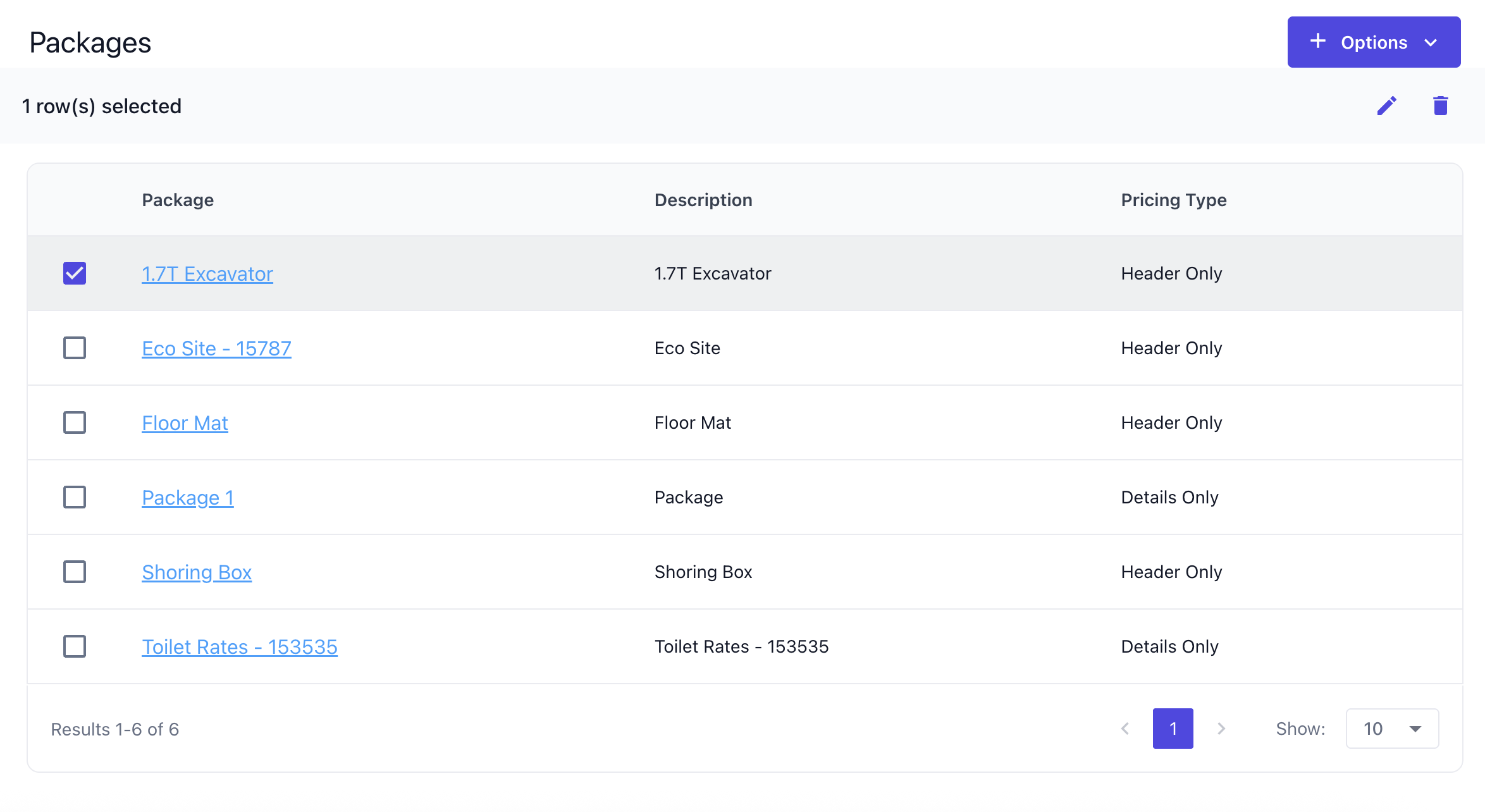
The basic configuration screen displays a straightforward list of data that can be managed. If links are available, clicking them will open the detailed configuration screen. New entries can be added through the Options menu, while some screens also allow editing or deleting existing entries by selecting the checkbox and using the corresponding icons.![]()
Detailed Configuration Screen
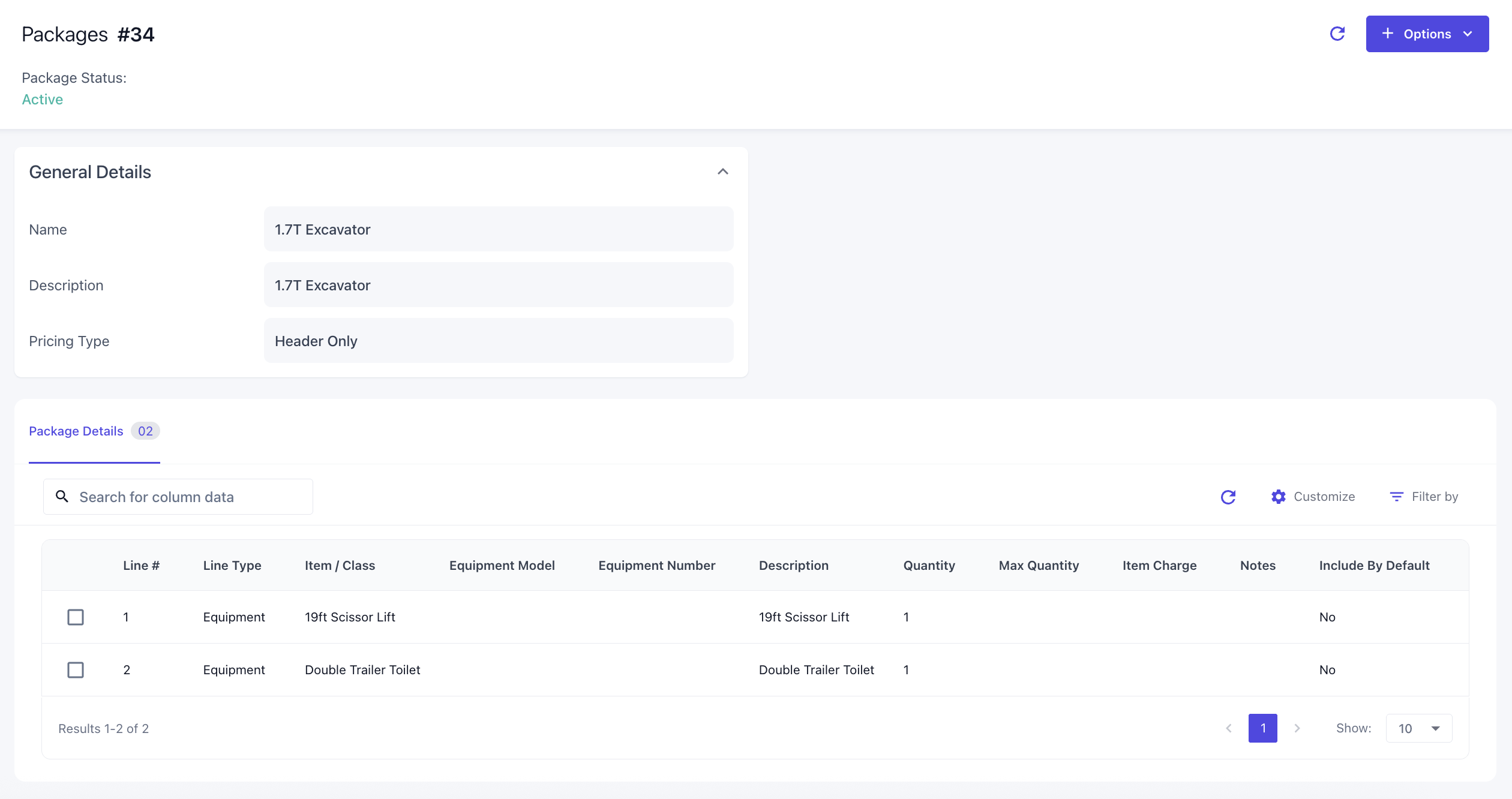
Once you click on a link, it will open the specific record you want to configure. Depending on the screen, this may include general information on the top left, more specific configuration fields on the top right, and detail configurable lines on the bottom that can be configured as required. Options menu let you add more of the detail configurable lines within that configuration.
Using an Integration Screen
You will most likely also run into Integration Screens within the Configurations to connect to a third party software.
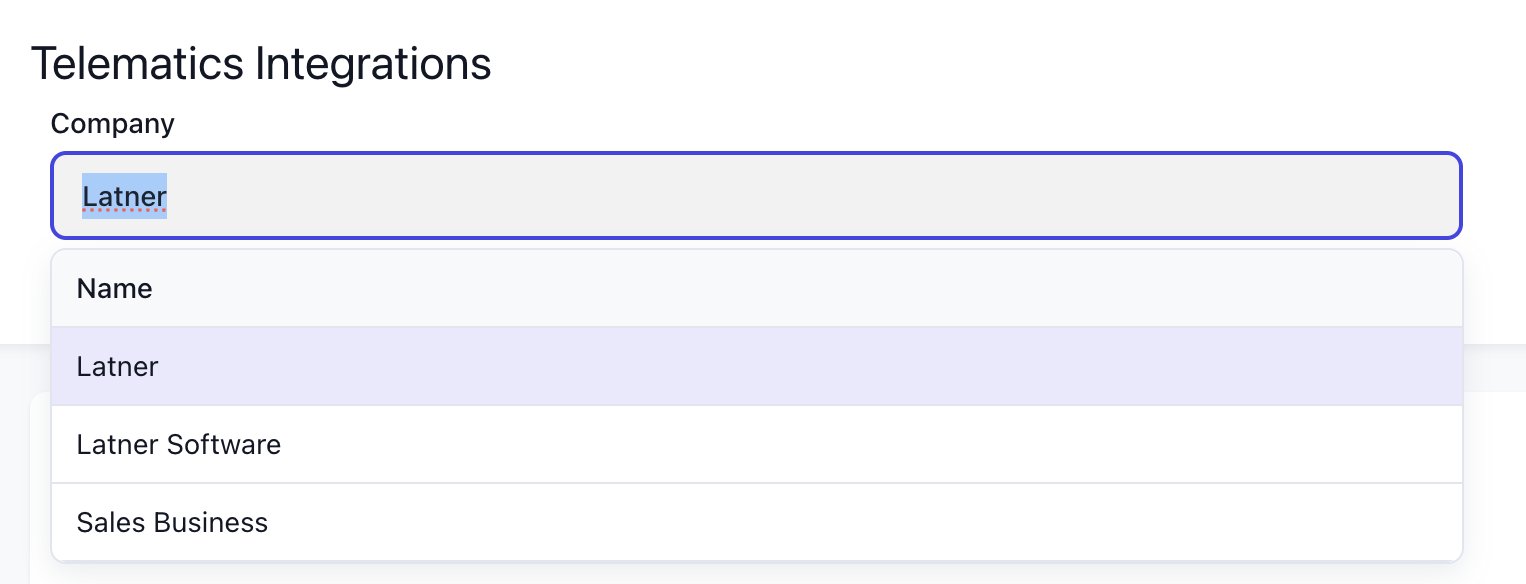
Reviewing Company Setup
Before using integrations, ensure your companies are set up in the top area. Most integrations support connecting multiple services per company, allowing you to tailor connections if different companies require different platforms (e.g., separate accounting systems or trackers).
Connecting to the External Integrations
Clicking the Connect button opens a prompt to establish the link with the third‑party platform.
This usually involves logging in with your account credentials, or entering a client ID and passcode provided by the external system. In some cases, the button may redirect you to the provider’s website, where you complete the login and authorise Latner to connect to the correct integration.
If a connection expires or needs to be refreshed, clicking Reconnect repeats the connection process. This re‑authenticates the link with the external platform, ensuring data continues to flow correctly.

Selecting Remove Connection disconnects the integration from the company. Once removed, Latner will no longer exchange data with that external system until a new connection is established.
Configuring the Connected Integrations
Some integrations include additional configuration options once connected. Click Configure to explore these options.

These settings define how information is exchanged between Latner and the external system - for example, mapping data fields, setting synchronisation rules, or enabling specific features. Adjusting these options ensures the integration behaves according to your operational needs.
Sales Module
Pipeline Groups
Opportunity Types
Opportunity Stages
Activity Types
Industries
Call Types
Regions
Rental Module
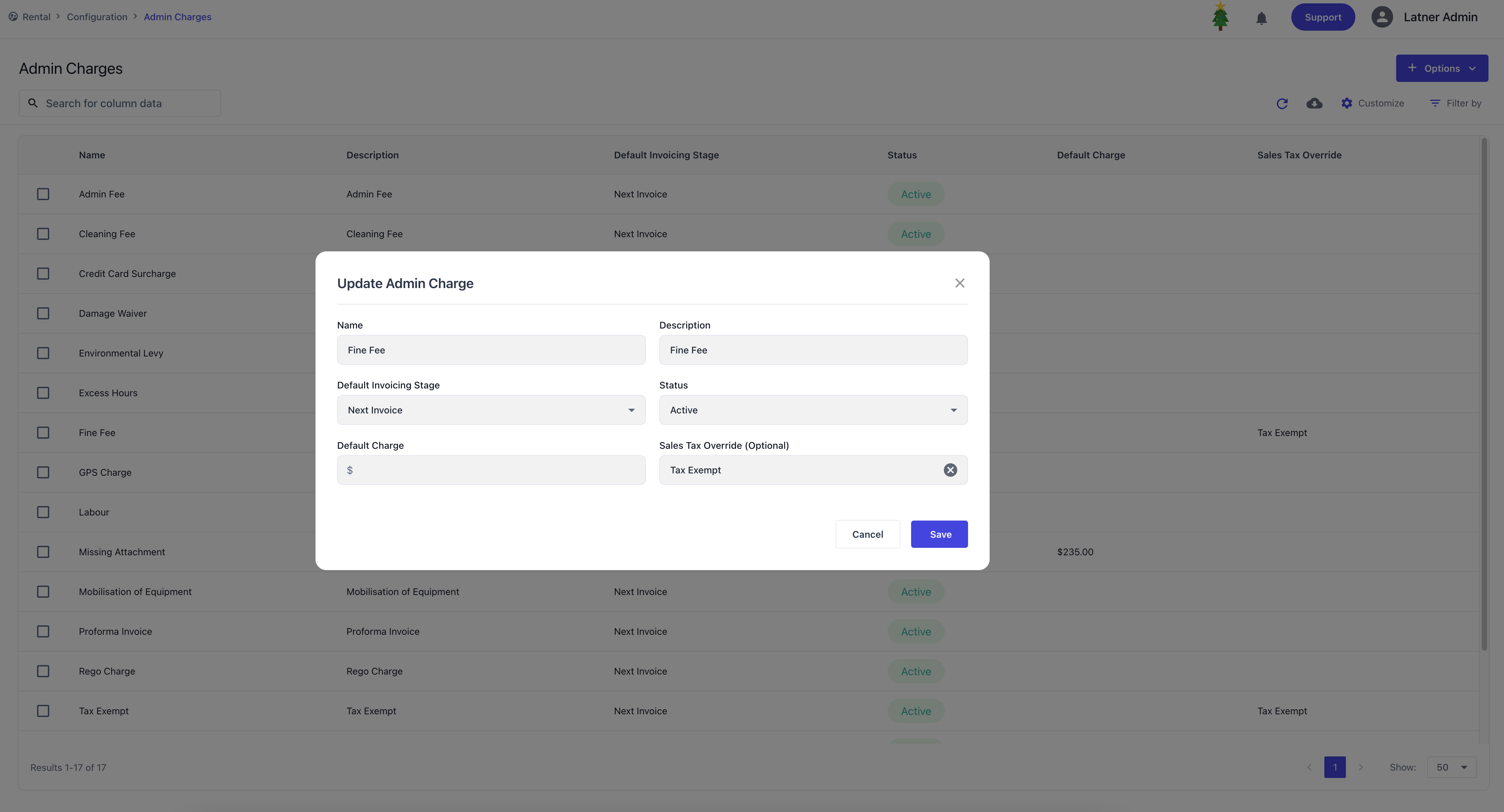
Admin Charges
Admin Charges are used to configure one‑off fees that can be applied to charge-ons. When setting up a charge, you define:
Default invoice stage: whether the charge is applied on return or on the next invoice.
Status: active or inactive.
Default charge amount: the standard fee to apply.
Sales tax override: whether the charge is subject to GST or exempt (default is GST).
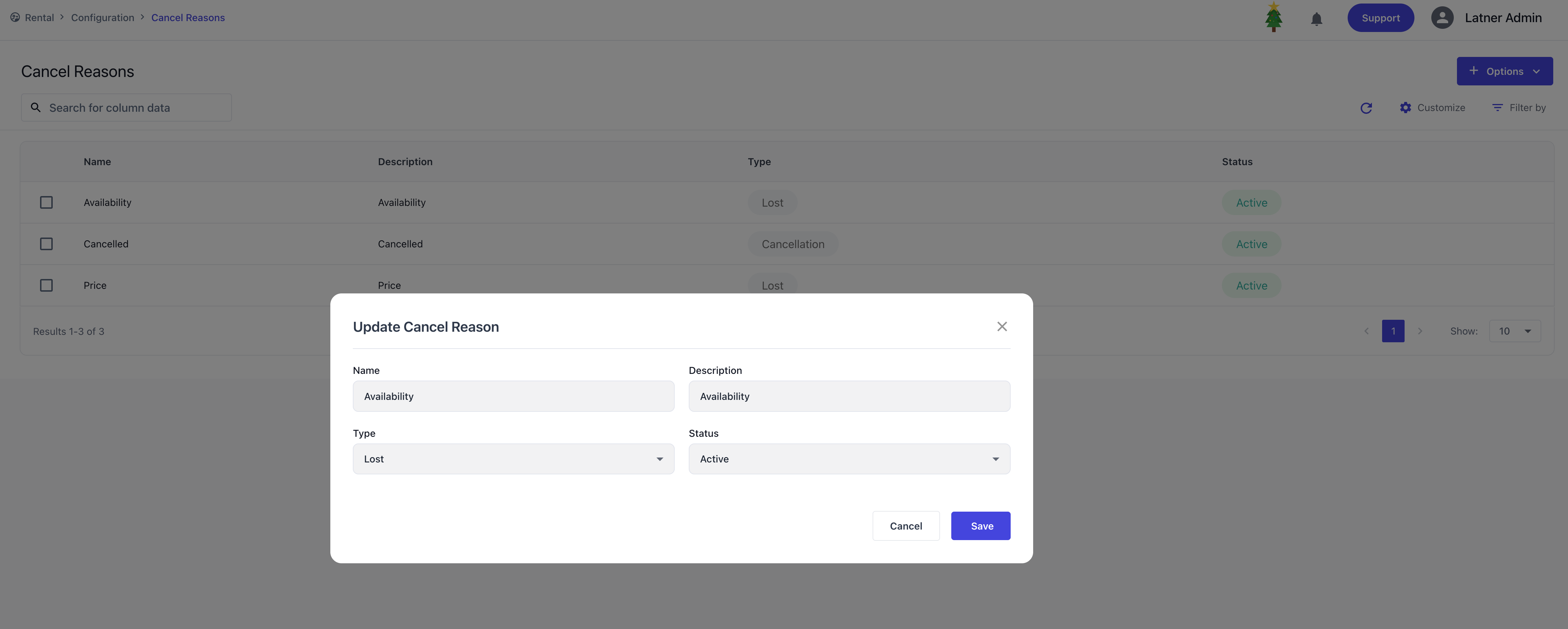
Cancel Reasons
Cancel Reasons define why a quote or contract was cancelled. Each reason includes:
Category: whether the cancellation is classified as “Cancelled” or “Lost.”
Status: active or inactive.
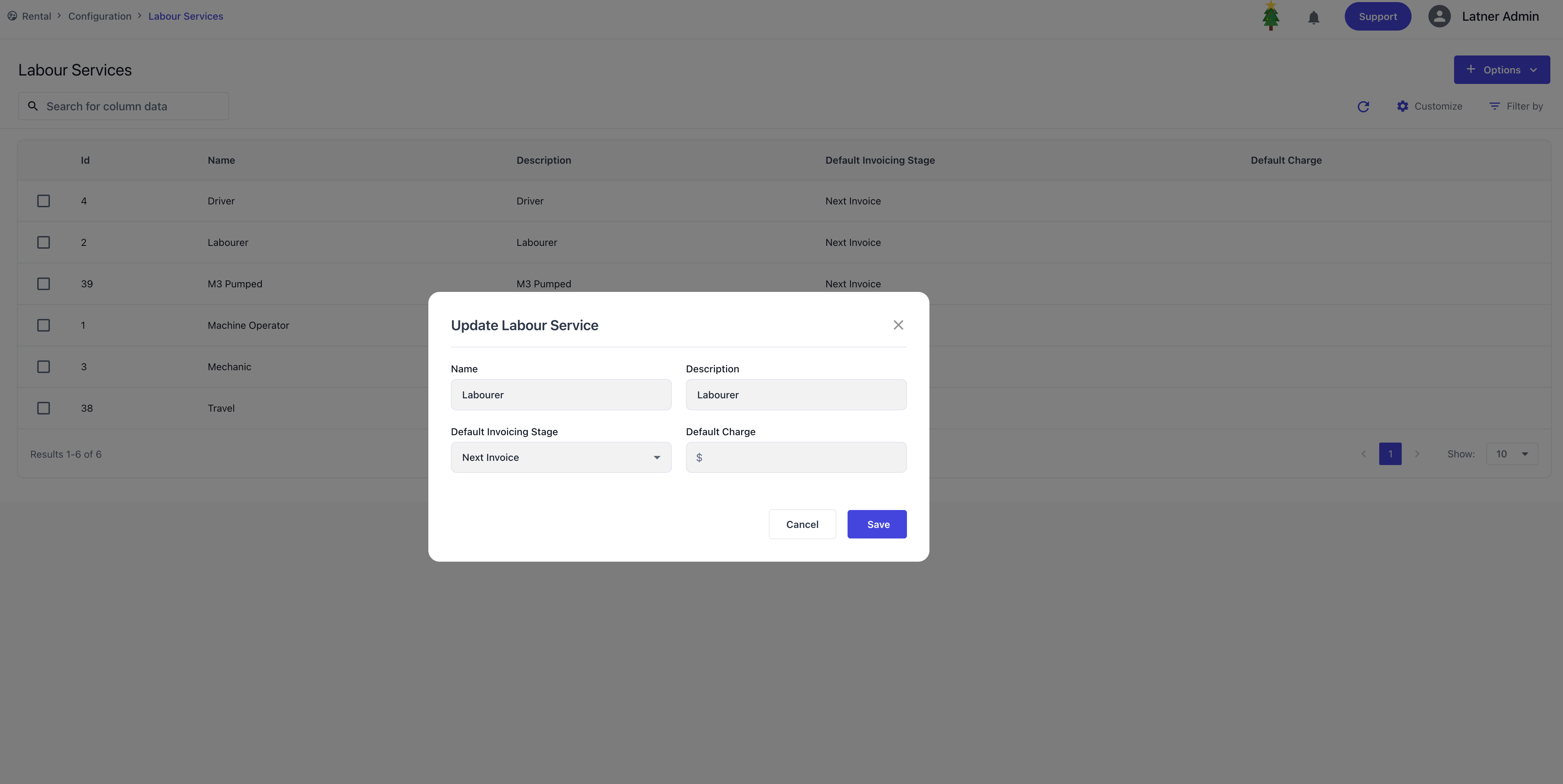
Labour Services
Labour Services are used to configure service charges for labour provided. Each service requires:
Default invoice stage: whether the service is billed on return or on the next invoice.
Default charge amount: the standard labour fee to apply.
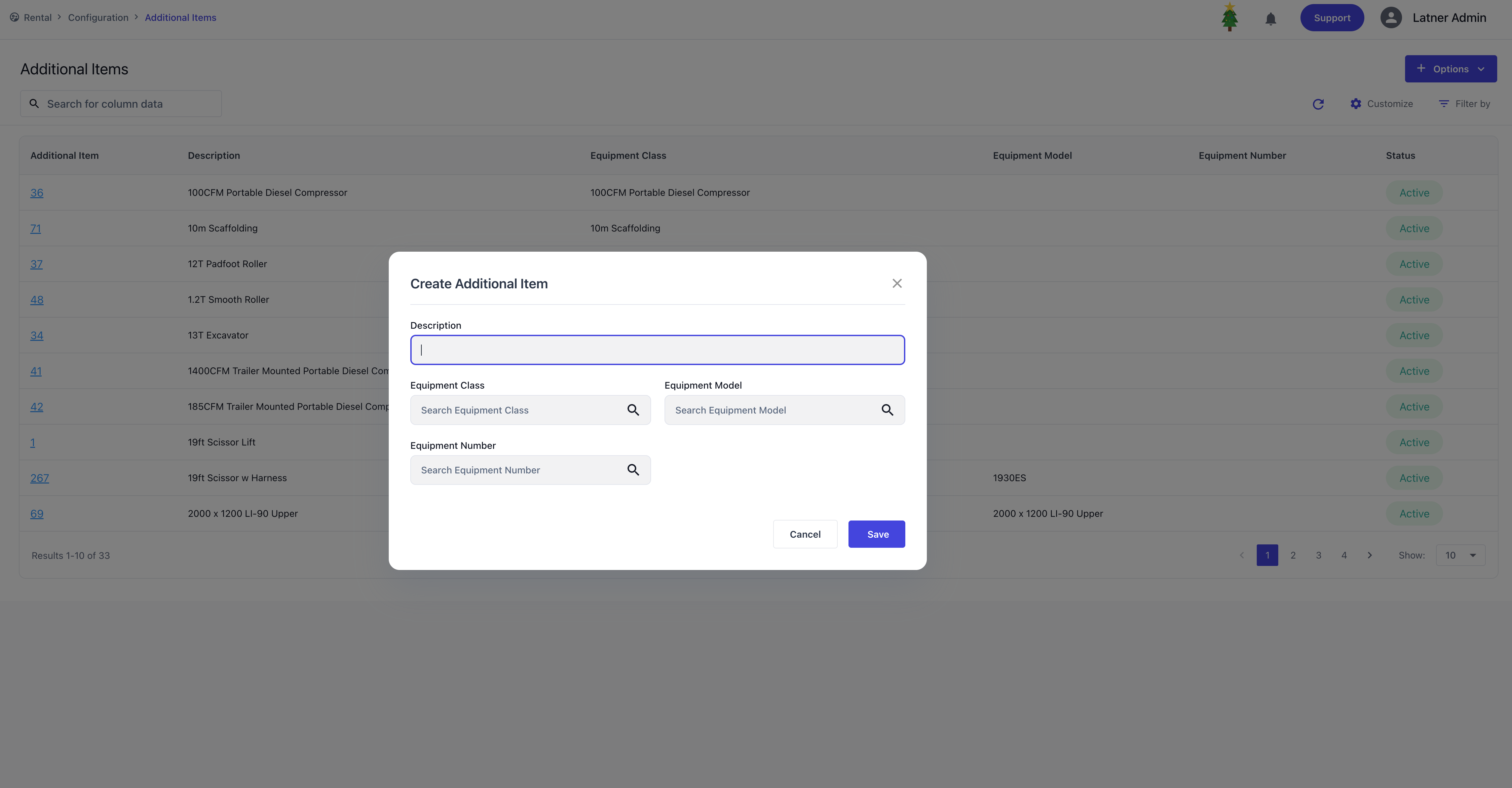
Additional Items
Additional Items are used to assign linked extra items/charges against a specific class, model, or equipment number. When creating an entry, you specify:
Class, model, or equipment number: where the items will be associated with.
Description: the purpose of the additional items.
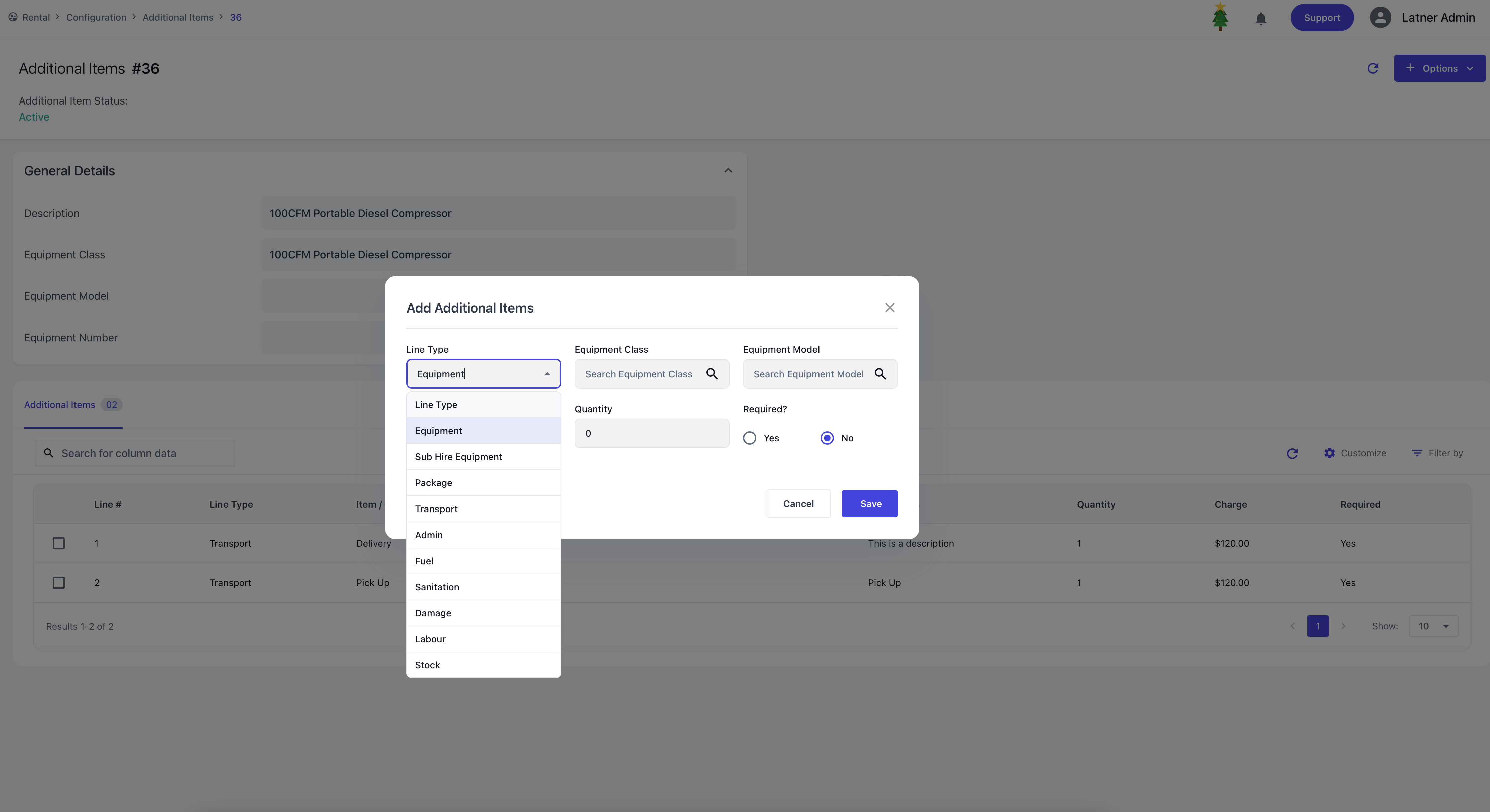
Once the entry is created, the system opens a detailed screen where you can add items to the category.
For each item, you configure:
Line Type: type of item to be added, can be Equipment (Class / Model), Sub Hire Equipment (Class / Model), Package, Transport, Admin, Fuel, Sanitation, Damage, Labour or Stock
Quantity: how many units of the item will be added.
Charge: the applicable fee per unit.
Required?: if marked as required, the item will automatically be included whenever the associated class, model, or equipment number is added to a contract.
Packages
Packages are used to group multiple equipment items into a single kit that can be priced and managed together. When creating a package, you define:
Name of the kit: the identifier for the package.
Pricing type:
Header Only – a single‑level pricing method where you set the header price. Each detail line can then have a revenue proportion allocated against the header.
Detail Only – a multi‑level pricing method where each detail line has its own price defined individually.
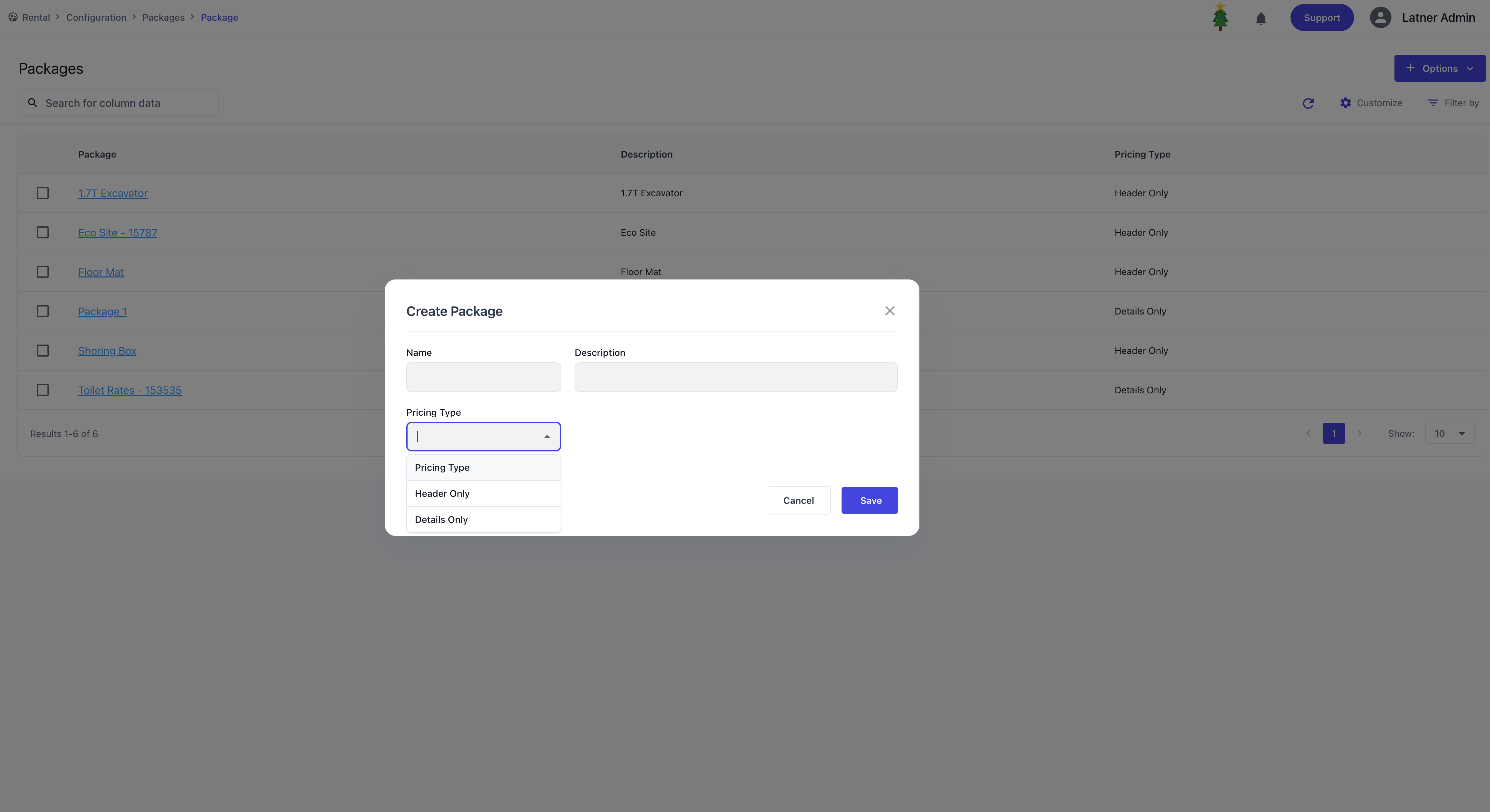
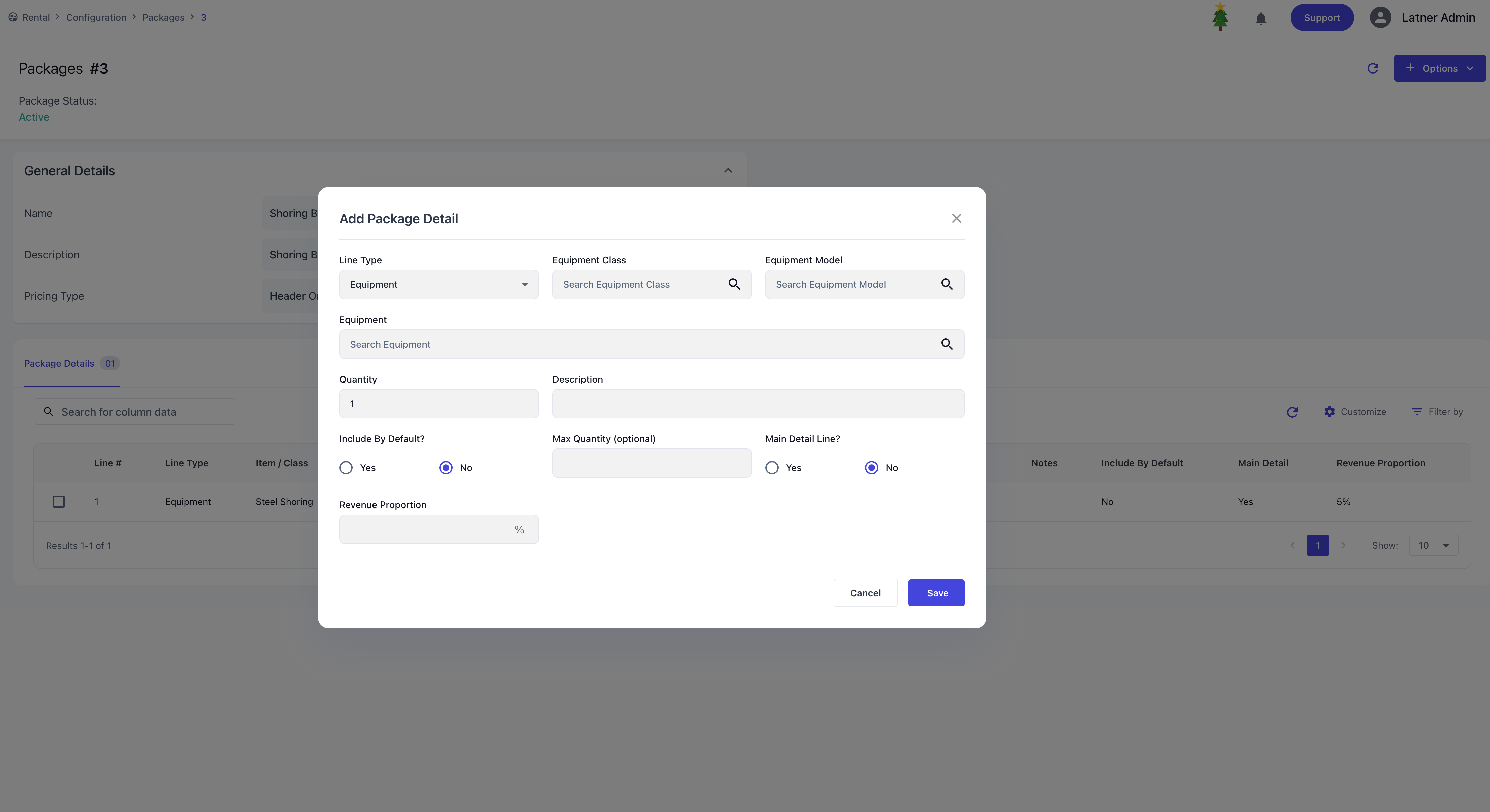
After the package is created, the system opens a detailed screen where you can add line types to the kit. For each detail line, you can specify:
Line Type: the type of detail line being included.
Quantity: the number of units.
Include by default?: determines if the item is automatically added when the package is used.
Max quantity (optional): sets a cap on how many units can be added, helping prevent undercharging.
Main detail line flag: identifies which line represents the package header on the contract (reserved, on rent, off hire). If not set, all lines are treated as main detail.
Revenue proportion or rates:
For Header Only pricing, you assign revenue proportions to each detail line.
For Detail Only pricing, you define rates directly for each line.
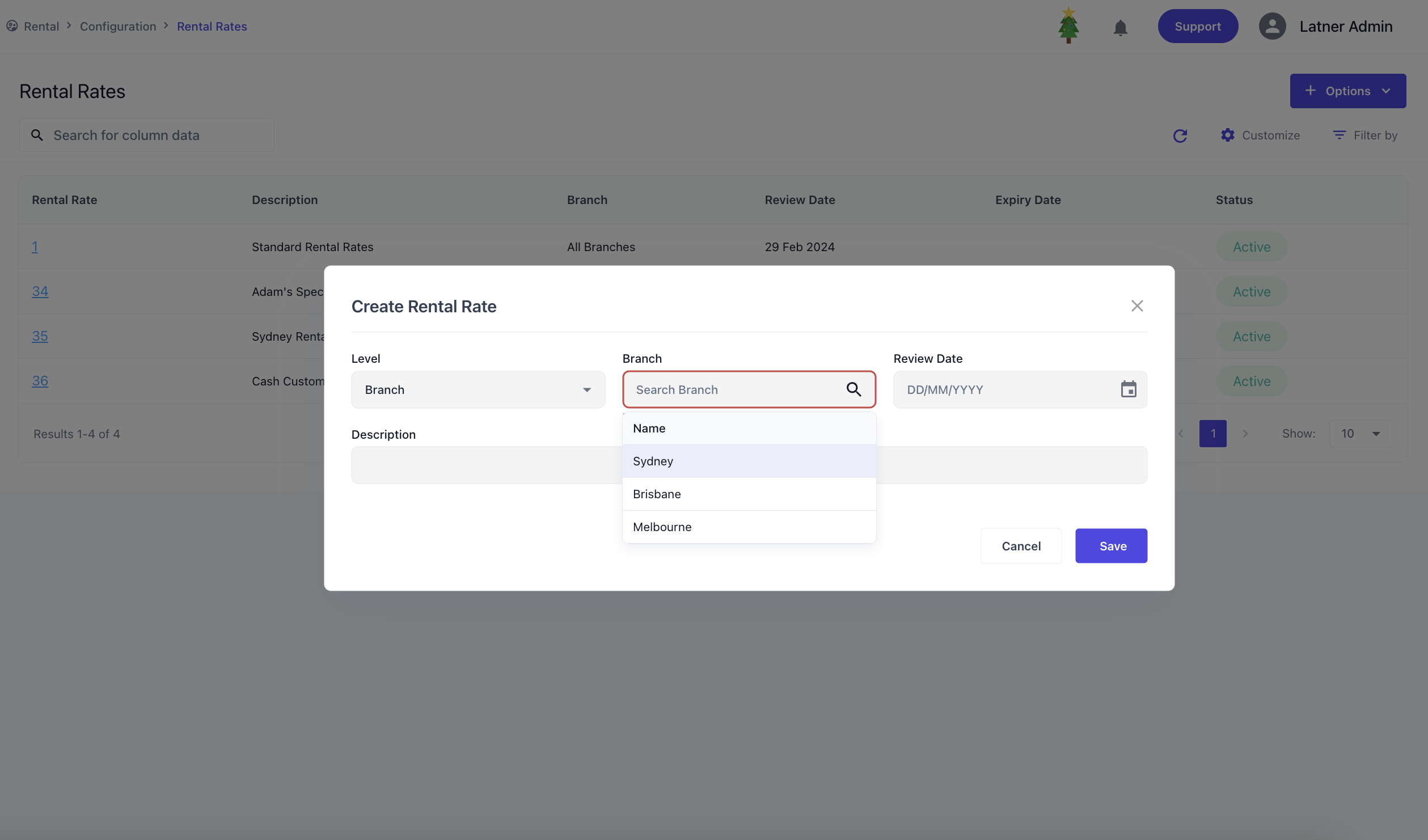
Rental Rates
Rental Rates are used to create and manage customer rate cards that define how charges are applied across equipment and services. These rates are able to be assigned through Customer or Customer Sites. When creating a rental rate, you specify:
Level: whether the card applies to all branches or a specific branch.
Branch (if applicable): the branch the rate card belongs to.
Review date: the date the rate card should be reviewed.
Description: an identifier for the rate card.
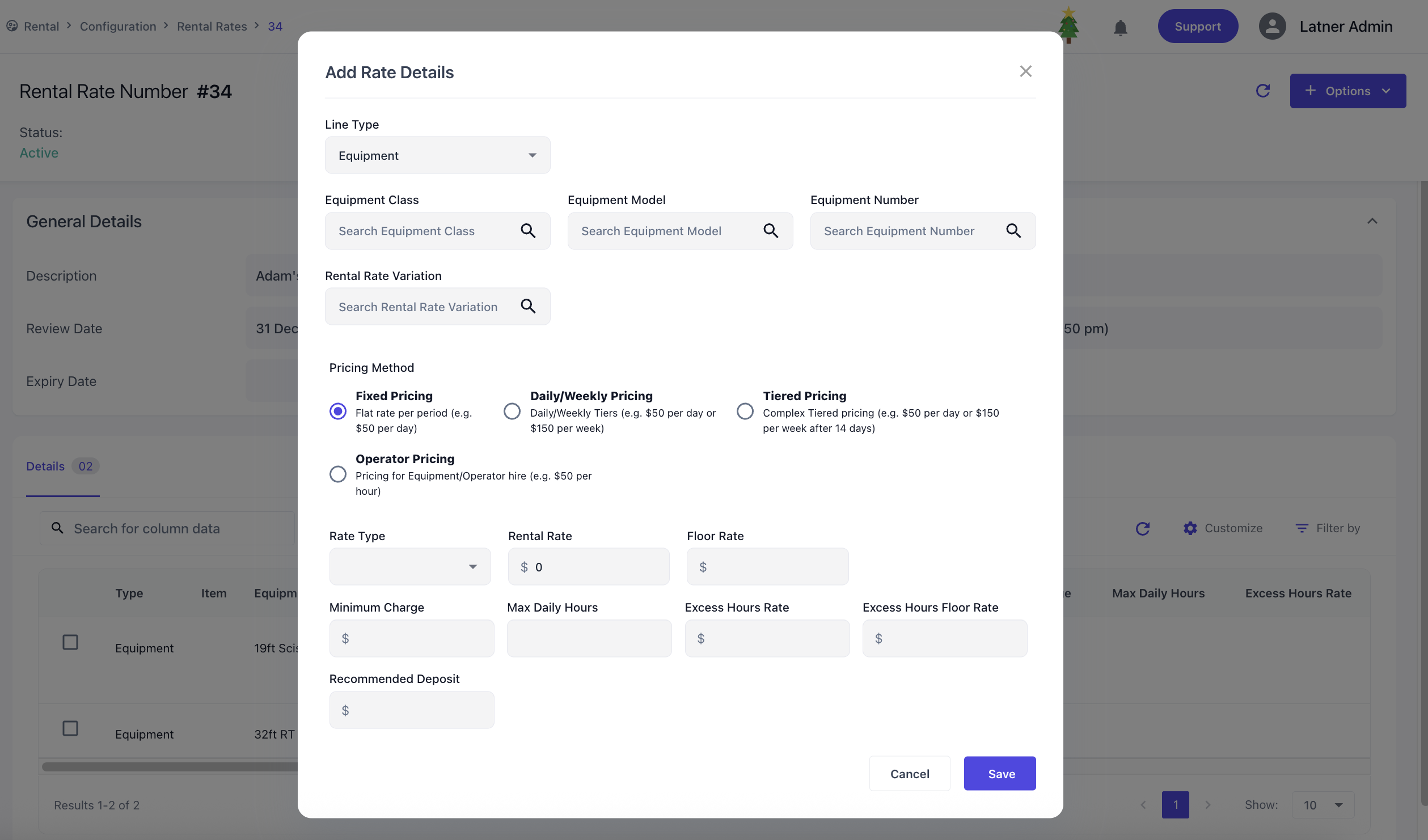
Once the rate card is created, the system opens a detailed screen where you can either copy the rental rates to another card or add rental details to this rental rate. Expiry dates can also be set to disable the rates accordingly through this detailed screen. Each rate detail line, you can specify
Line Type: the category being charged (Equipment, Package, Transport, Admin, Sanitation)
Equipment Class / Model / Number linked: For non‑complex charges (Transport, Admin, Sanitation), you link the charge to an Equipment Class, Model, or Number.
Rates / Charges:
Equipment & Package follow the rate system with optional floor rates to enforce
Transport, Admin & Sanitation lines require a single charge amount.
Sub Hire Rental Rates
Sub Hire Rental Rates are used to create and manage supplier rate cards specifically for equipment or services sourced from external suppliers. These rate cards define how costs are applied when items are sub‑hired and are assigned through Suppliers. When creating a sub hire rental rate card, you specify:
Level: whether the card applies to all branches or a specific branch.
Branch (if applicable): the branch the rate card belongs to.
Review Date: the date the rate card should be reviewed for accuracy.
Description: an identifier or purpose for the rate card.
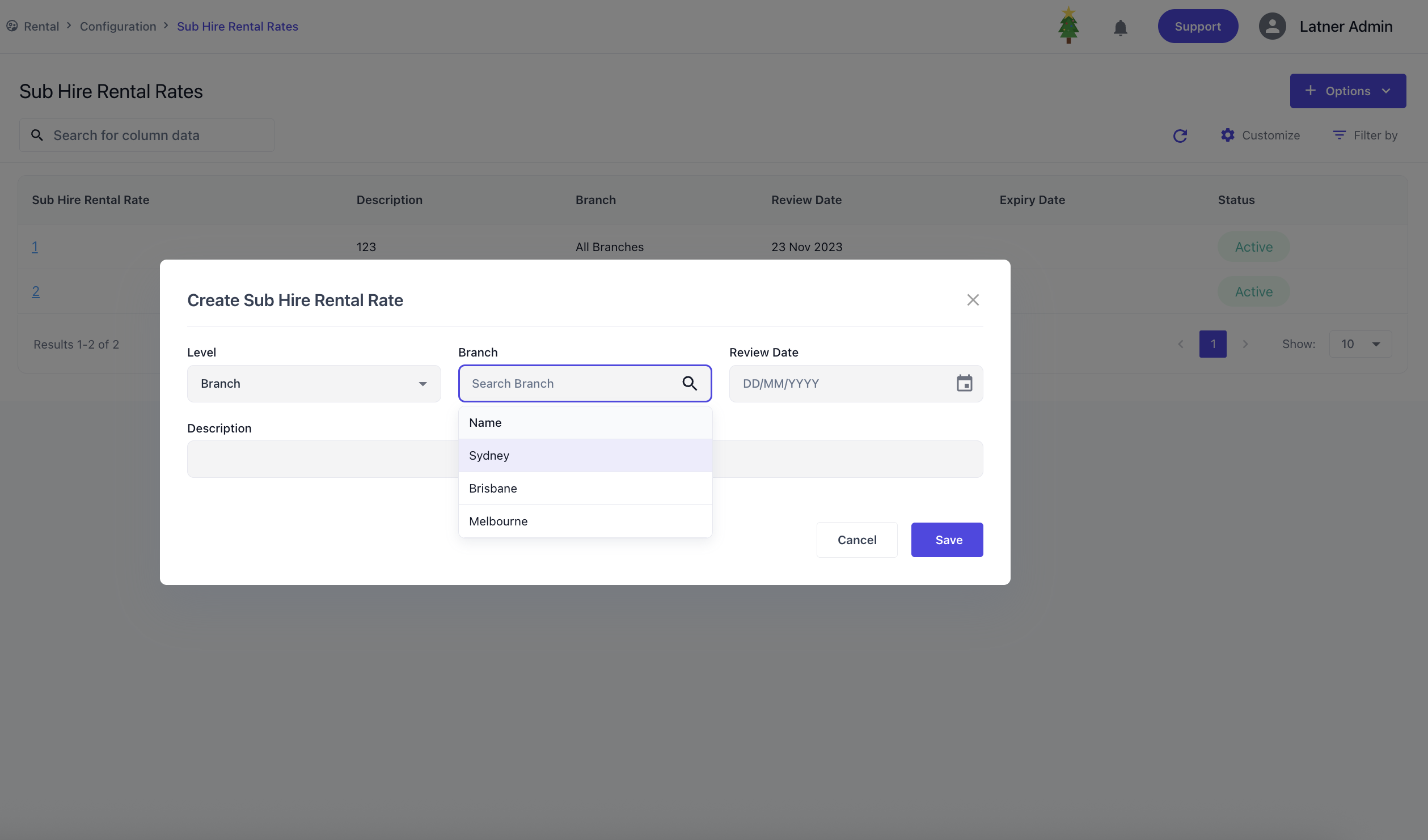
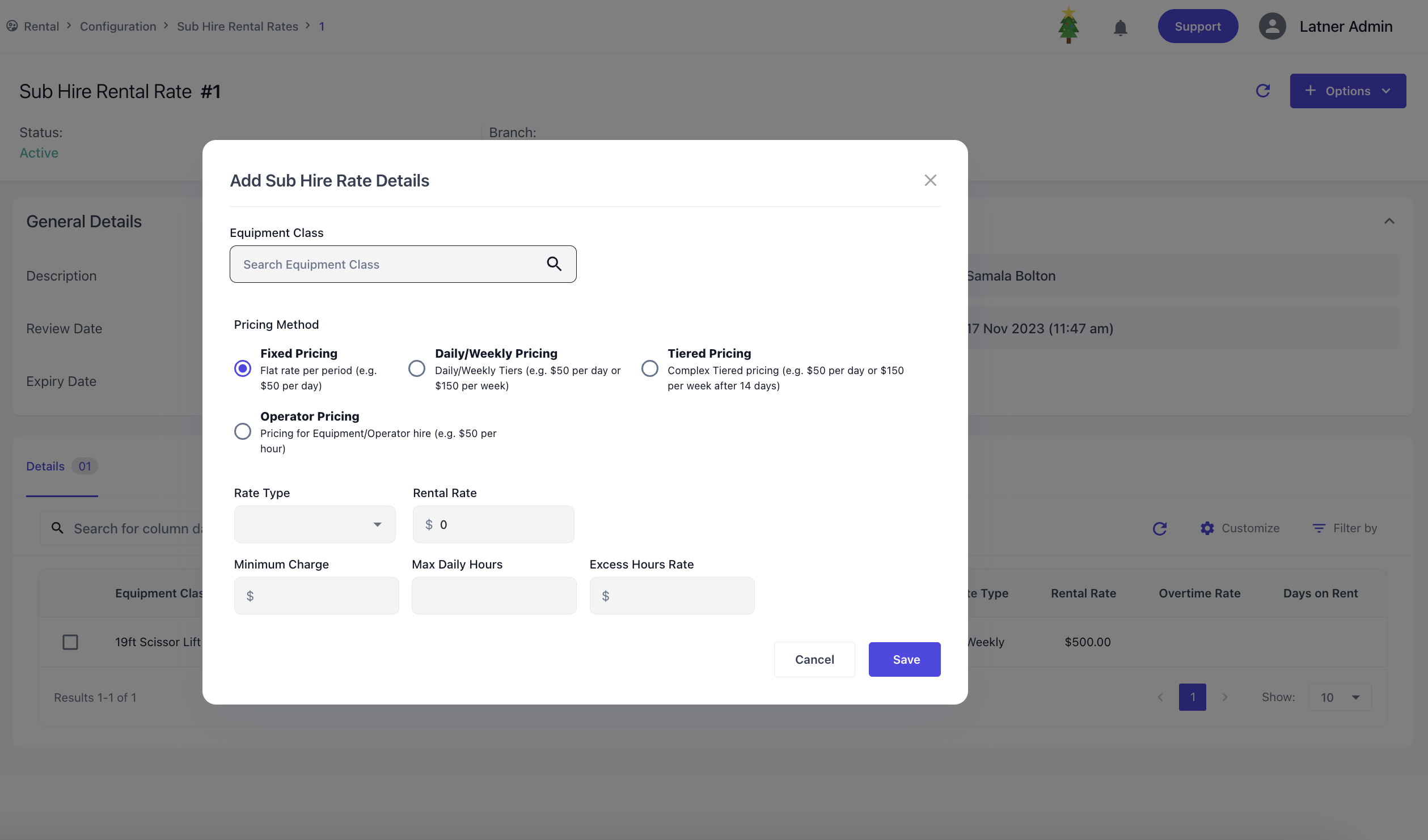
Once the rate card is created, the system opens a detailed screen where you can add rental details to this rental rate. Expiry dates can also be set to disable the rates accordingly through this detailed screen. Each rate detail line, you can specify
Equipment Class: the type of equipment being sub hired.
Rates: follows the rate system to be charged
Rental Rate Variations
Rental Rate Variations let you create multiple pricing options for the same equipment / package, giving flexibility to apply the correct rate during quoting or invoicing. When setting up rental rate variations, you define the name & description to best describe the use-case.
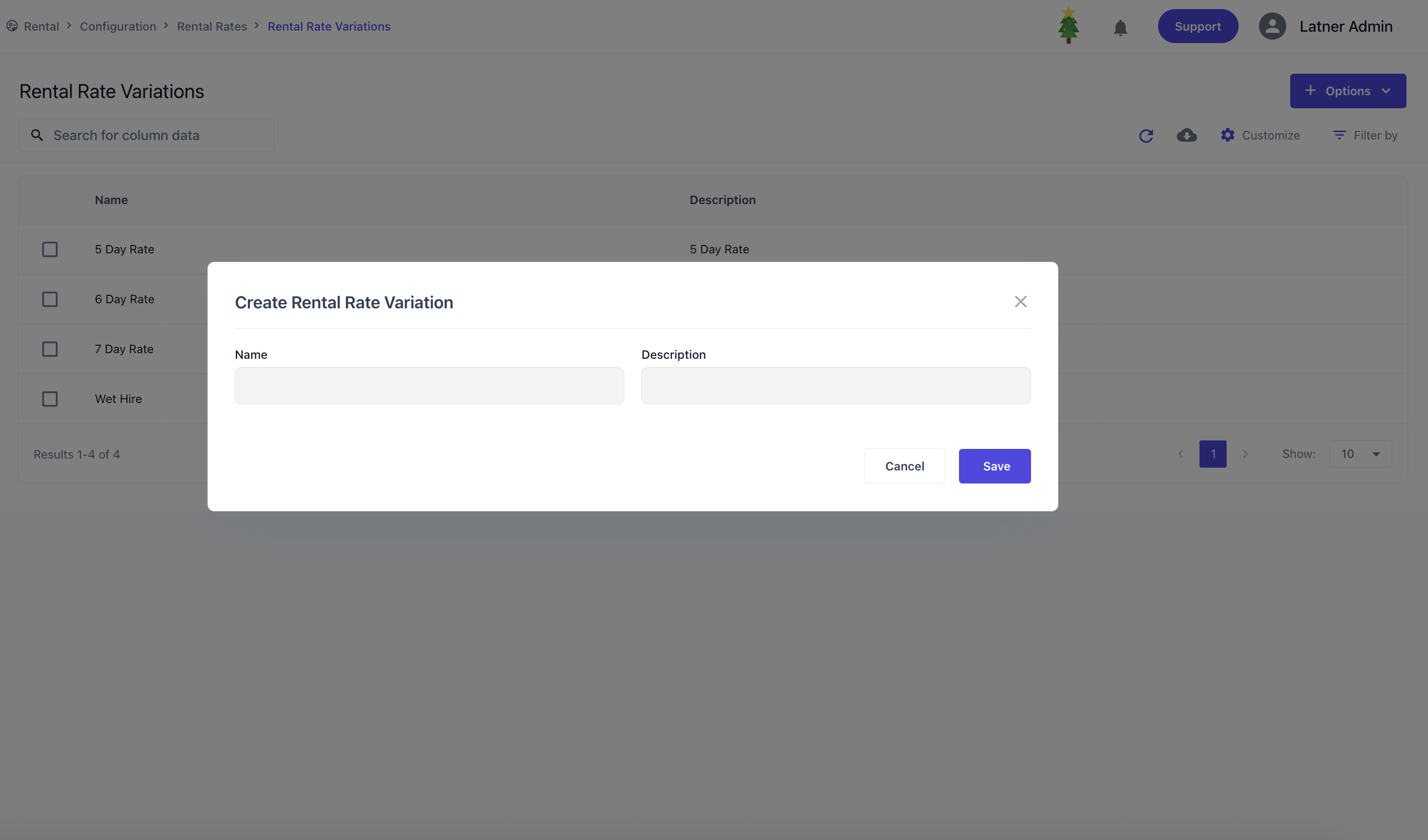
These variations are then set on the Rental Rates. Once this is done, when selecting a variation on a contract or quote, the system will display all variations for that equipment so you can choose the most appropriate one.
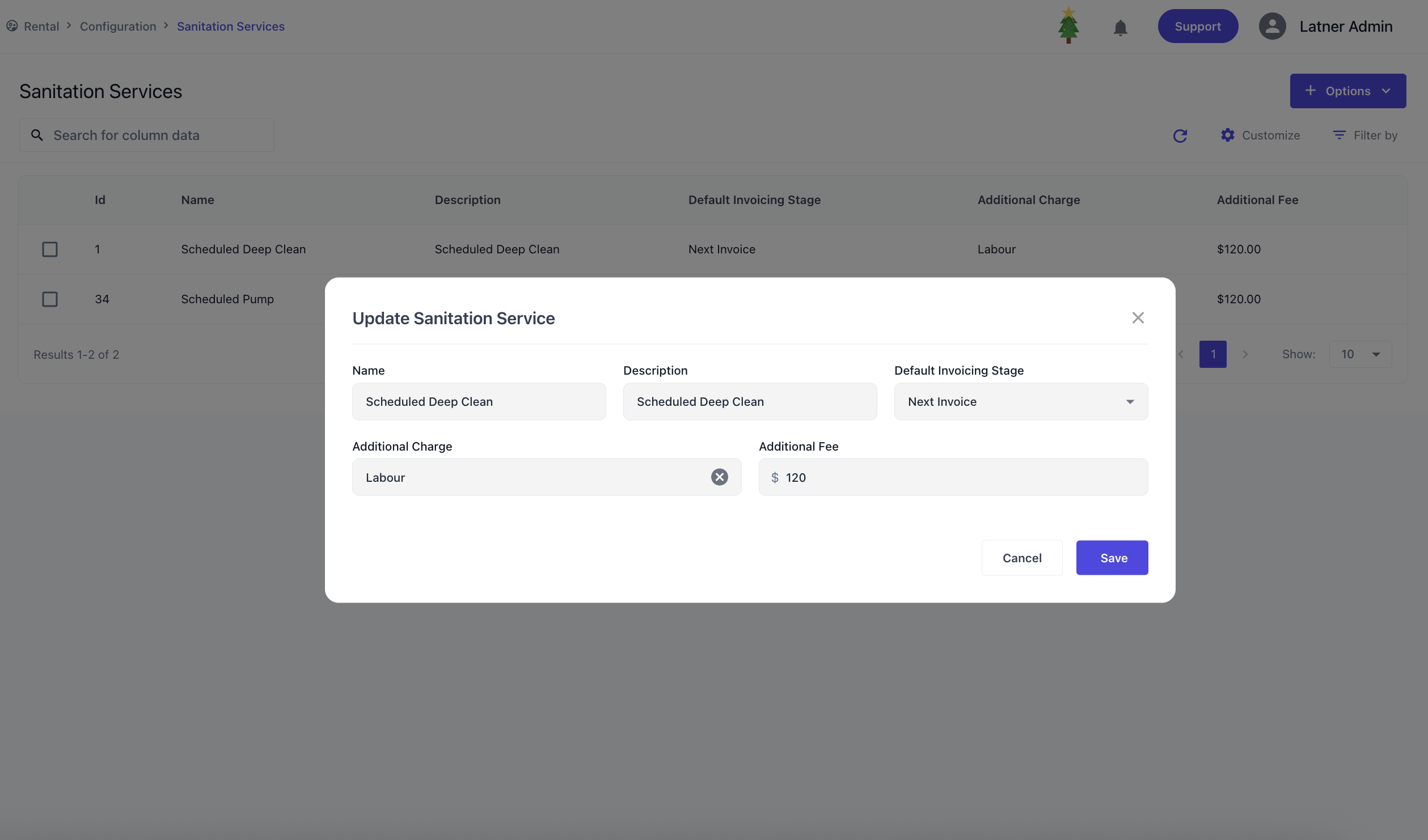
Sanitation Services
Sanitation Services are used to configure sanitation charges that can be applied to contracts. When setting up a sanitation charge, you define:
Default invoice stage: whether the charge is applied on return or on the next invoice.
Additional Charge: an additional charge with the sanitation consisting of Admin Charges
Additional Fee: the additional fee against the charge.
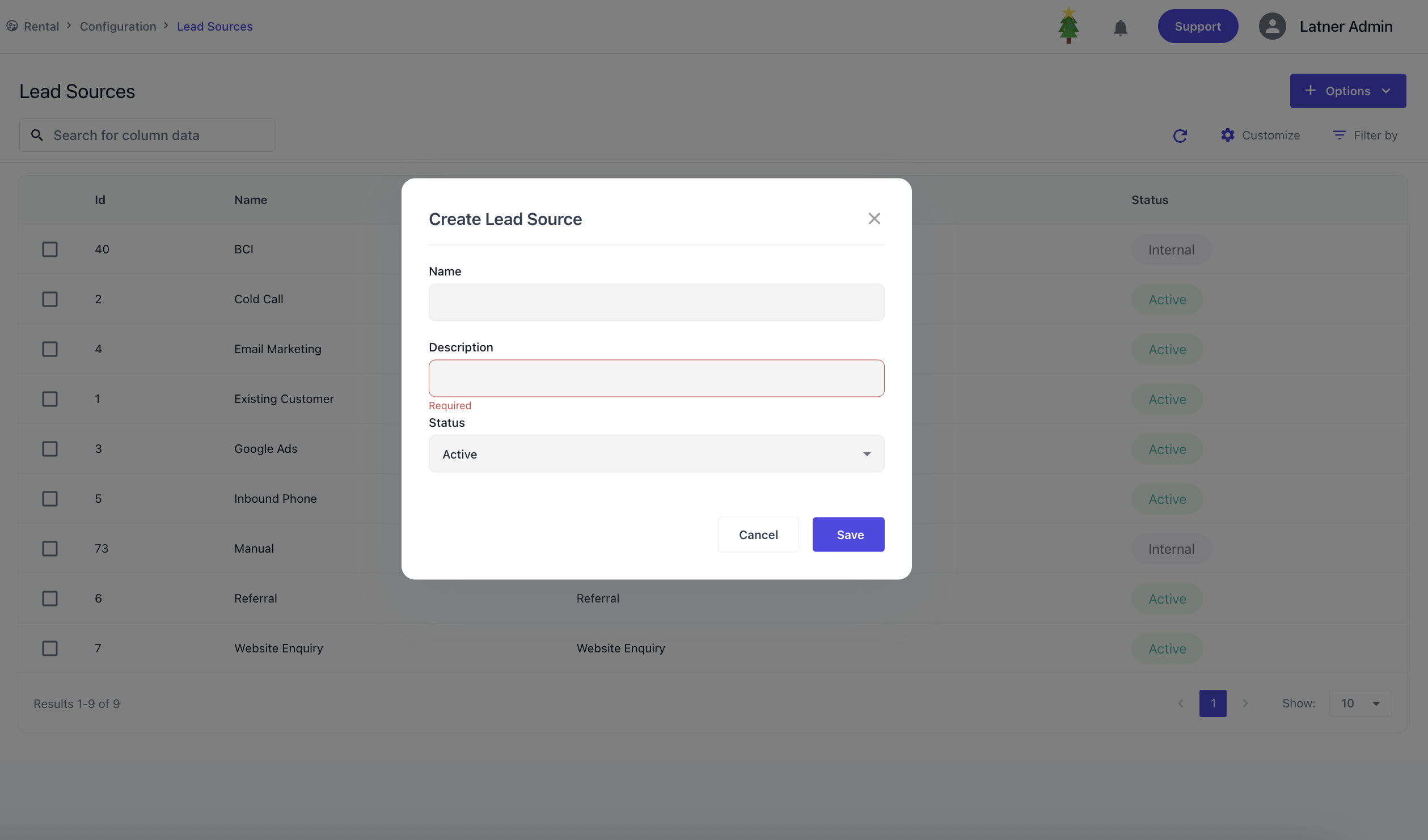
Lead Sources
Lead Sources are used to configure origin points for incoming leads, typically used in rental quotes, sales orders, and CRM tracking. When configuring a lead source, you define the name / description to best describe the use-case and setting the status to active or inactive to use.
Stand Down Reasons
Stand Down Reasons let you record why a rental contract has been temporarily stood down, providing visibility for reporting and analysis. When setting up a stand down reason, you define the name and description to best describe the scenario.
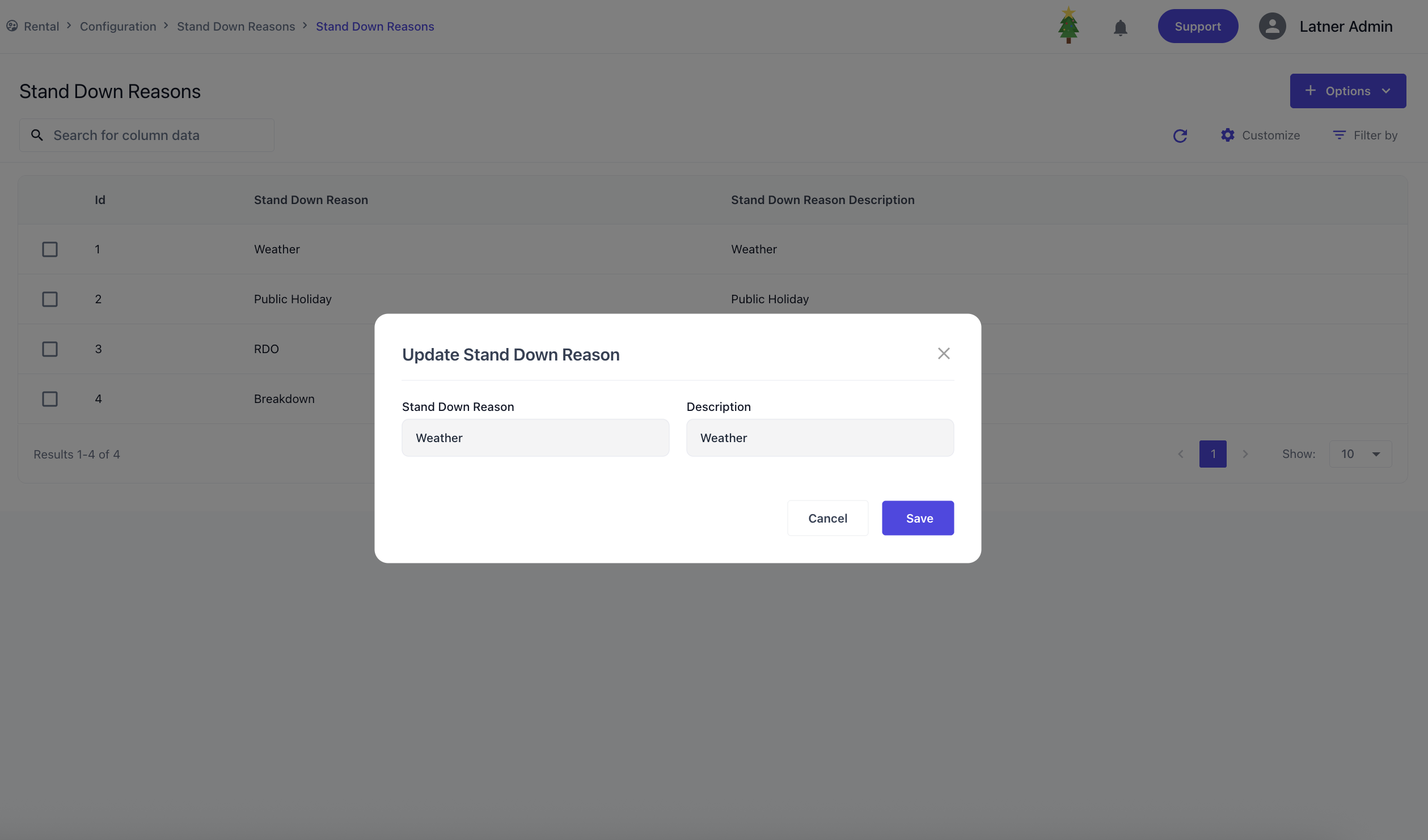
These reasons are then applied to rental contracts whenever a stand down occurs. Once selected, the system records the reason against the contract, ensuring accurate tracking and allowing trend analysis.
Transport Runs
Rental Quote PDF Template
Rental Contract PDF Template
Equipment Module
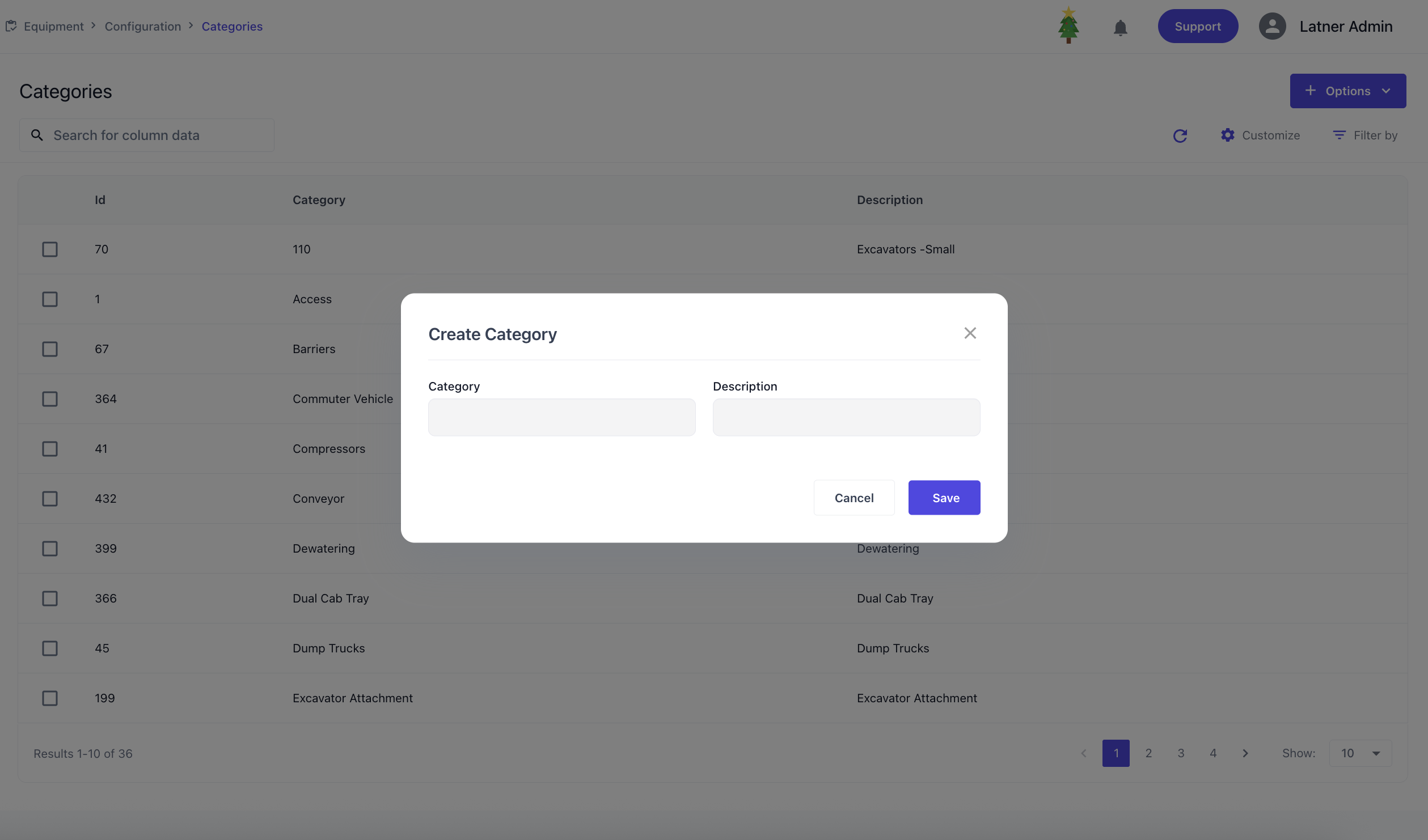
Categories
Equipment Categories are used to configure broad groupings of equipment types. When setting up a category, you define the name and description.
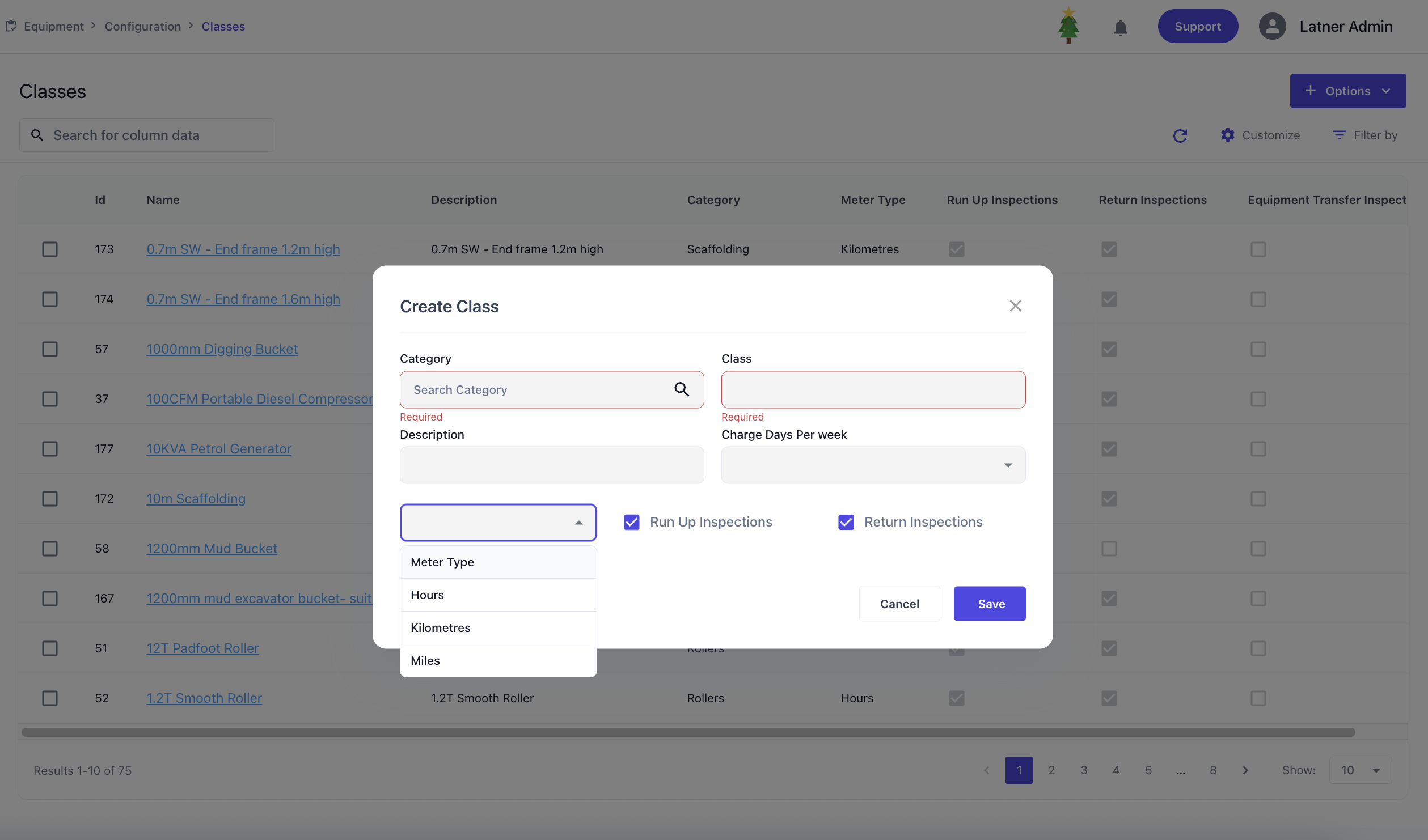
Classes
Equipment Classes are used to define sub-groups within a category, typically based on size, function, or operational role. When setting up a class, you define:
Category: the parent category this class belongs to
Default charge days per week: sets the standard billing cycle for the equipment with this class
Meter type: Specifies the type of usage meter used to track equipment activity
Run‑up inspection: flags if inspection is required when the equipment with the same class is put on hire; checklist can optionally be added on detail screen
Return inspection: flags if inspection is required when the equipment with the same class has returned; checklist can optionally be added on detail screen
Once the class is created, the system opens a detailed screen where you can configure:
Damage waiver: defines the damage waiver on class level; can be set per hierarchy.
Default charge days per week: sets the standard billing cycle for the equipment with this class
Default inspection time: establishes the expected time allocation for inspections
Meter type: Specifies the type of usage meter used to track equipment activity
Run‑up inspection: flags if inspection is required when the equipment with the same class is put on hire; checklist can optionally be added on detail screen
Return inspection: flags if inspection is required when the equipment with the same class has returned; checklist can optionally be added on detail screen
Equipment transfer checklist: flags if inspection is required when the equipment with the same class has transferred branches; checklist can optionally be added
Pre‑start checklist: set a checklist template for operators to complete on an operator docket before starting equipment with the same class
Account depreciation type: defines how the equipment with the same class is depreciated for accounting purposes
Tax depreciation type: specifies the depreciation method used for tax reporting, ensuring compliance with regulations
Minimum markup for sub‑hire: sets the minimum profit margin applied when equipment is sub‑hired from a supplier, preventing undercharging.
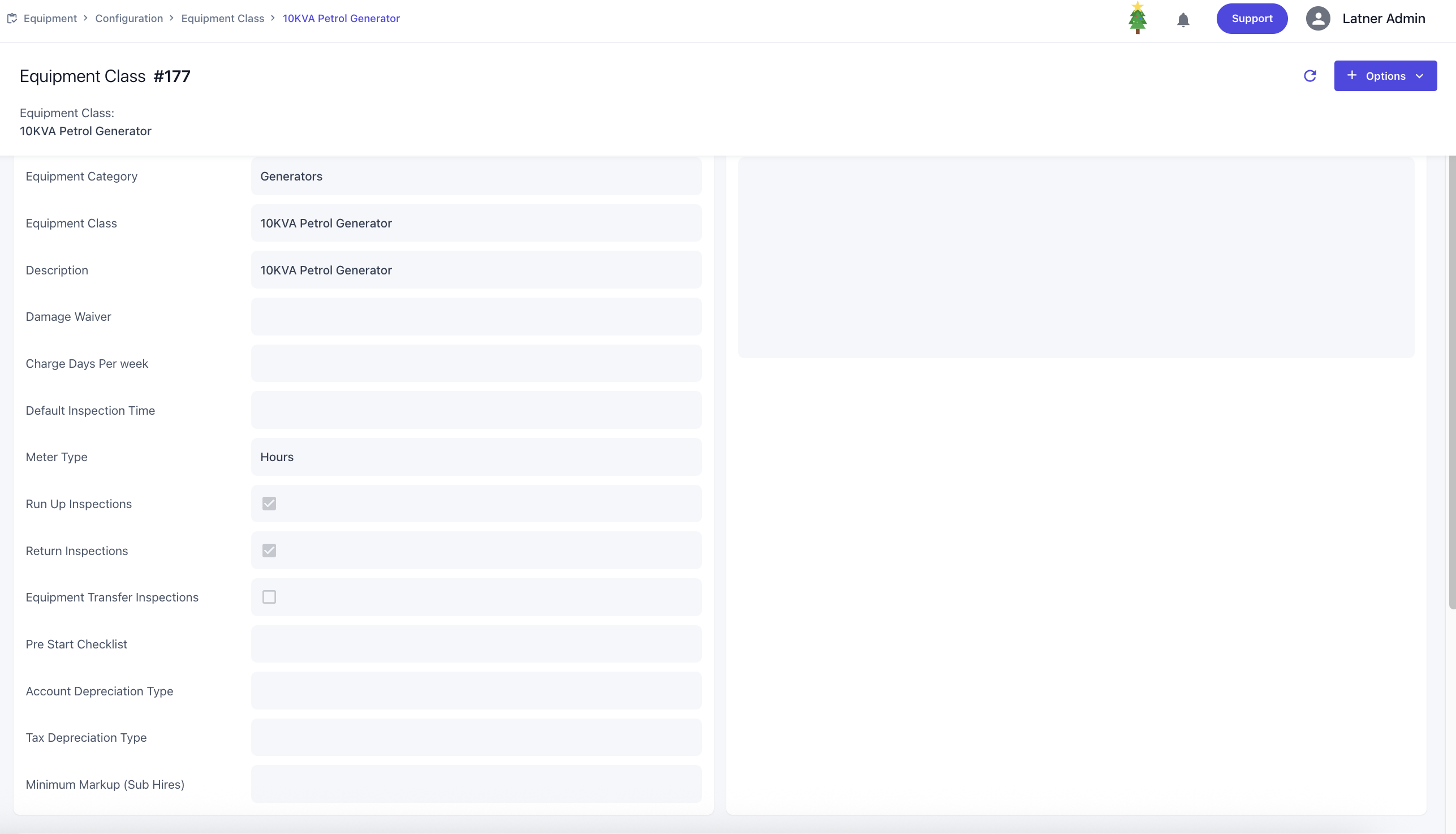
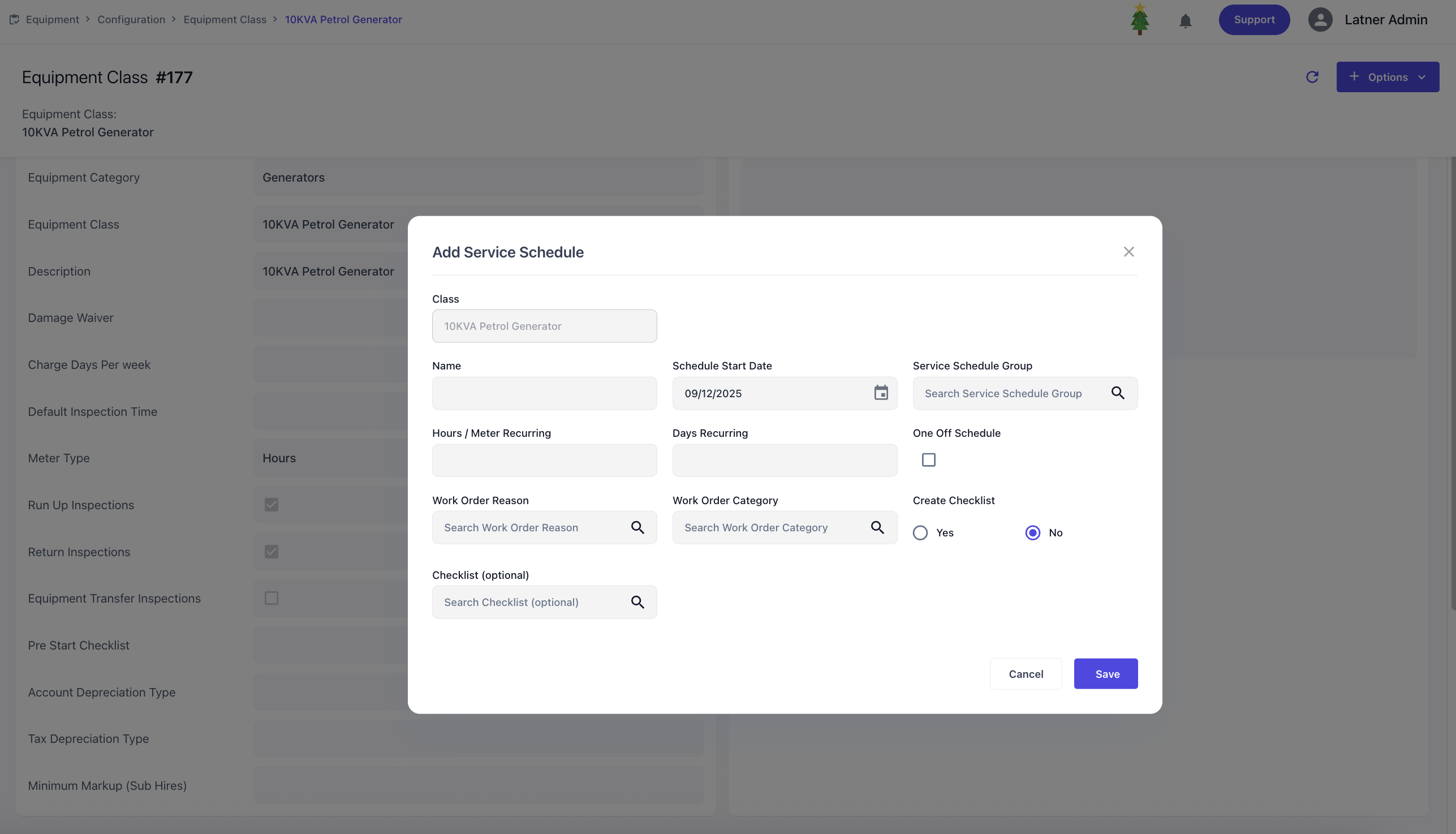
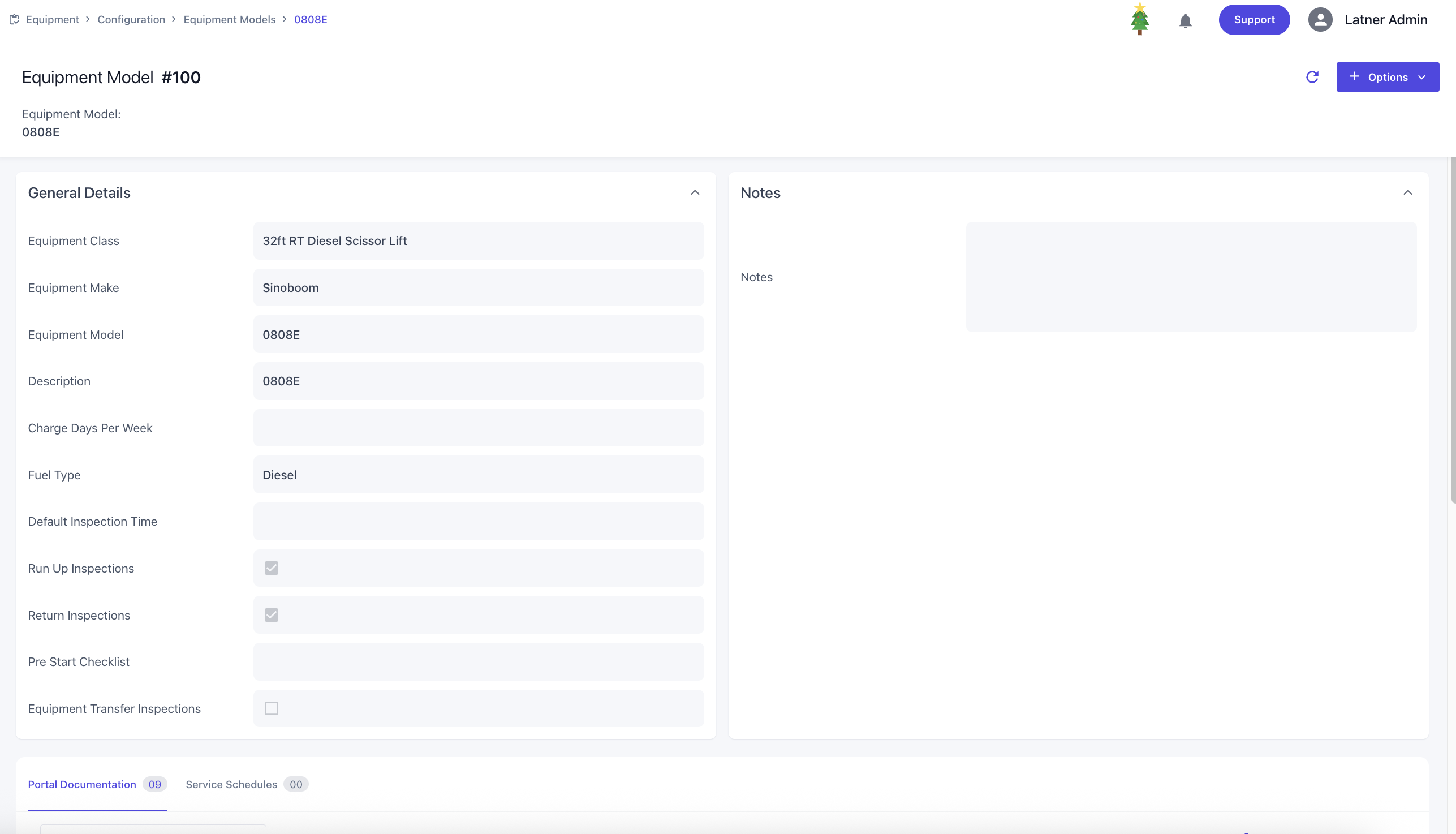
You can also add service schedules against the class, where you define:
Schedule start date: the date the service schedule begins
Service schedule group: groups related schedules together for calculating frequency how one schedule that takes over after another
Recurring frequency: determines how often the service occurs, based on hours meter, days, or both
One‑off schedule flag: marks the schedule as a single occurrence rather than recurring
Work Order Reason and Category: classifies the service work order for operational reporting
Create Checklist flag: either generates a new checklist for the schedule or links an existing checklist template to this schedule
See more detailed information on How to Assign a Service Schedule to Equipment
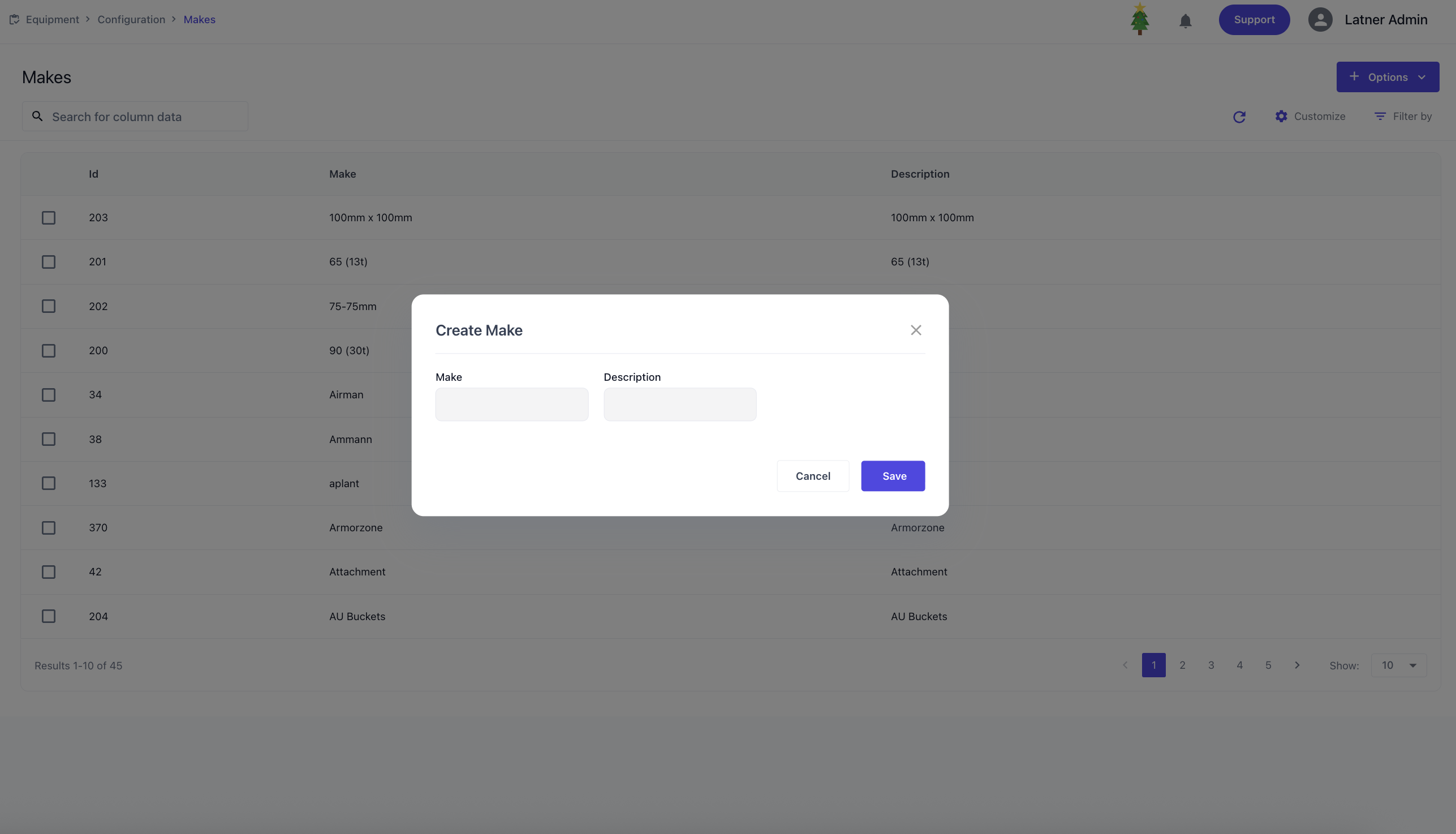
Makes
Equipment Makes are used to configure the manufacturer or brand of the equipment. When setting up a make, you define the name and description.
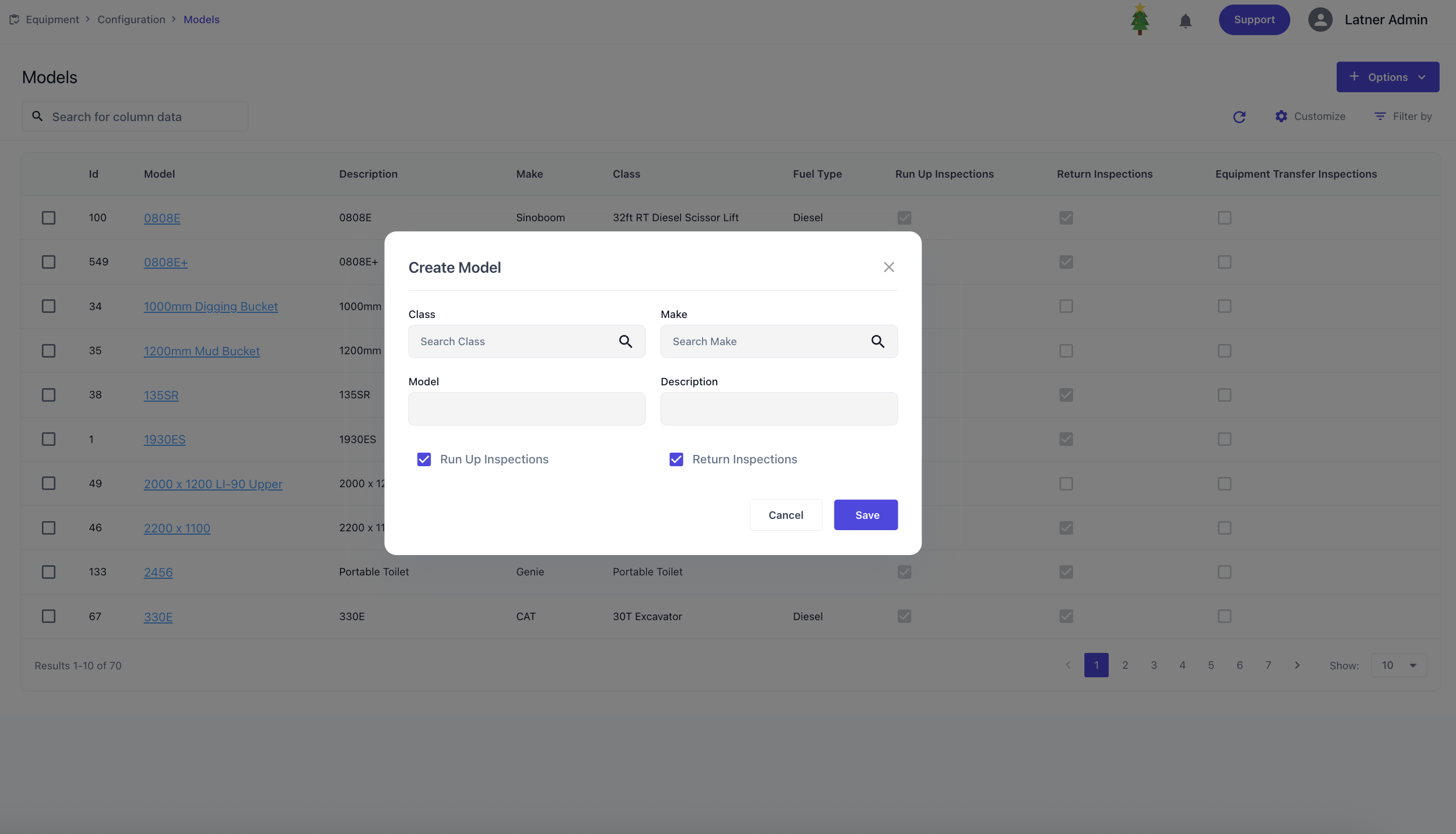
Models
Equipment Models are used to define the specific version of equipment within a class and make. When setting up a model, you define the name / description and the following:
Class: the equipment class the model belongs to
Make: the manufacturer or brand it links to
Run‑up inspection: flags if inspection is required when the equipment with the same model is put on hire; checklist can optionally be added; takes over what is set on class
Return inspection: flags if inspection is required when the equipment with the same model has returned; checklist can optionally be added; takes over what is set on class
Once the model is created, the system opens a detail screen where you can configure:
Default charge days per week: sets the standard billing cycle for the equipment with this class; takes over what is set on class
Default inspection time: establishes the expected time allocation for inspections; takes over what is set on class
Fuel type: identifies the fuel required for the equipment with the same model
Run‑up inspection: flags if inspection is required when the equipment with the same model is put on hire; checklist can optionally be added; takes over what is set on class
Return inspection: flags if inspection is required when the equipment with the same model has returned; checklist can optionally be added; takes over what is set on class
Equipment transfer checklist: flags if inspection is required when the equipment with the same model has transferred branches; checklist can optionally be added; takes over what is set on class
Pre‑start checklist: set a checklist template for operators to complete on an operator docket before starting equipment with the same model; takes over what is set on class
You can also add service schedules against the class, where you define:
Schedule start date: the date the service schedule begins
Service schedule group: groups related schedules together for calculating frequency how one schedule that takes over after another
Recurring frequency: determines how often the service occurs, based on hours meter, days, or both
One‑off schedule flag: marks the schedule as a single occurrence rather than recurring
Work Order Reason and Category: classifies the service work order for operational reporting
Create Checklist flag: either generates a new checklist for the schedule or links an existing checklist template to this schedule
See more detailed information on How to Assign a Service Schedule to Equipment
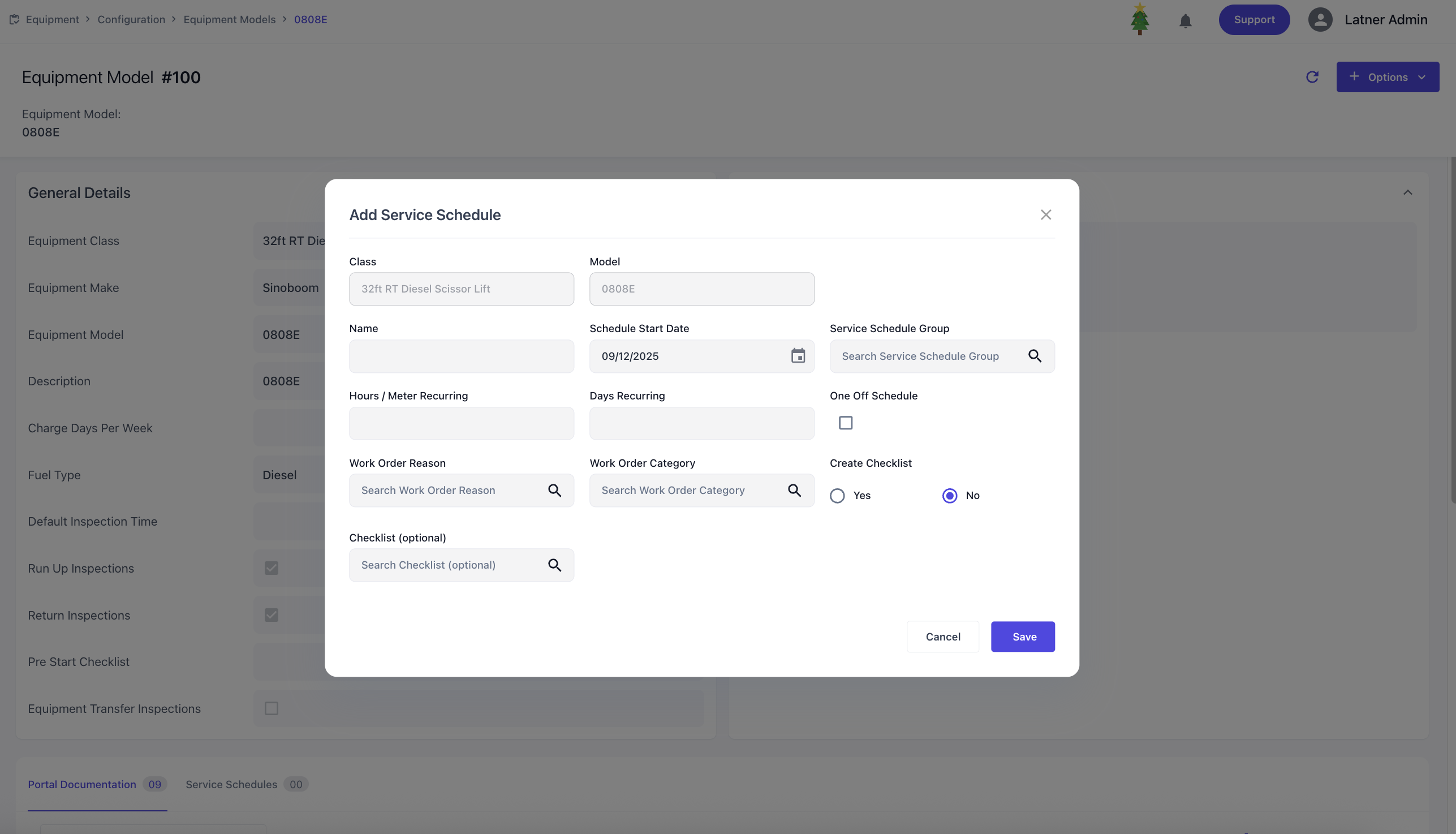
Within the Model detail screen, you can configure Portal Documentation that customers can access through the public portal via QR code or link. You can upload documents against their types, these documents become visible to customers through the portal, ensuring they have direct access to the correct information for the equipment.
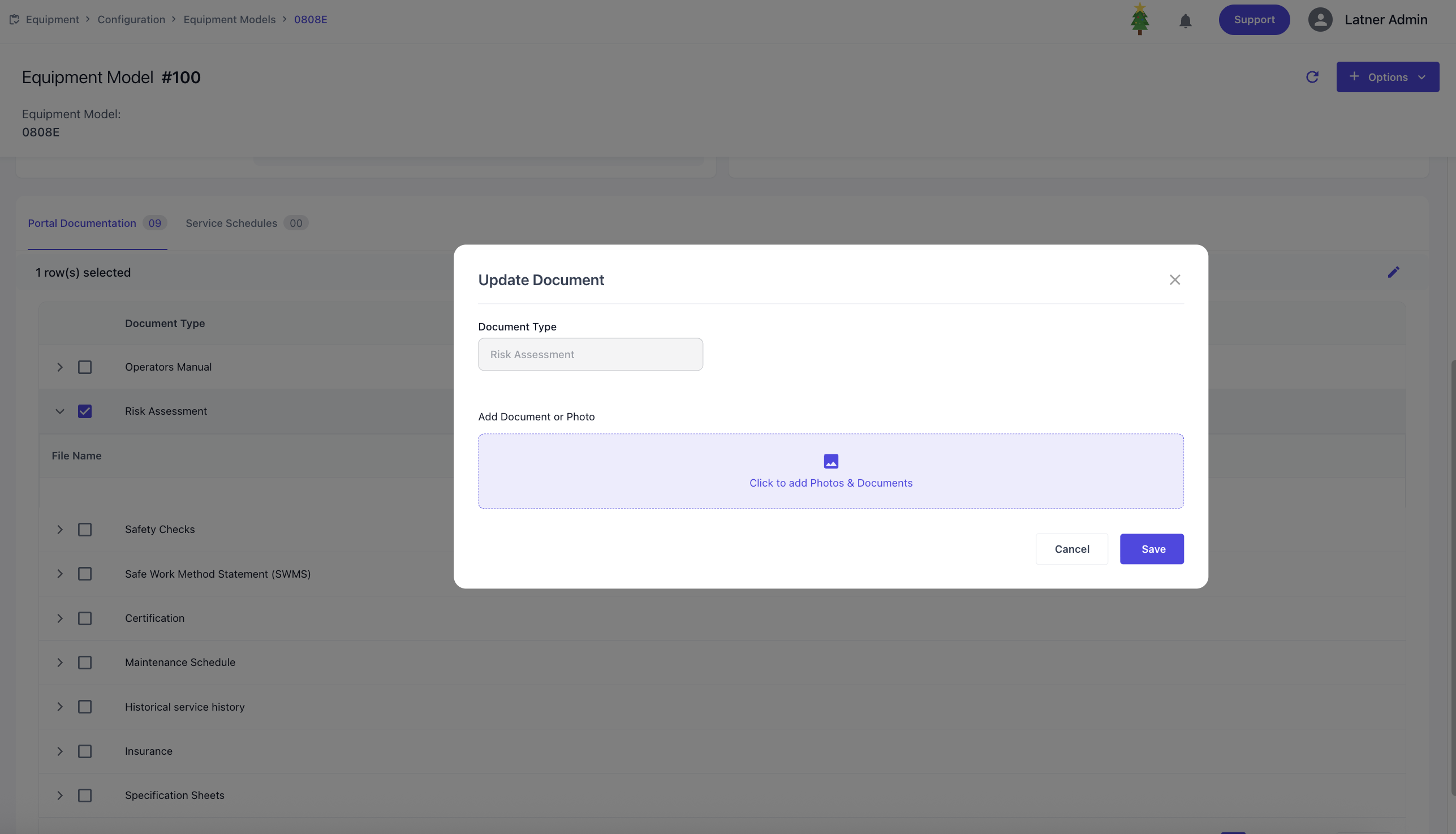
Fuel Types
Fuel Types are used to configure the type of fuel along with the associated costs and charges. When setting up a fuel type, you define:
Cost: the internal cost of the fuel
Charge: the fee applied to customers when fuel is billed
This ensures that fuel usage is consistently recorded, correctly charged, and visible in both operational and financial reporting.
Bulk Equipment Adjustment Reasons
Bulk Equipment Adjustment Reasons are used to configure categories for bulk equipment adjustments, providing clarity and consistency when large groups of equipment records are updated. When setting up an adjustment reason, you define the name, description and status.
Disposal Reasons
Disposal Reasons are used to configure categories for equipment disposals, providing clarity and consistency when assets are retired or removed from service. When setting up a disposal reason, you define name and description.
Transfer Reasons
Transfer Reasons are used to configure categories for equipment transfers between branches, ensuring clarity and consistency when assets are moved across locations. When setting up a disposal reason, you define name and description.
Portal Documentation Types
Portal Documentation Types are used to configure categories for documents that can be uploaded and made available to customers through the public portal (via QR code or link). These types act as the framework against which specific documents are stored, ensuring consistency and easy access. When setting up a portal documentation type, you define name and status.
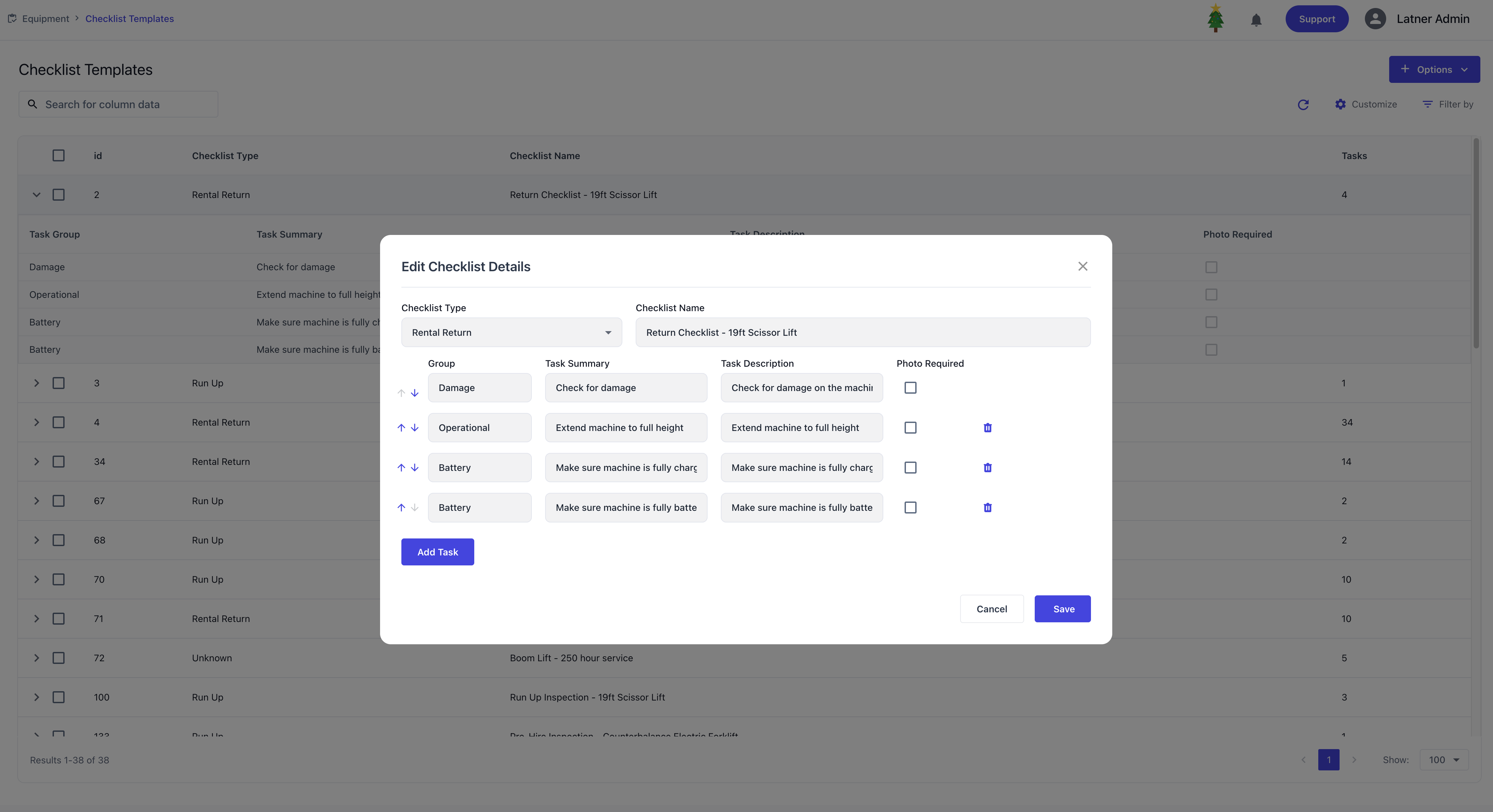
Checklist Templates
Checklist Templates are used to configure standardised checklists that can be imported, exported, or created directly within the system. These templates ensure consistency across inspections, service schedules, and operational processes.
When adding a checklist details, you define:
Type: the category of checklist. Available types include:
Service: used for scheduled service tasks
Run‑up inspections: performed before equipment is put on hire
Return inspections: completed when equipment is returned
Equipment transfer inspections: applied when equipment is moved between branches
Pre‑sale inspections: carried out before selling equipment
Pre‑start inspections: completed by operators before starting equipment
Name: the identifier for the checklist.
Task list: a structured list of tasks, including:
Group: tasks grouped together for PDF output.
Task summary: a short label for the task.
Task description: detailed instructions for completing the task.
Photo required: whether a photo must be attached to complete the task.
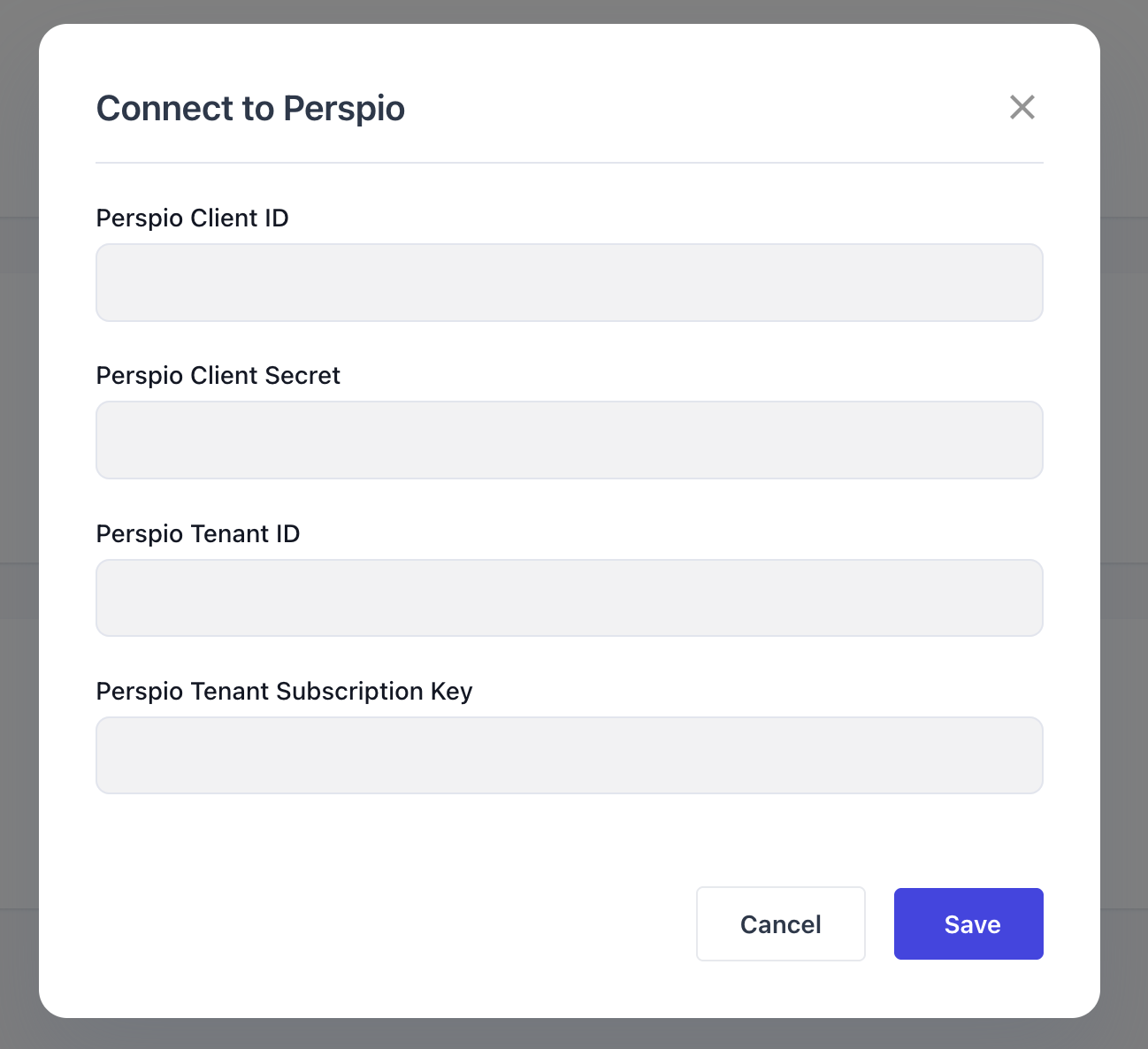
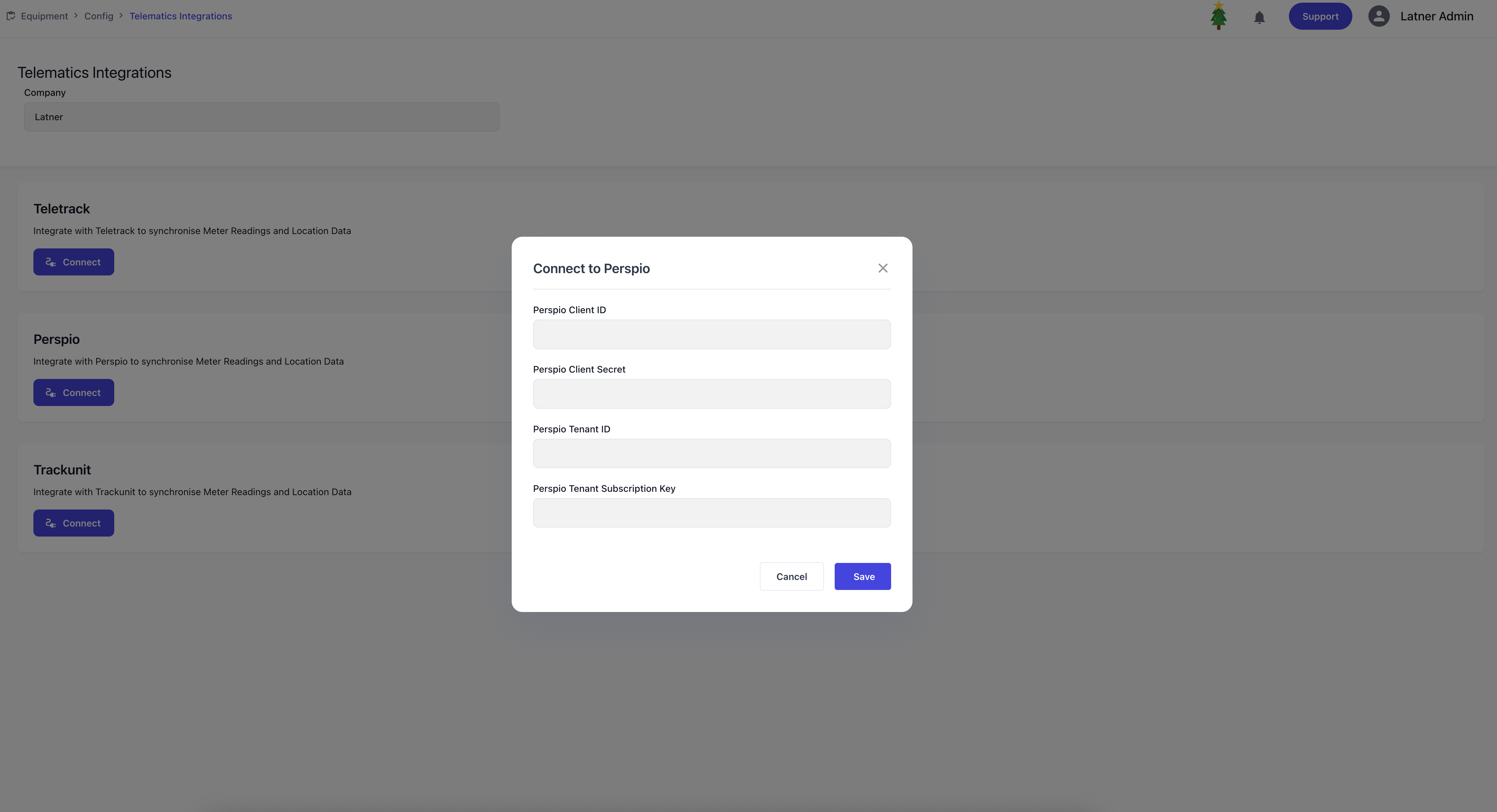
Telematics Integrations
Telematics Integrations are used to connect the system to third‑party tracker software, enabling automated equipment tracking and data syncs. These integrations ensure that fleet and asset information remains accurate and up to date.
When setting up a telematics integration, you define:
Company: the company that will use the tracker software.
Connection credentials: the ID and password required to connect, which vary depending on the tracker software configuration.
Once configured, clicking the Connect button will prompt you to enter the required credentials. The connection process differs by provider, with specific steps available for supported trackers such as Teletrack, Trackunit, and Perspio.
Service Module
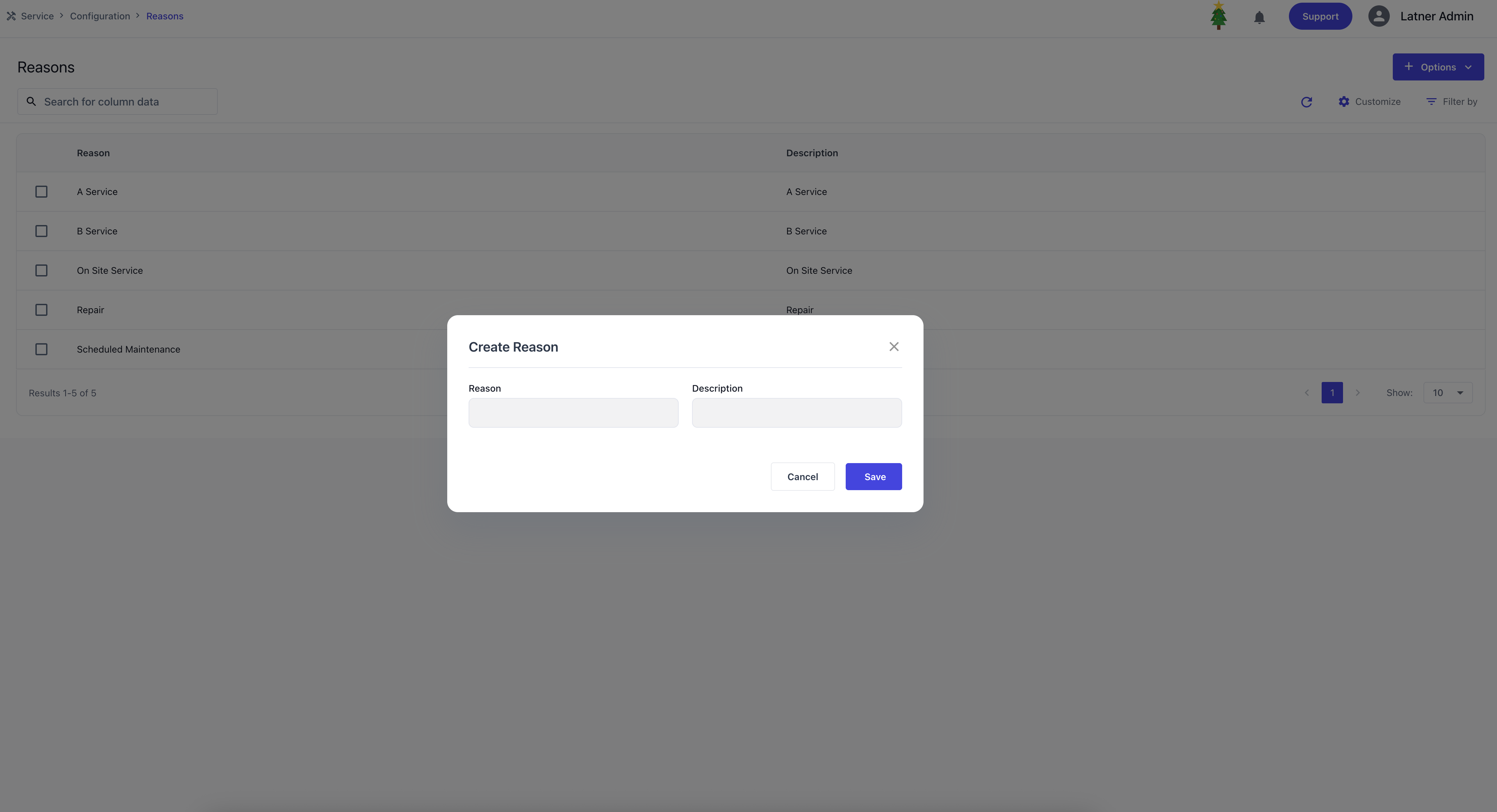
Reasons
Reasons are used to configure the top‑level categorisation for Work Orders, identifying the purpose of each job. These reasons define why a work order is created and provide a structured way to classify operational activities. When setting up a work order reason, you define the name and description.
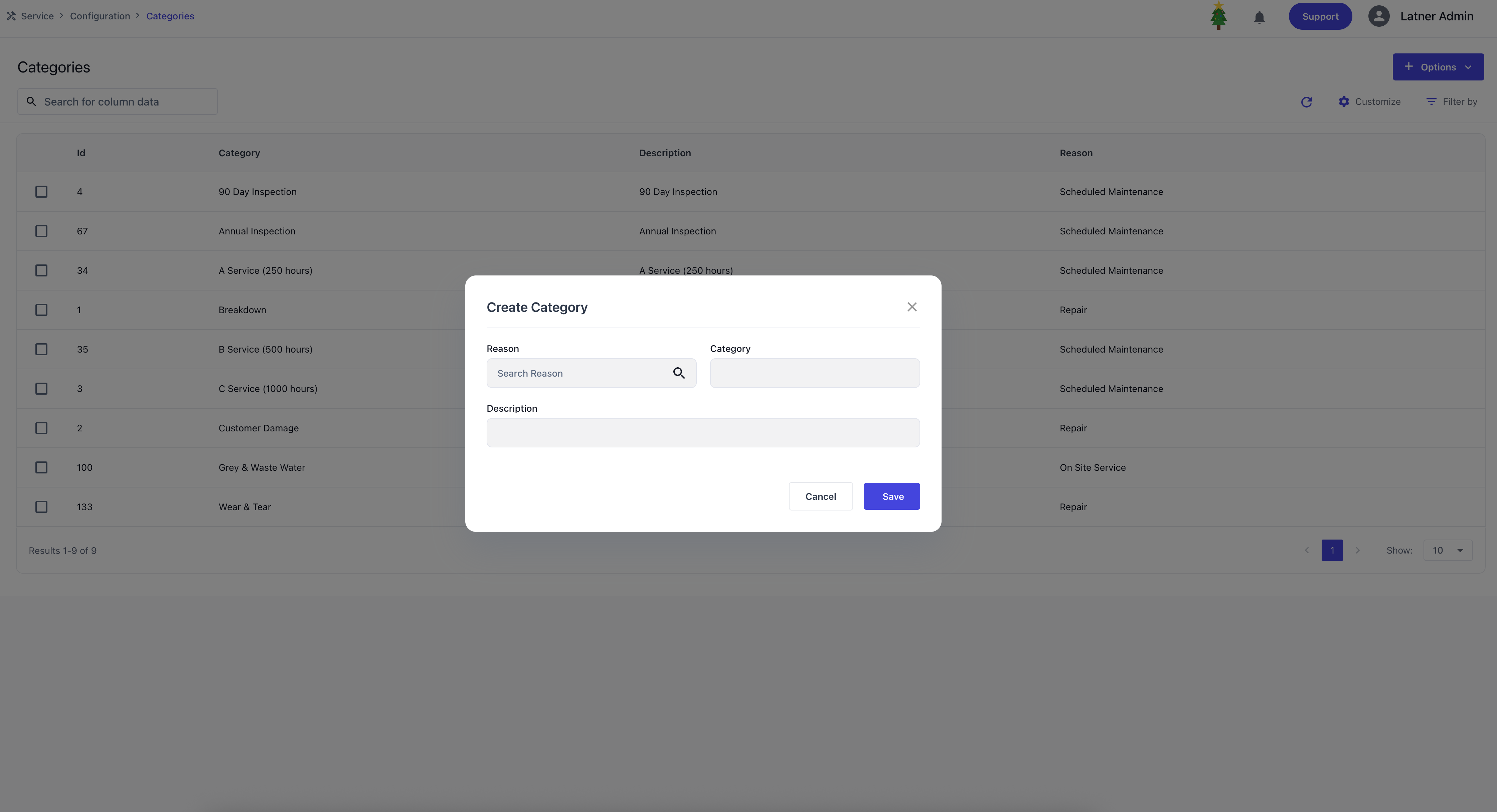
Categories
Categories are used to configure sub‑classifications under Work Order Reasons, providing greater detail and structure when categorising jobs. They allow work orders to be grouped more specifically within a reason, ensuring clarity in reporting and operational tracking. When setting up a category, you define the parent reason it links to, name and description.
Skills
Skills are used to record the specific abilities or competencies applied by a skilled person while completing a job. These entries are not tied to billing or customer‑facing outputs, but instead serve as an internal tool for operational analysis.
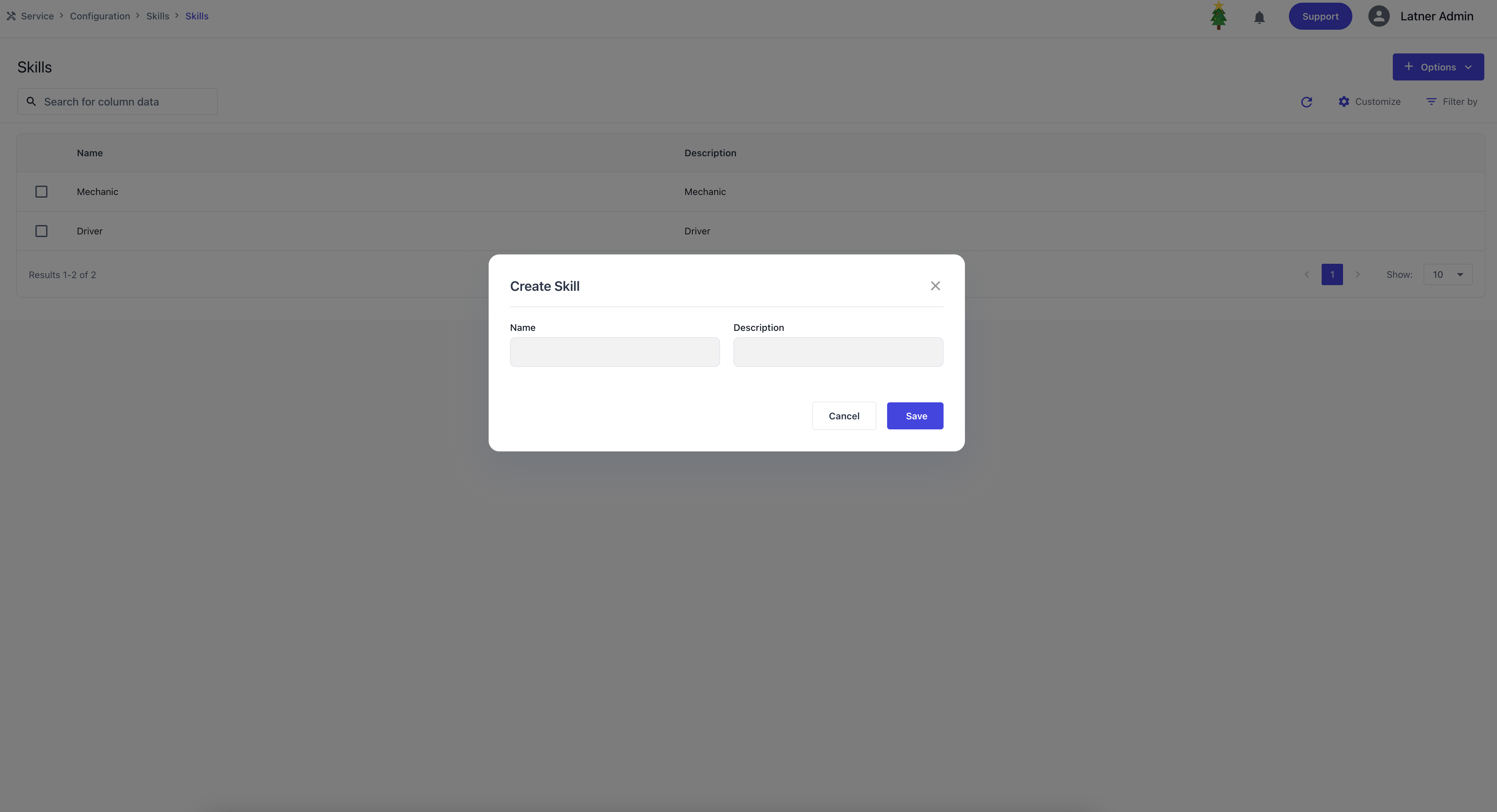
Skilled Persons
Skilled Persons are users configured in the system who have access to completing certain jobs. They represent the operational workforce and can be allocated to tasks based on their roles and skills.
When creating a Skilled Person, you specify:
User: the system user account that the skilled person is tied to.
Warehouse: the warehouse of a branch the skilled person belongs to.
Cost: the internal cost rate associated with the person.
Retail Price: the charge‑out rate for their work.
Call Out Price: the rate applied for call‑out jobs.
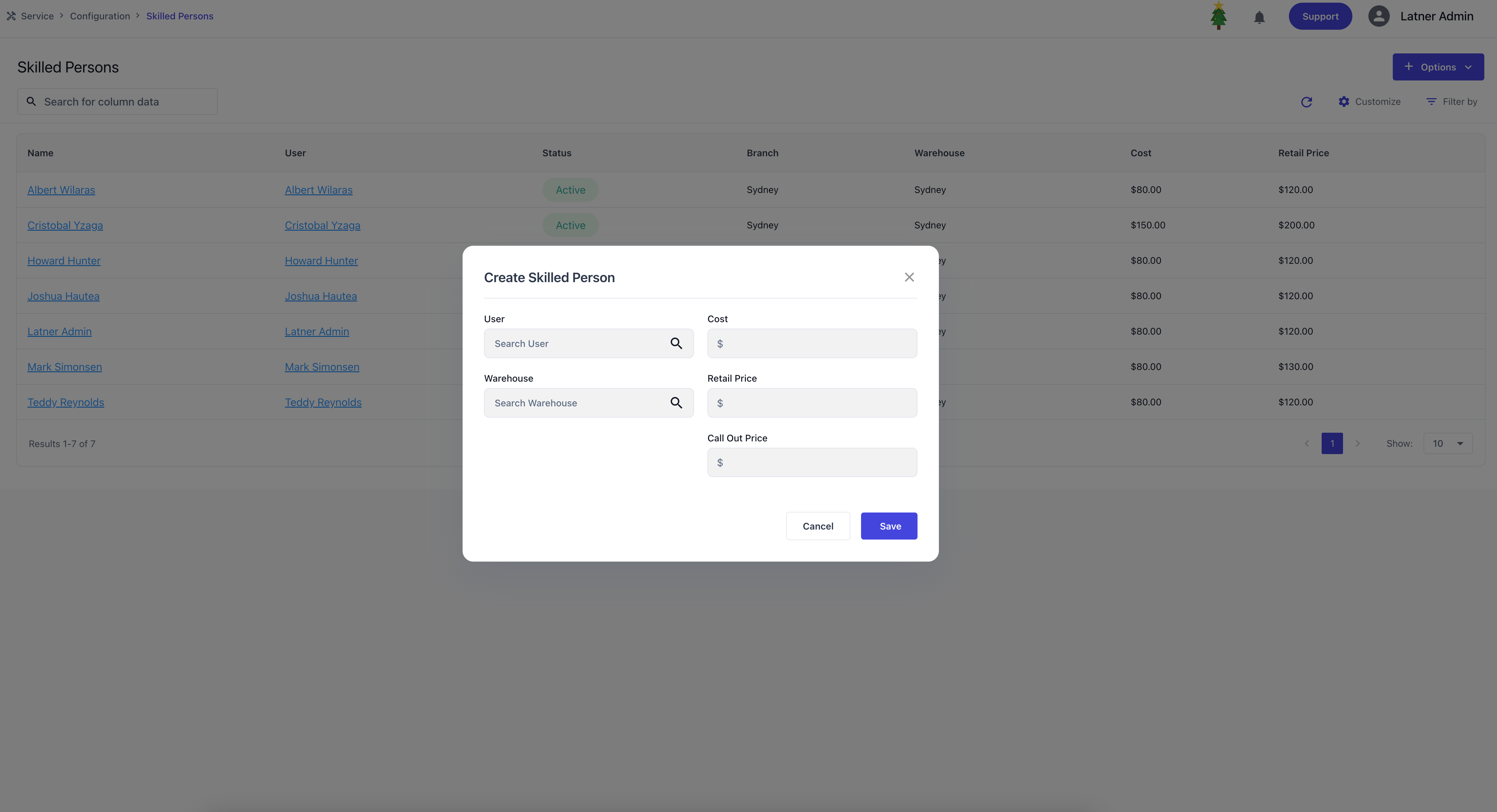
Once created, you can assign roles to the skilled person. Roles determine which mobile functionalities they can access and make them available for allocation on specific scheduling screens.
Driver: gains access to Mobile Transport and can be filtered out on Transport Allocation.
Yard Staff: gains access to Mobile Inspections and can be filtered out on Inspection Allocation.
Workshop / Field Technician: gains access to Mobile Work Order and can be filtered out on Service Allocation per category.
Pump Driver: gains access to Mobile Sanitation.
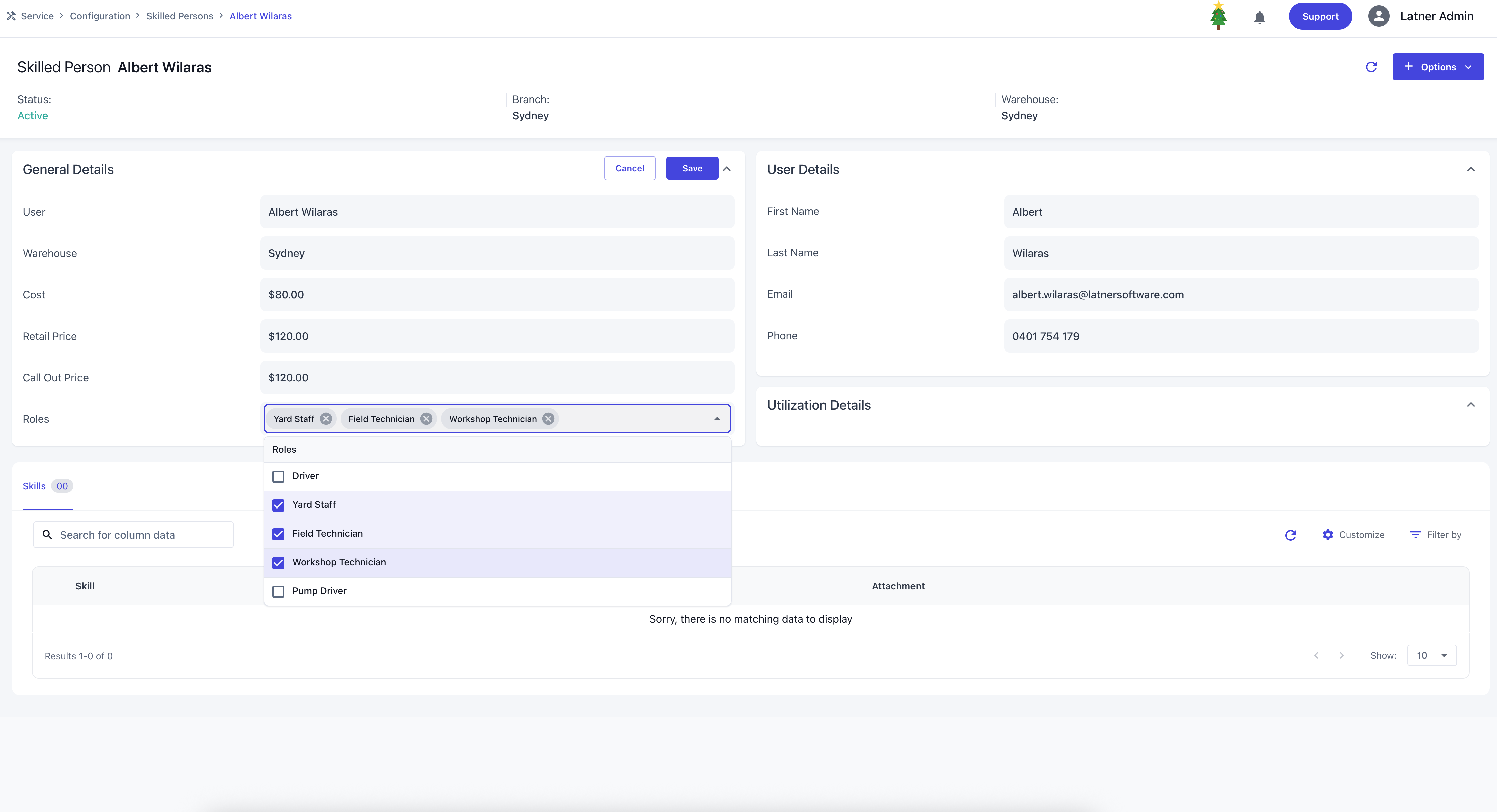
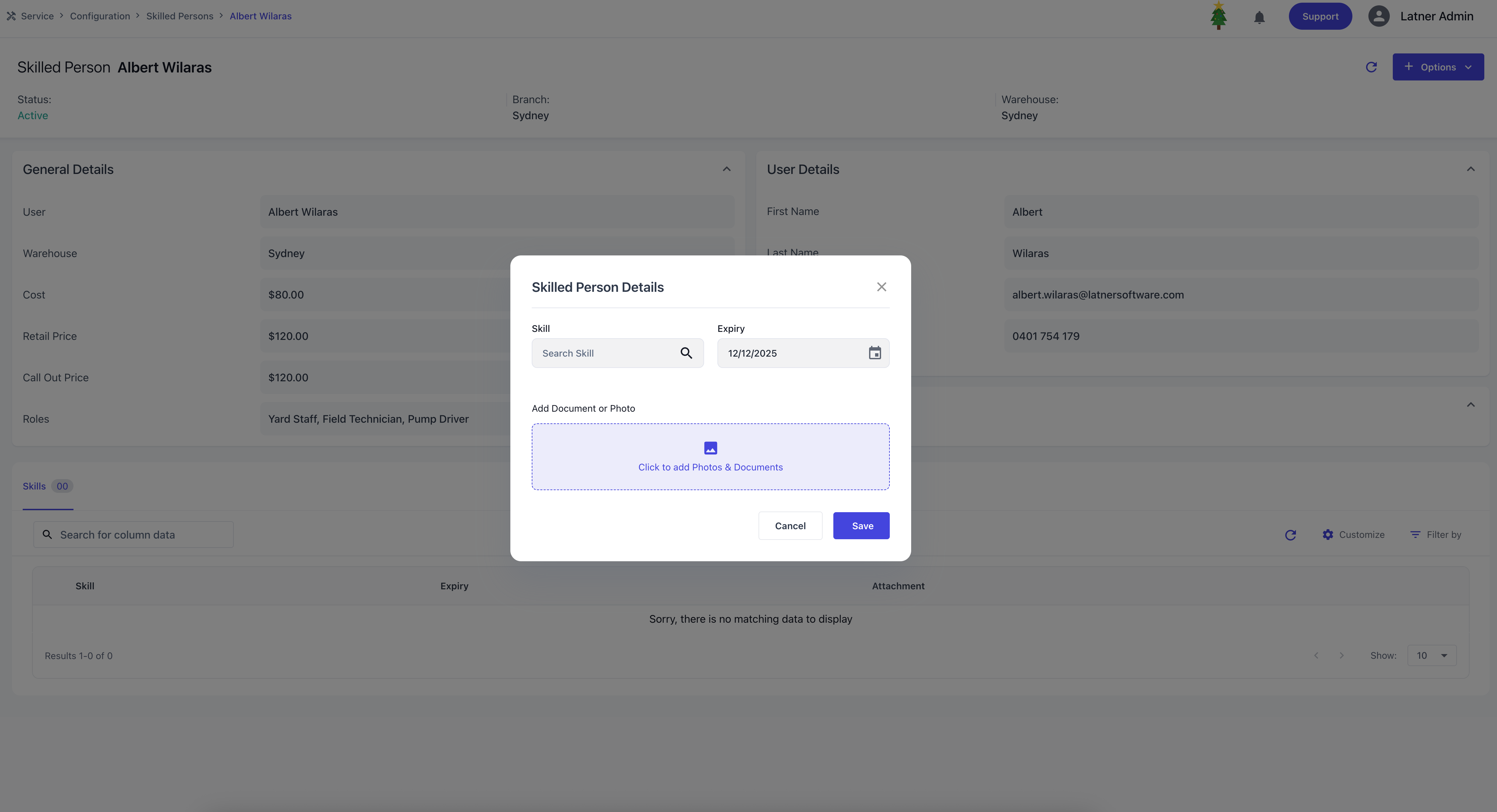
Clicking Options allow you to Deactivate the skilled person if they are no longer active or Assign skills by specifying:
Skill: the competency being recorded.
Expiry: the date the skill or certification expires.
Document/Photo: supporting evidence, typically certificates.
Skilled Person Rate Books
Skilled Person Rate Books are used to create and manage rate cards that define how charges are applied for work performed by skilled persons. These rate books ensure that timesheet entries and work orders are billed consistently according to equipment class or model. Rate books can be assigned directly to a Customer. When creating a Skilled Person Rate Book, you specify:
Level: whether the card applies to all branches or a specific branch.
Branch (if applicable): the branch the rate card belongs to.
Review Date: the date the rate card should be reviewed for accuracy.
Description: an identifier or purpose for the rate card.
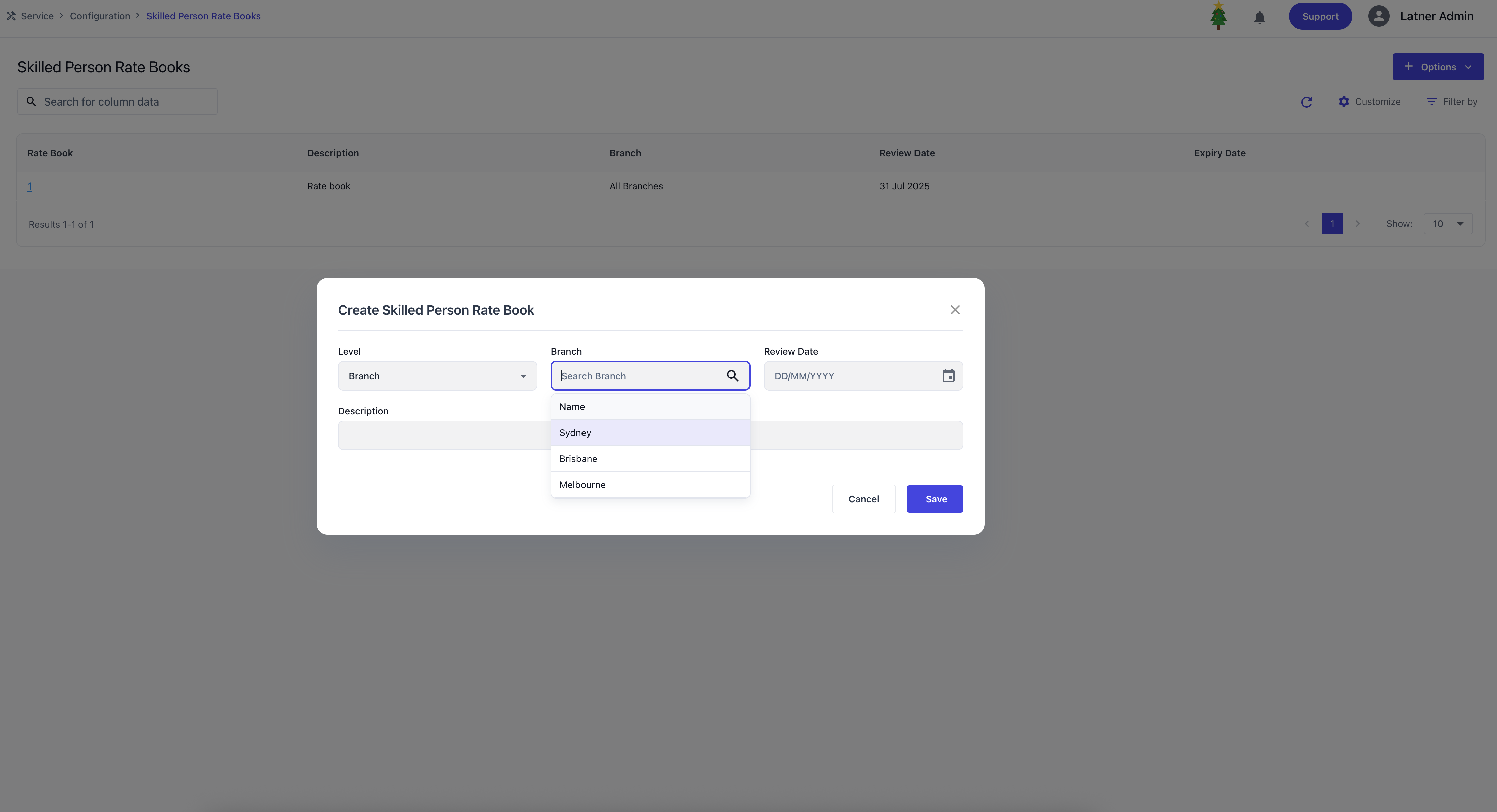
Once the rate book is created, there are options where you can either copy existing rates to another card or add new rate details. Expiry dates can also be set to disable rates accordingly through this detailed screen.
Each rate detail line allows you to specify:
Equipment Class and/or Model: the equipment type the rate applies to.
Call Out Price: the rate charged for call‑out jobs.
Retail Price: the standard charge‑out rate for that equipment.
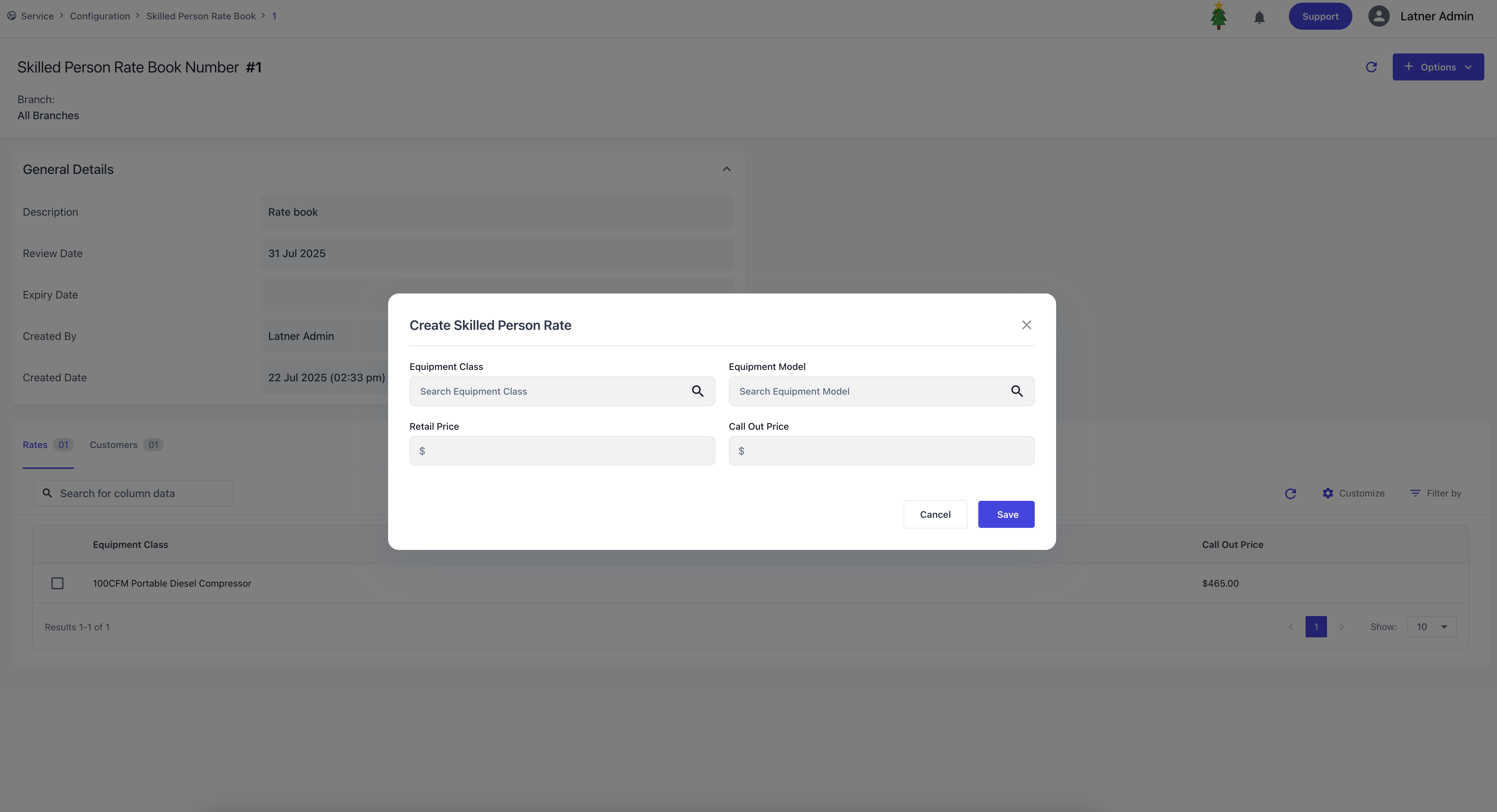
When a work order is completed, the system will identify the equipment class or model linked to the job, match the applicable rate from the Skilled Person Rate Book which will override the default skilled person rate and apply the lowest available rate across all rate books to ensure fair and consistent billing.
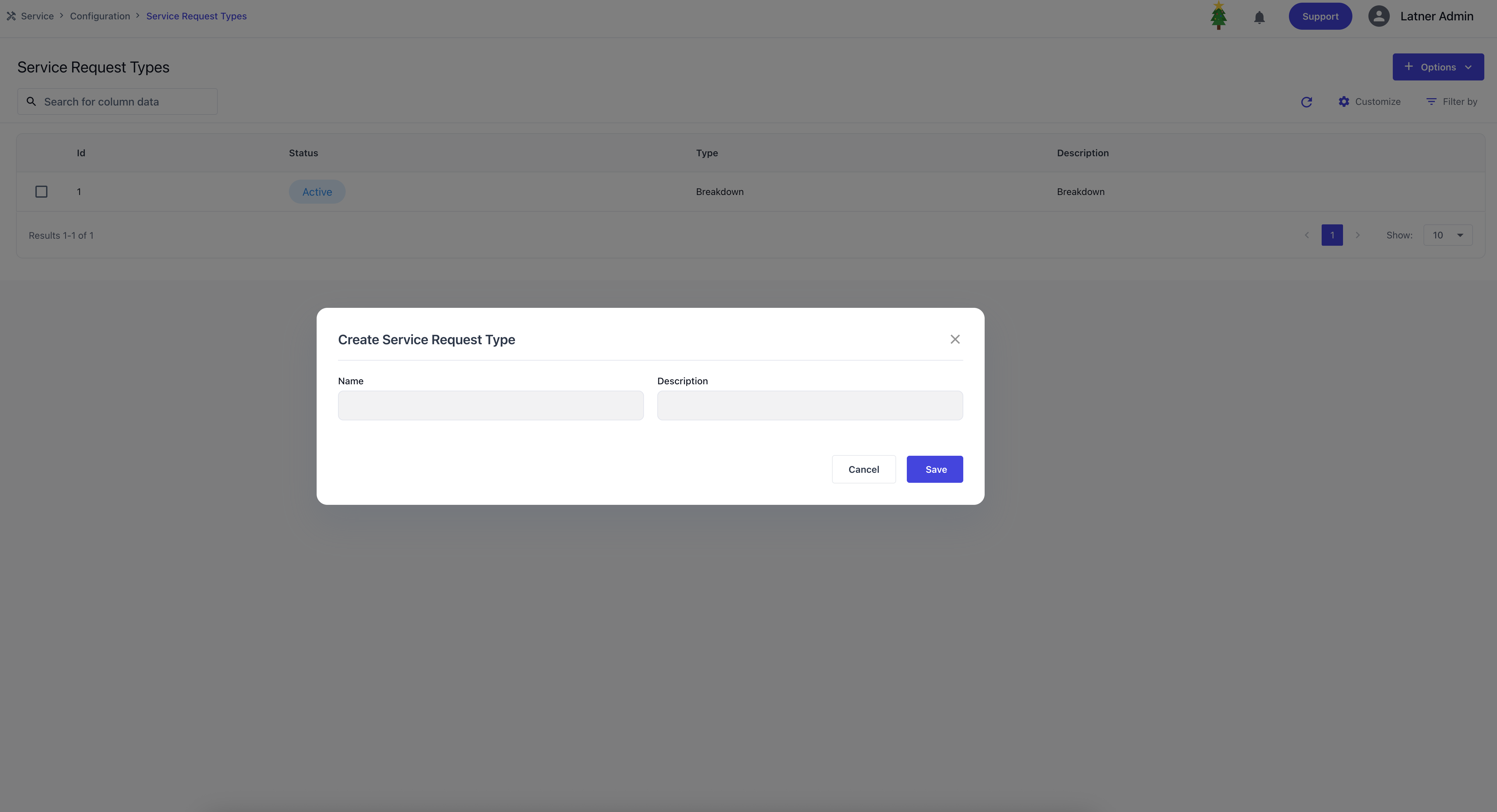
Service Request Types
Service Request Types are used to categorise and identify the purpose of the request. They act as the preliminary step before creating a work order e.g. Breakdown Request or Customer Enquiry. When setting up a service request type, you define the name and description.
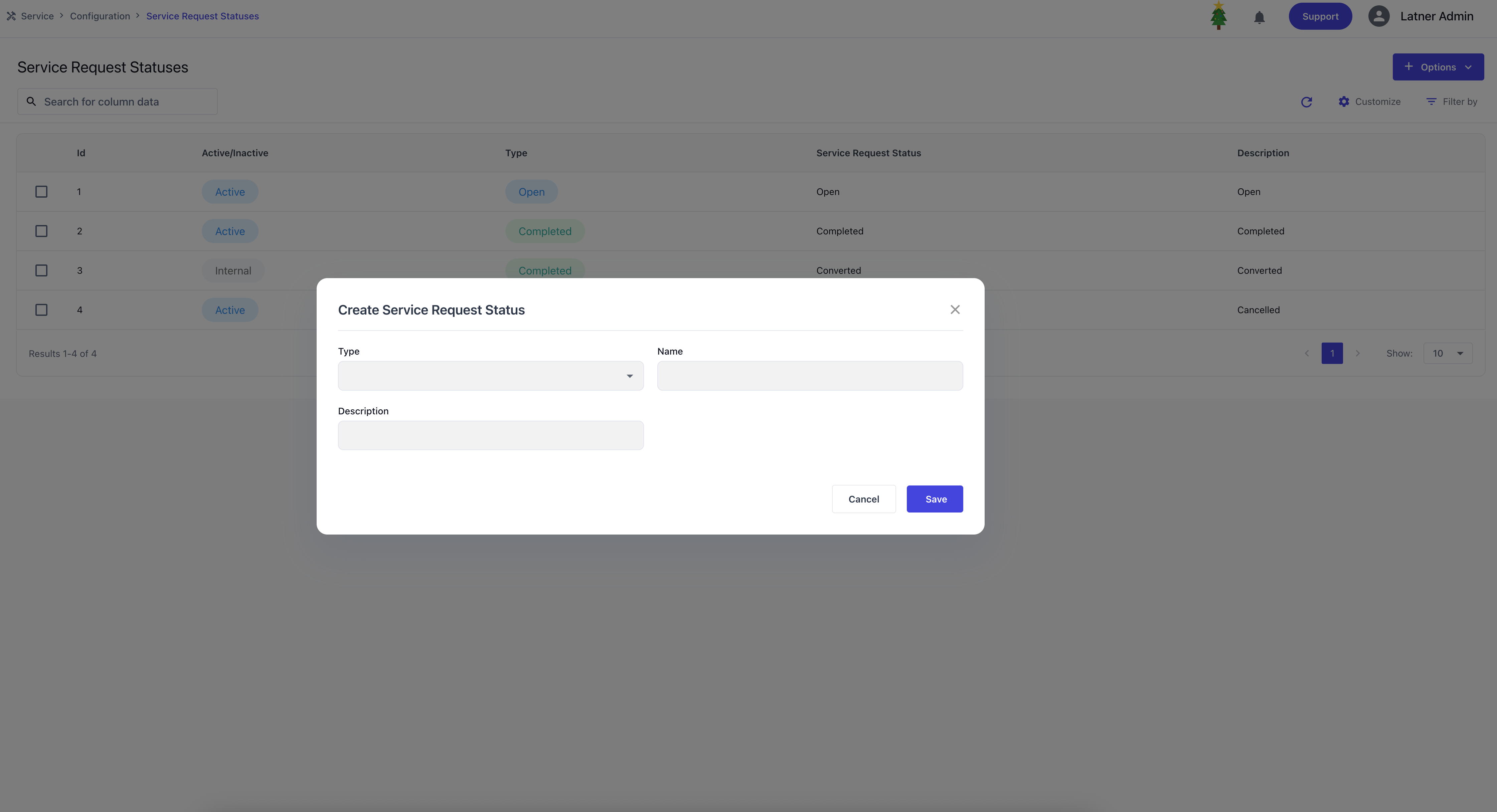
Service Request Statuses
Service Request Statuses are used to categorise the progress of a service request. They are mostly used to track what has been done and lifecycle of requests before or after they are converted into work orders. When creating a service request status, you define the name, description and types:
Open: indicates the request is still active or awaiting action (e.g., “Waiting for Customer” or “Under Investigation”).
Completed: indicates the request has been resolved (e.g., “Solved on phone”).
Cancelled: indicates the request was closed without further action (e.g., “Equipment now works”).
Converted is also created as an Internal status that cannot be deleted. It completes the request and creates a work order when converted.
Timesheet Groups
Timesheet Groups are used to categorise and organise timesheets in how different types of time entries are tracked. When creating a timesheet group, you define the name, description, and status (active or inactive). There are also predefined internal timesheets that cannot be deleted: work orders, operator dockets, inspections.
Timesheet Sub Groups
Timesheet Sub Groups are used to further categorise and organise timesheets under their parent Timesheet Groups, providing more detailed tracking of time entries. When creating a timesheet sub group, you define the parent group it belongs to, name, description, and status (active or inactive). There are also predefined internal timesheet sub groups that cannot be deleted for labour belonging to work orders, operator dockets, inspections groups.
Stock Module
Stock Types
Stock Types are used as optional, independent labels for stock records. They provide an additional layer of identification but do not control or restrict the items beneath them. When setting up a stock type, you define the name and description.
See How to Create Stock Types, Groups & Sub Groups to see common ways to categorise stock items.
Group
Stock Groups are used to configure the major systems or areas of stock, serving as the first structural layer in inventory organisation. They categorise items at a high level, ensuring clarity and consistency in reporting. When setting up a stock group, you define the name and description.
See How to Create Stock Types, Groups & Sub Groups to see common ways to categorise stock items.
Sub Group
Stock Sub Groups are used to break down stock groups into more specific components, providing finer detail and structure beneath the main group. They ensure that inventory records are consistently classified at both the group and sub group level. When setting up a stock sub group, you define the name, description, and the parent group it connects to.
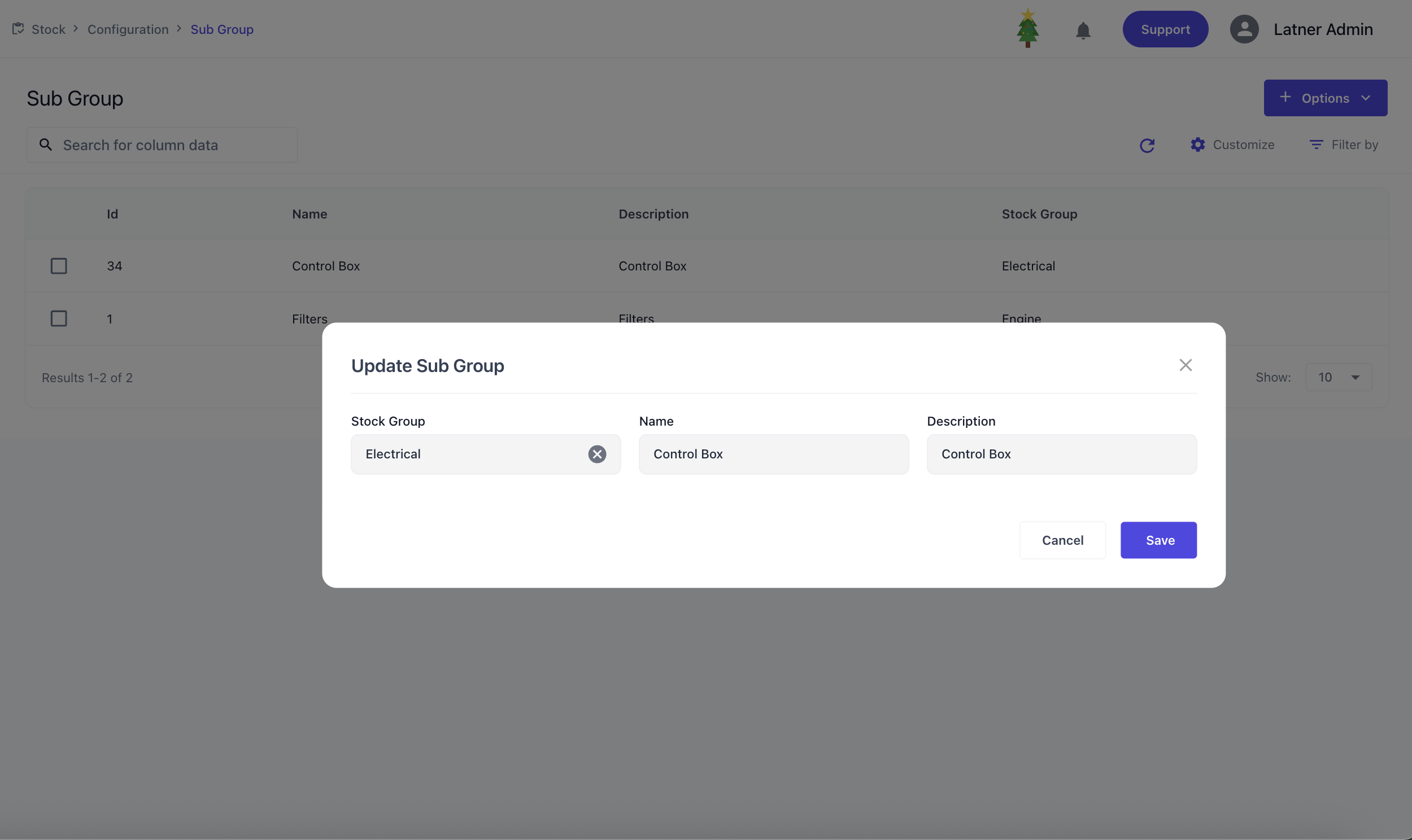
See How to Create Stock Types, Groups & Sub Groups to see common ways to categorise stock items.
Stock Adjustment Reasons
Stock Adjustment Reasons are used to configure reasons for stock adjustments, providing clarity and consistency when inventory records are updated. They ensure that changes to stock levels are properly classified and traceable for reporting. When setting up an adjustment reason, you define the name, description and status.
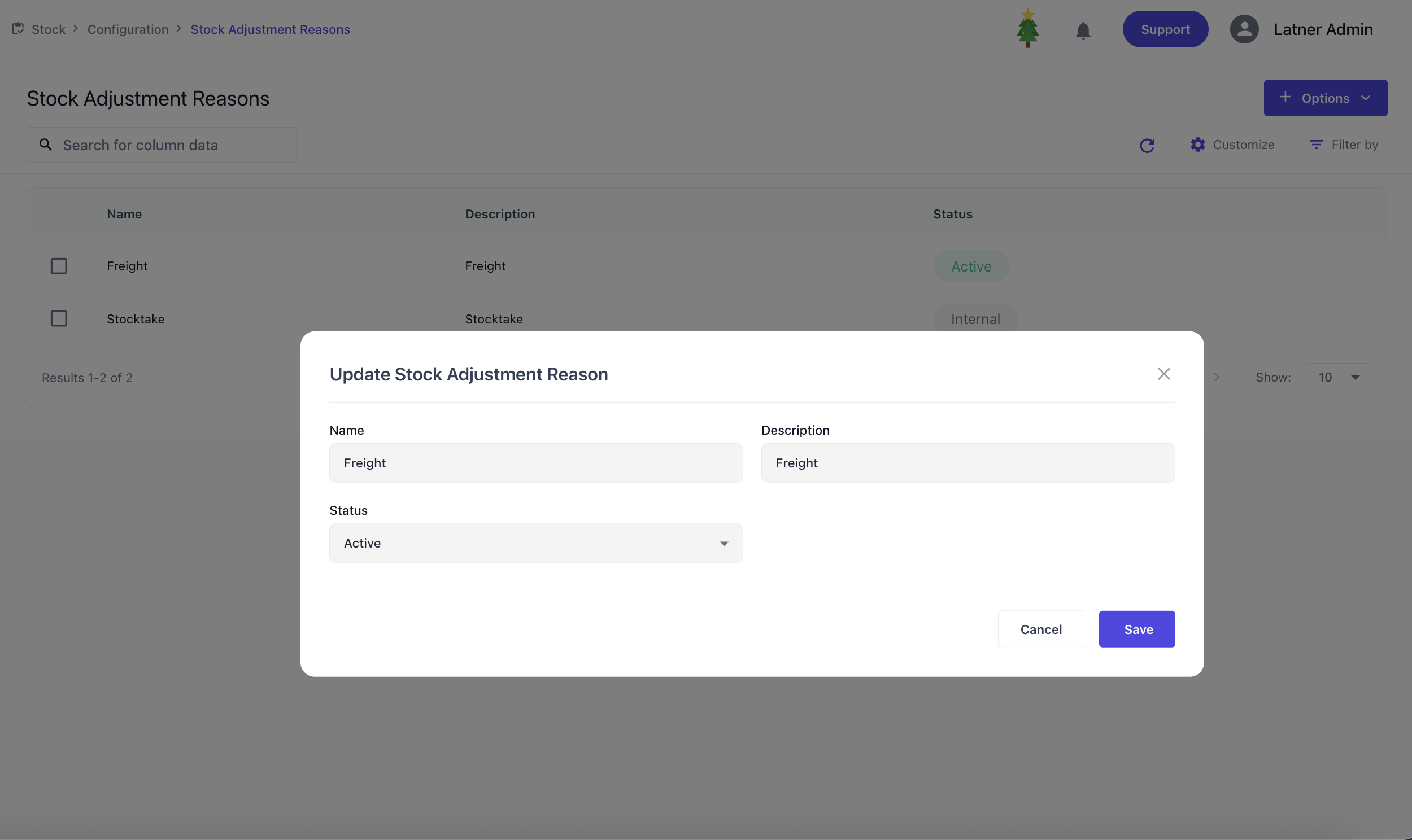
Customers Module
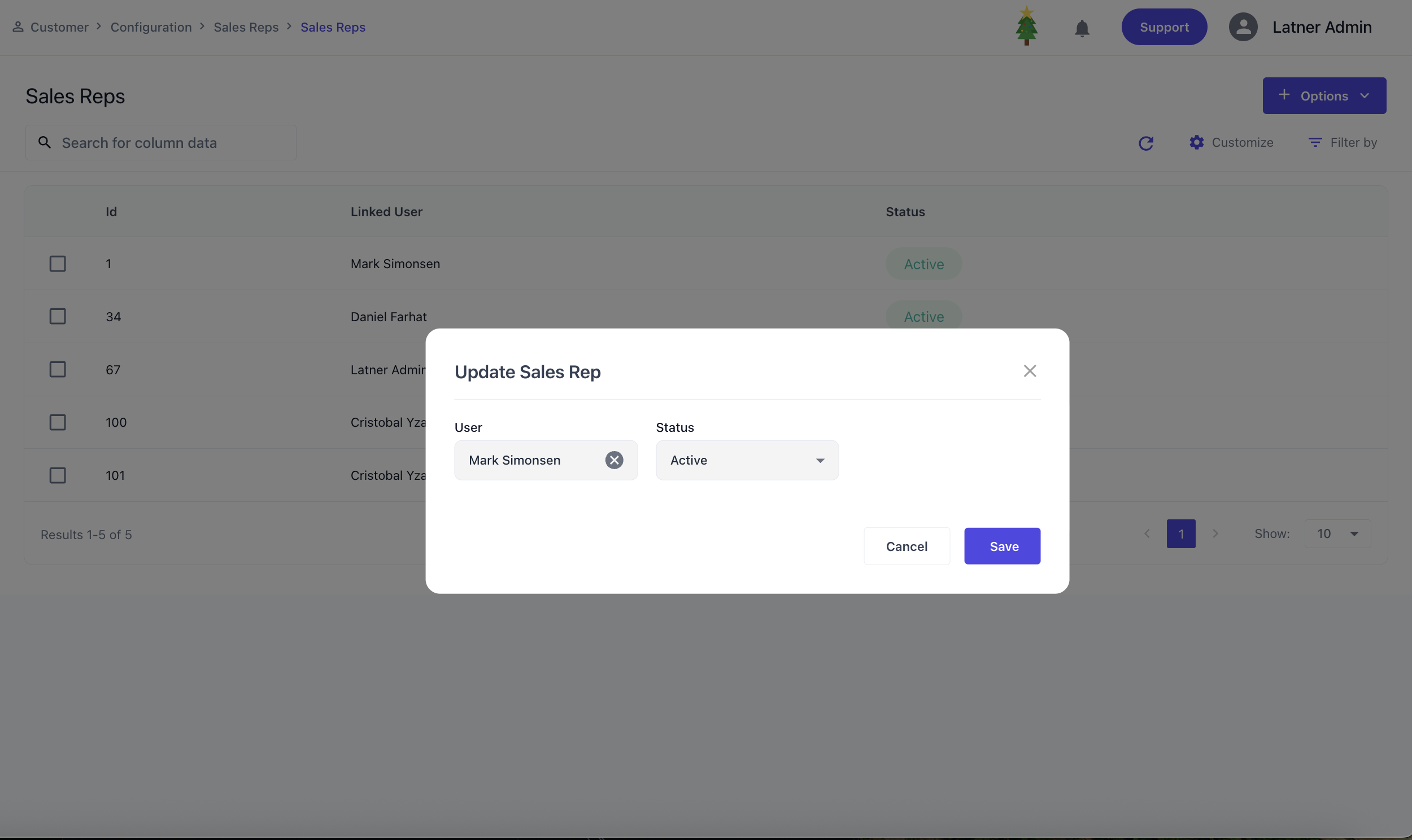
Sales Reps
Sales Reps are users configured in the system who represent the sales workforce. They can be assigned to customers, opportunities, or CRM, and their activity is tracked for reporting and performance analysis.
When creating a Sales Rep, you specify:
User: the system user account that the sales rep is tied to.
Status: whether the sales rep is active or inactive.
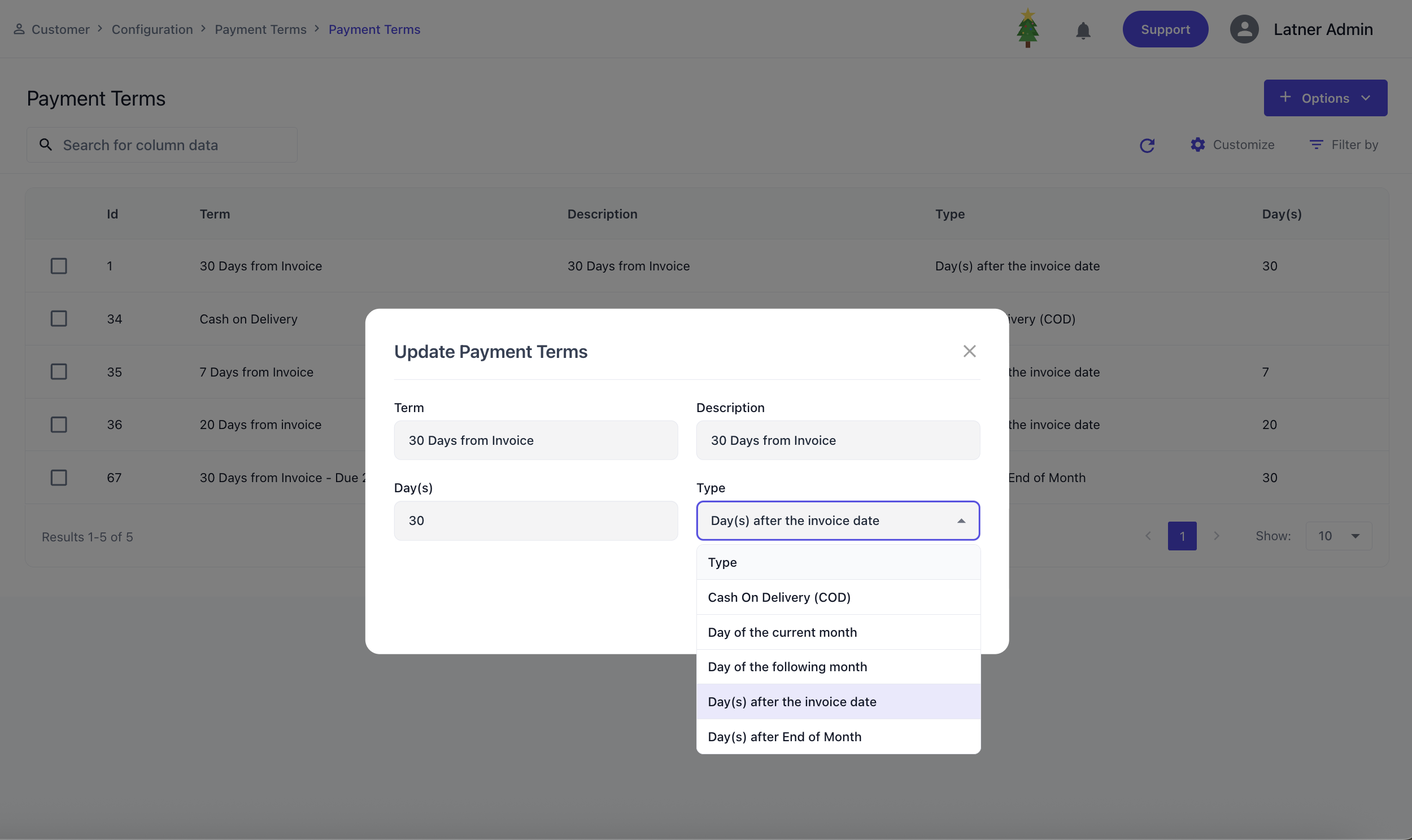
Payment Terms
Payment Terms are used to configure how customer invoices are due, providing consistency in billing and collections. They define the rules for when payments must be made and ensure that due dates are automatically calculated based on the selected term.
When setting up a payment term, you define:
Description: a short explanation of the term’s purpose.
Day(s) field is available to enter the number of days for types that require a day count. This value determines how the system calculates the due date from the invoice date or end of month.
Type: the method by which the due date is calculated including:
Cash On Delivery (COD): payment is due immediately.
Day of the Current Month: payment is due on a specified day within the current month.
Day of the Following Month: payment is due on a specified day in the next month.
Day(s) after Invoice Date: payment is due a set number of days after the invoice date.
Day(s) after End of Month (EOM): payment is due a set number of days after the end of the month in which the invoice was issued.
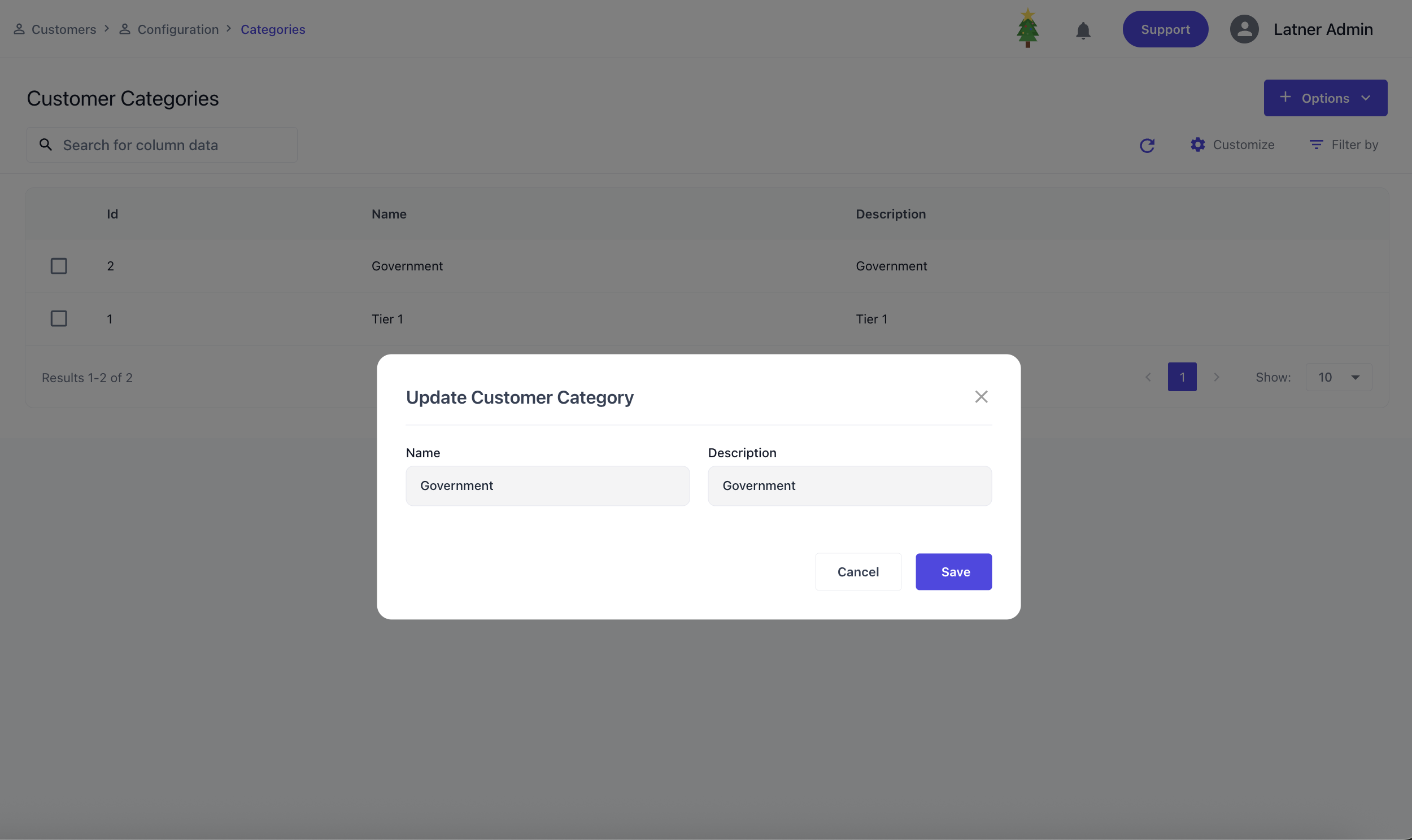
Customer Categories
Customer Categories are used to configure classifications for customers. When setting up a customer category, you define the name and description.
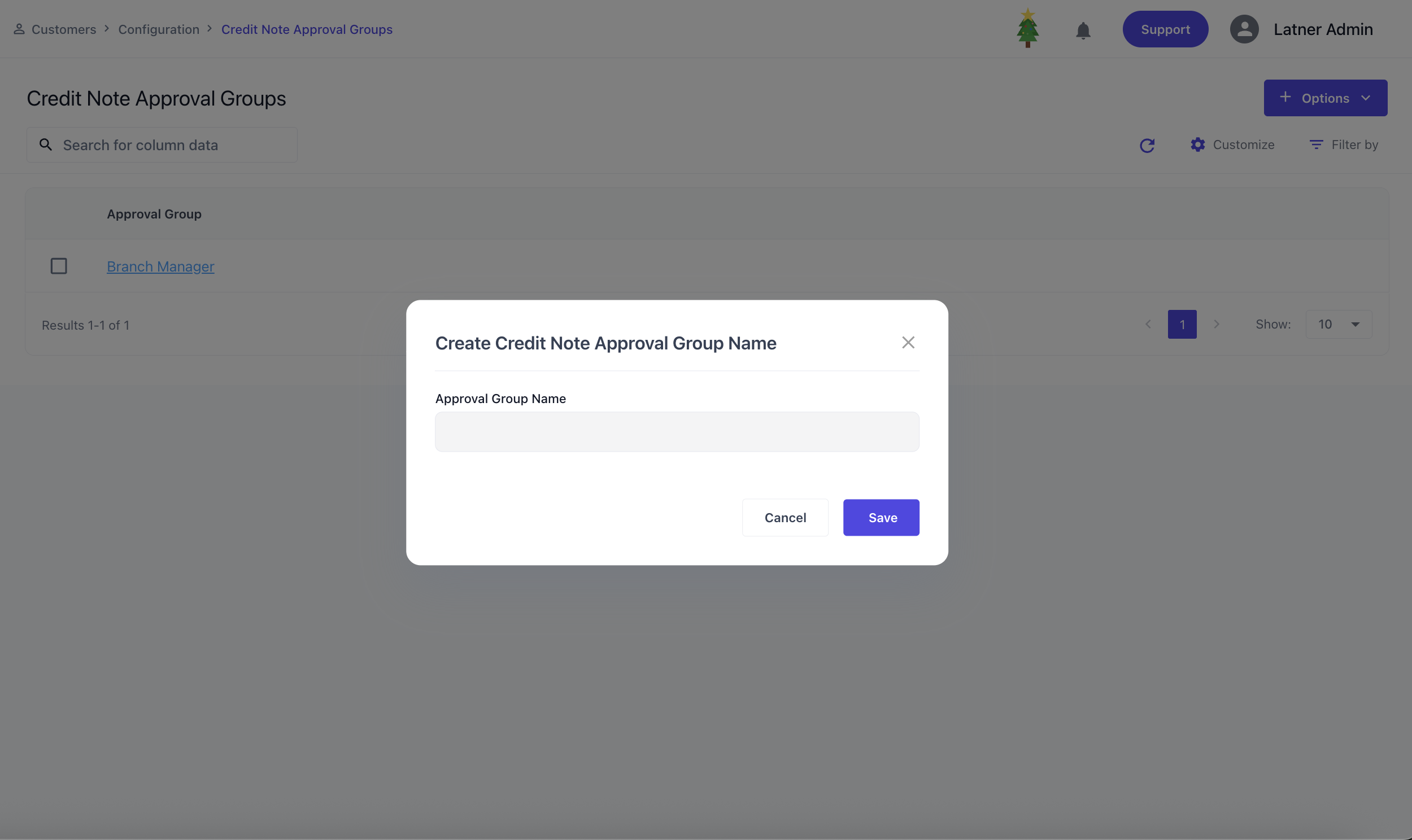
Credit Note Approval Groups
Credit Note Approval Groups are used to manage approval rules that control who can authorise credit notes and up to what value. These groups ensure that credit processing is consistent, auditable, and aligned with internal financial controls.
A global setting Enforce Credit Note Approval Limits needs to be turned on for the limits to take affect.

When creating a Credit Note Approval Group, you specify the name which commonly would be the department that has limits on the approval.
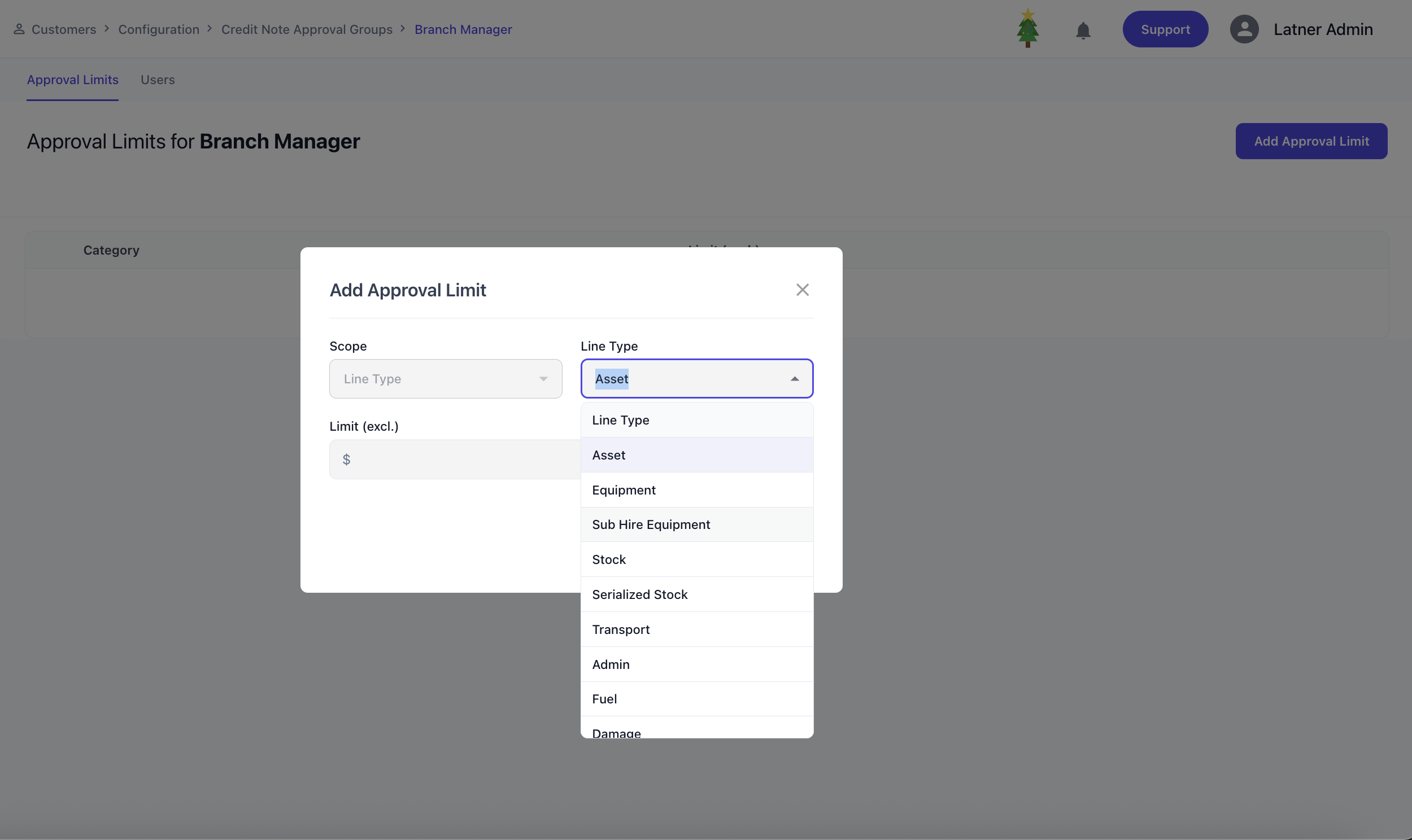
Once the approval group is created, the system allows you to add one or more approval limits. Each approval limit defines:
Line Type: the type of item being credited (e.g., equipment, transport, damage).
Approval Limit (excl. GST): the maximum credit amount the user can approve for that line type.
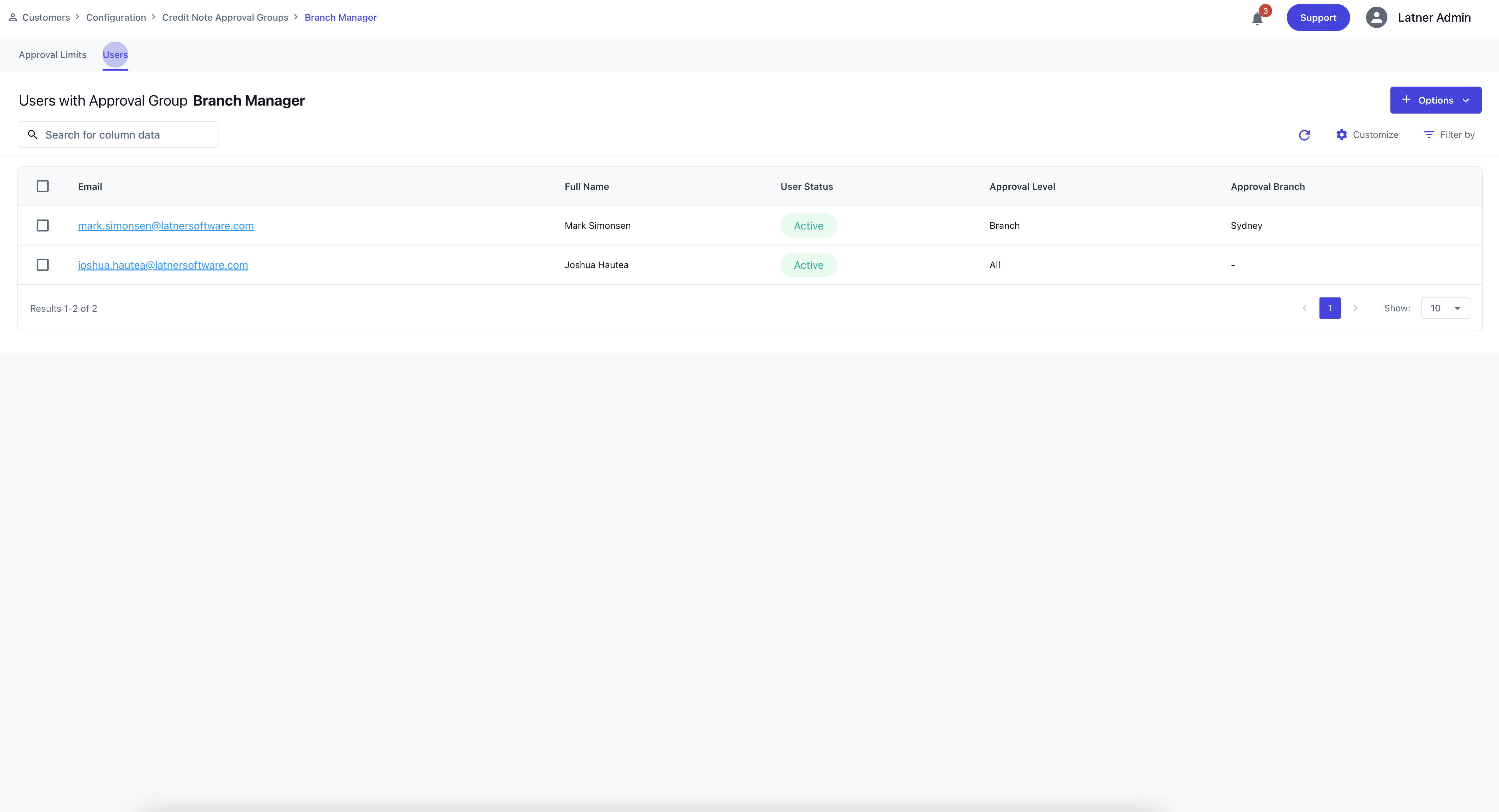
Approval groups are later assigned to Users through their user settings, determining the credit limits they are authorised to approve. See this section on Users on how to assign Approval Groups. You could also see the Users that are currently assigned on this group on the top tab.
Insurance Companies
Insurance Companies are used to store and manage insurer records that can be linked to customer insurance details. When creating an Insurance Company, you specify the name.
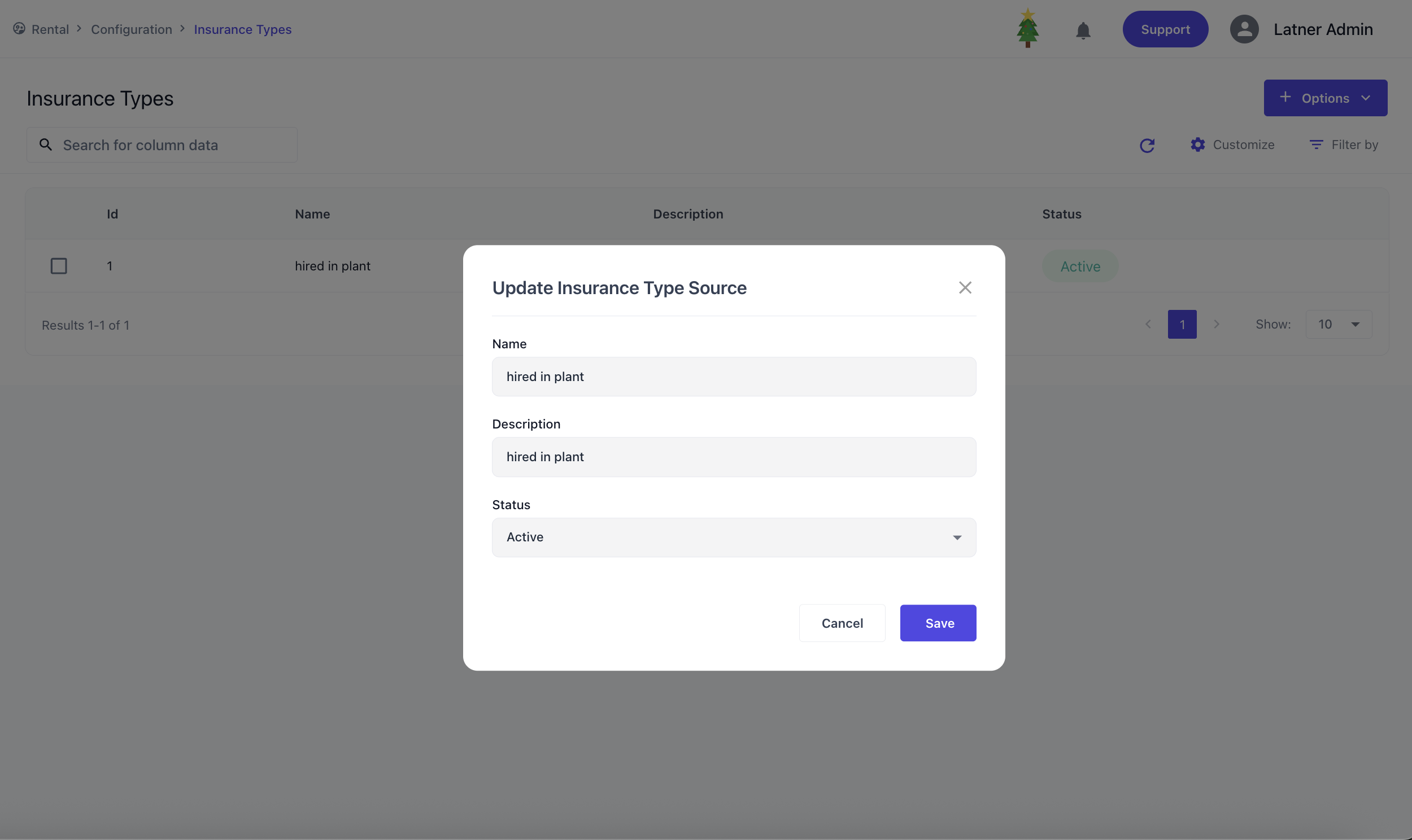
Insurance Types
Insurance Types are used to categorise the different kinds of insurance that may apply to customers or equipment. When creating an Insurance Type, you specify the name, description and status.
Suppliers Module
Expense Types
Expense Types are used to categorise supplier expenses that are not stock items. They ensure that operational costs are recorded consistently and can be reported accurately. When creating an Expense Type, you specify the name and description.
Financials Module
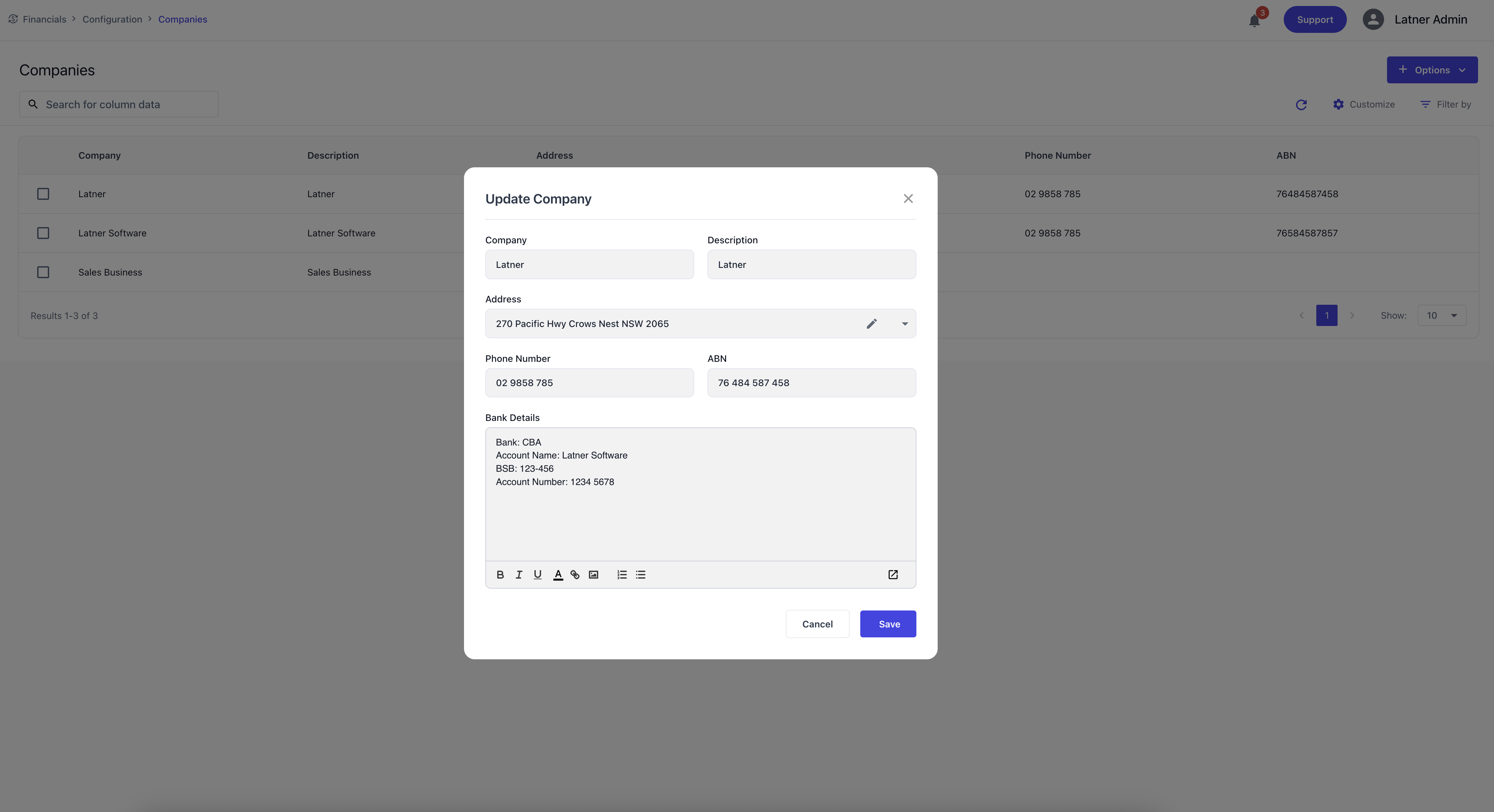
Companies
Companies represent the top‑level financial entities within the system and are primarily used for accounting integration and financial reporting. They define the organisational structure and financial identity of your business.
When creating a Company, you specify:
Company Name: the legal or operational name of the company.
Description: additional context or internal notes.
Address: the company’s physical or mailing address.
Phone Number: the company’s primary contact number.
ABN: the Australian Business Number for compliance.
Bank Details: the banking information used for financial transactions.
Companies form the foundation for divisions, branches, and financial configuration.
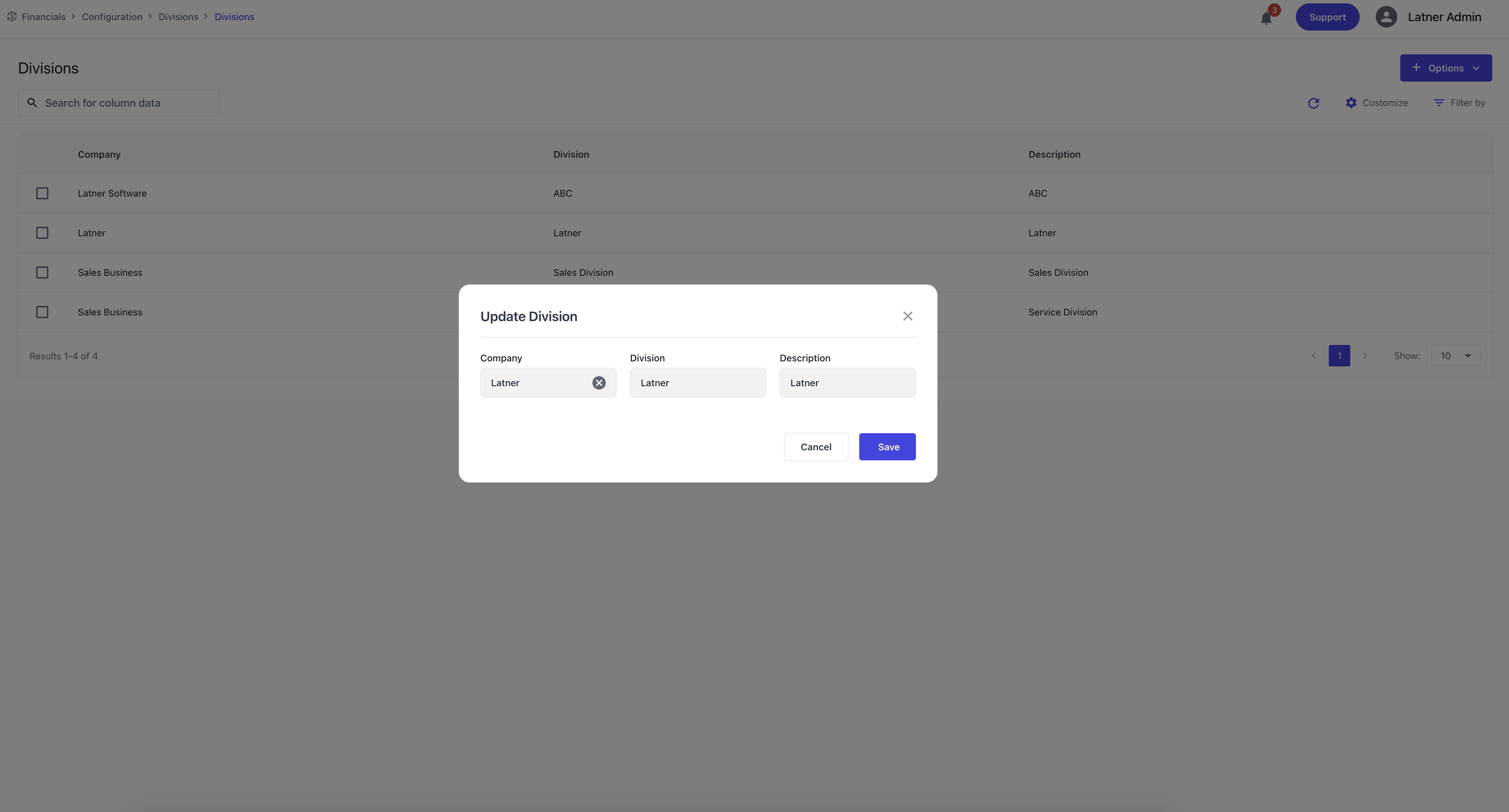
Divisions
Divisions sit under Companies and are used to segment the organisation for CRM and operational purposes. They help structure customer management and internal reporting.
When creating a Division, you specify:
Company: the parent company the division belongs to.
Division Name: the identifier for the division.
Description: additional context or purpose.
Branches
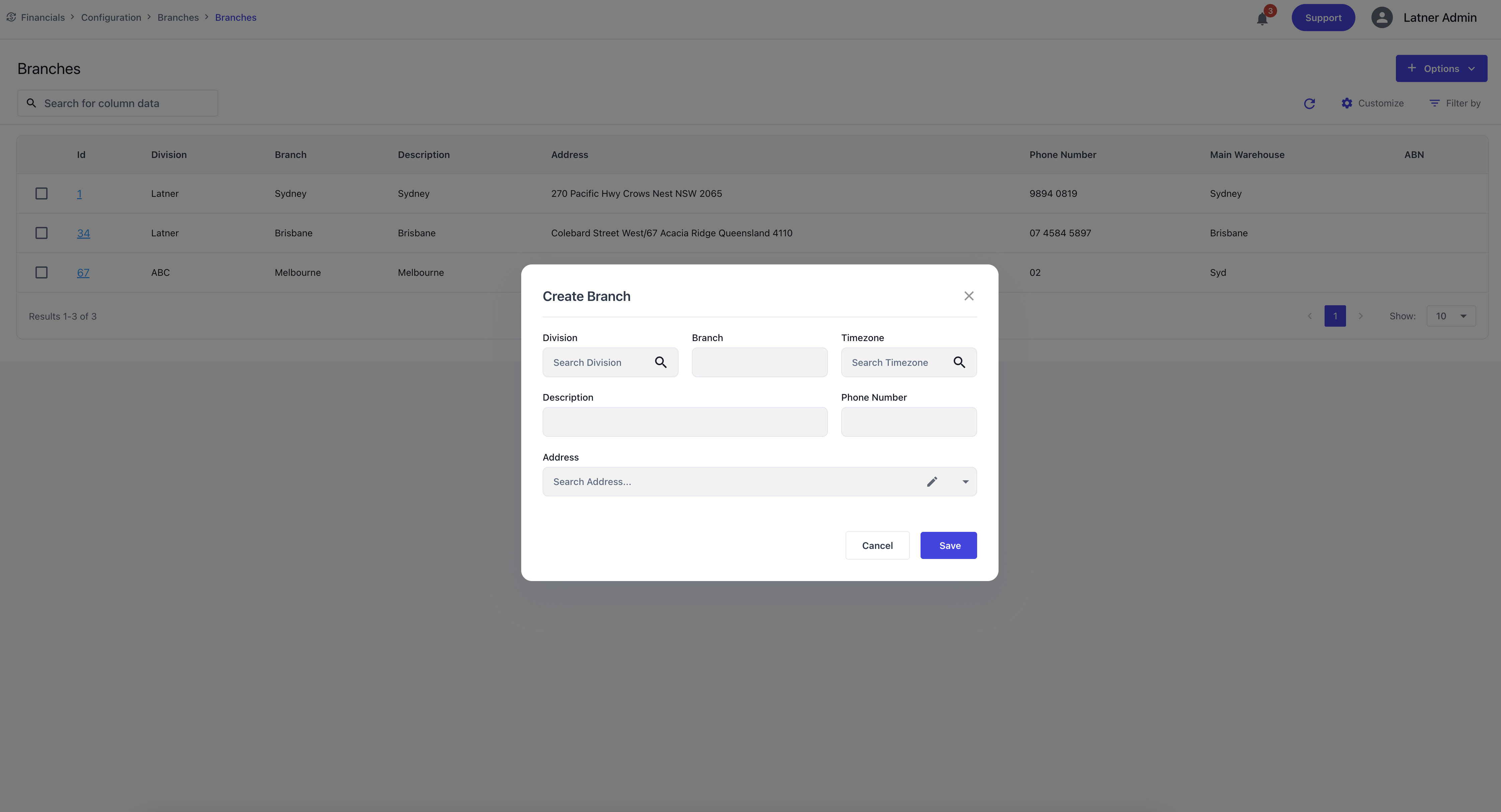
Branches sit under Divisions and represent operational locations used throughout service, rental, and logistics workflows. They define where work is performed and where resources are managed.
When creating a Branch, you specify:
Division: the parent division.
Branch Name: the identifier for the branch.
Timezone: the timezone the branch operates in.
Description: additional context or purpose.
Phone Number: the branch’s contact number.
Address: the physical location of the branch.
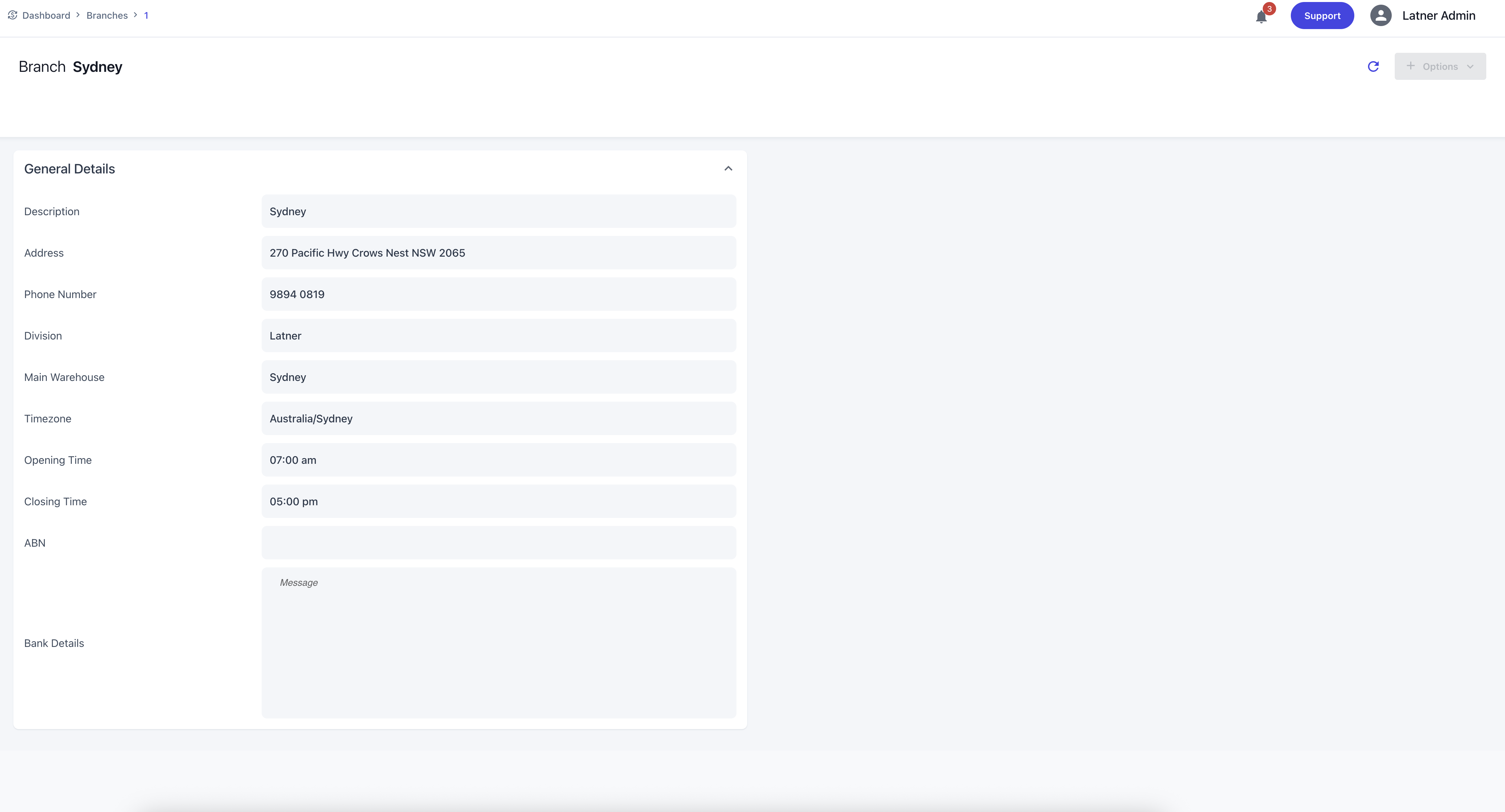
Once created, branches allow configuration of:
Opening and Closing Times
ABN and Bank Details (if different from the company)
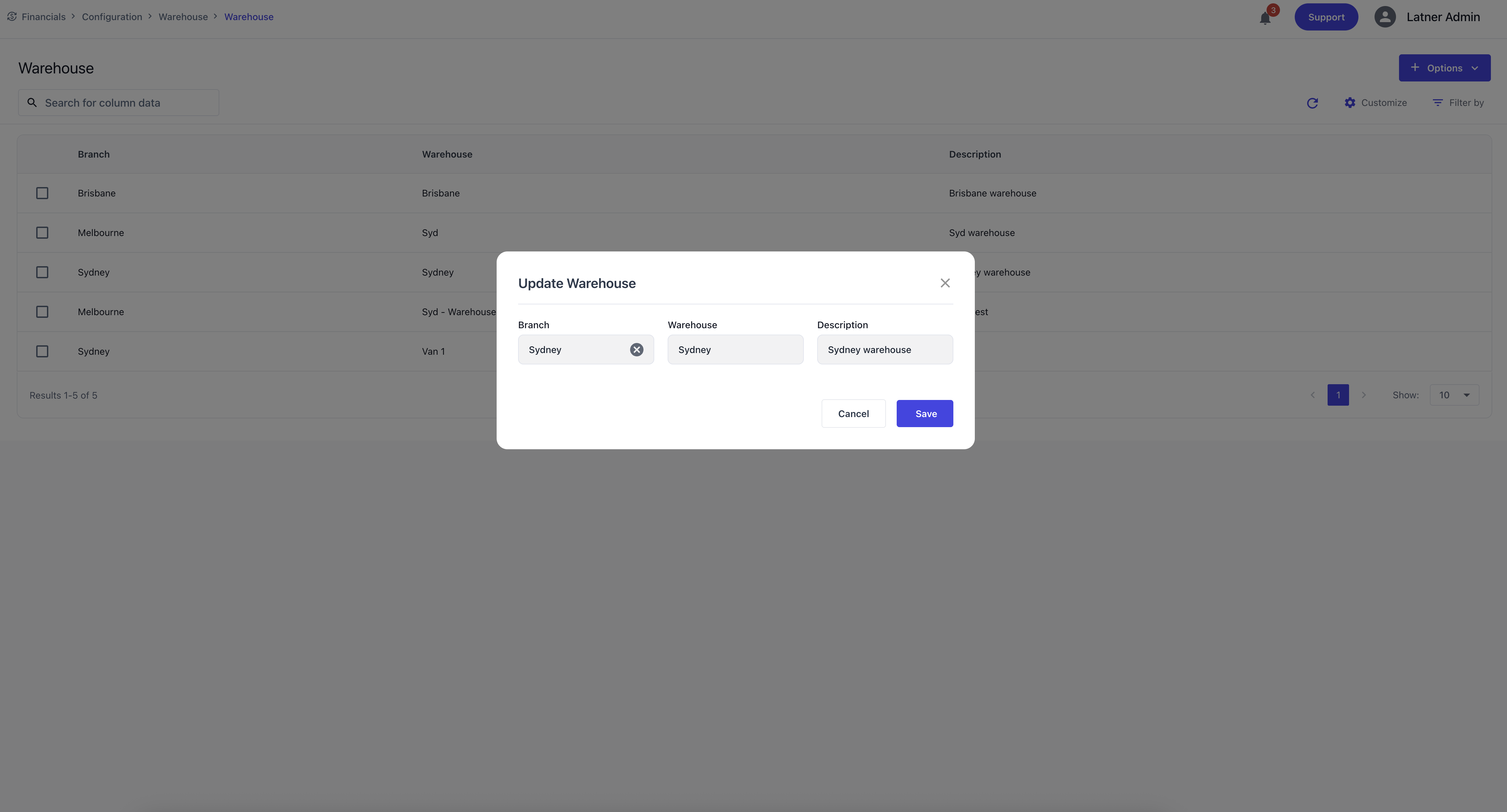
Warehouse
Warehouses sit under Branches and represent stock‑holding locations used for inventory management. They ensure stock items are organised and traceable across the business.
When creating a Warehouse, you specify:
Branch: the parent branch.
Warehouse Name: the identifier for the warehouse.
Description: additional context or purpose.
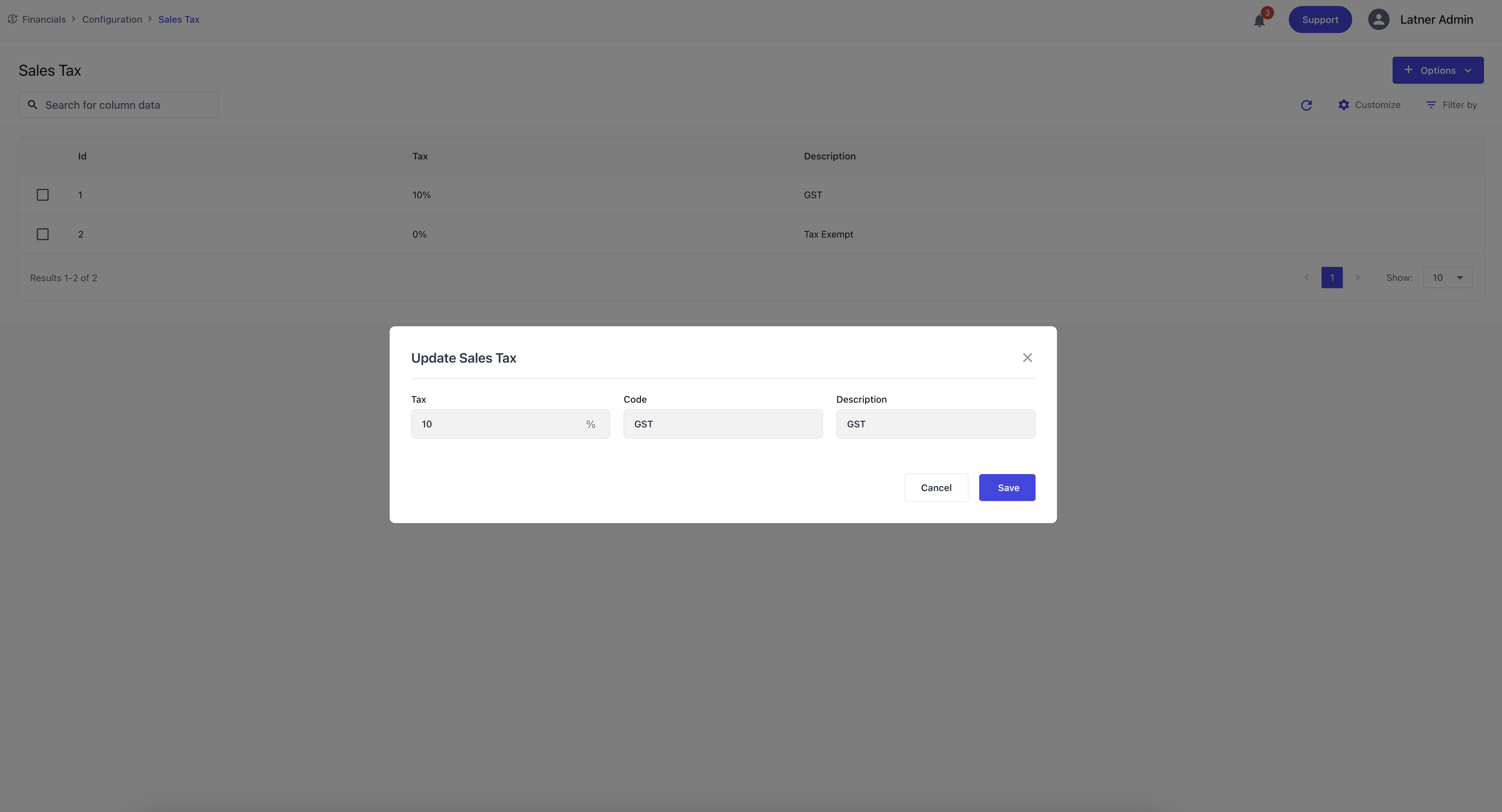
Sales Tax
Sales Tax entries define the tax rates applied to sales transactions. They ensure that invoices are calculated correctly and comply with tax requirements.
When creating a Sales Tax entry, you specify:
Tax Percentage: the rate applied (e.g., 10%).
Code: the tax code (e.g., GST, TAXEXEMPT).
Description: the purpose or context of the tax.
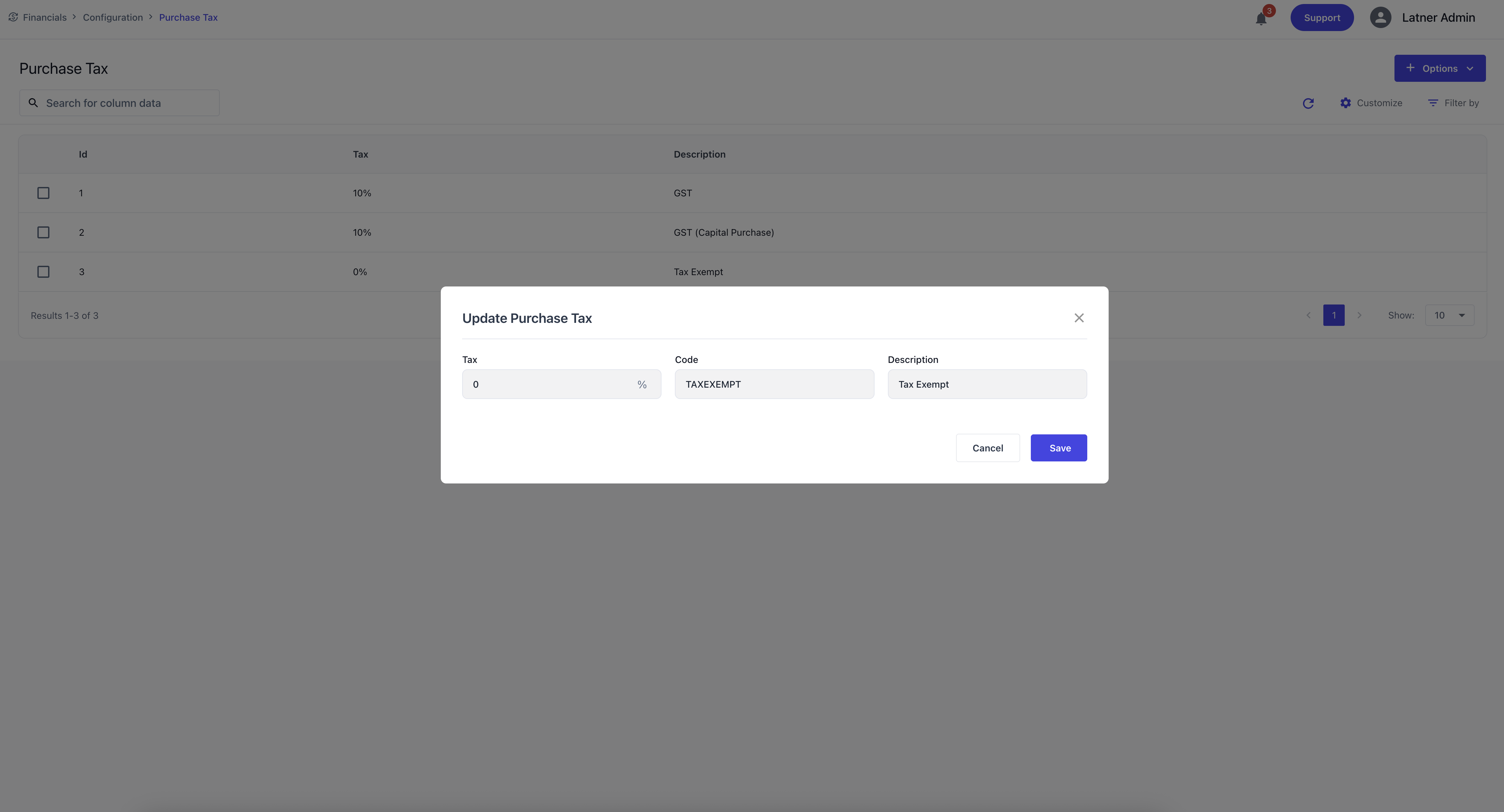
Purchase Tax
Purchase Tax entries define the tax rates applied to supplier invoices. They ensure that purchasing transactions are recorded accurately and comply with tax rules.
When creating a Purchase Tax entry, you specify:
Tax Percentage: the rate applied (e.g., 10%).
Code: the tax code (e.g., GST, TAXEXEMPT).
Description: the purpose or context of the tax.
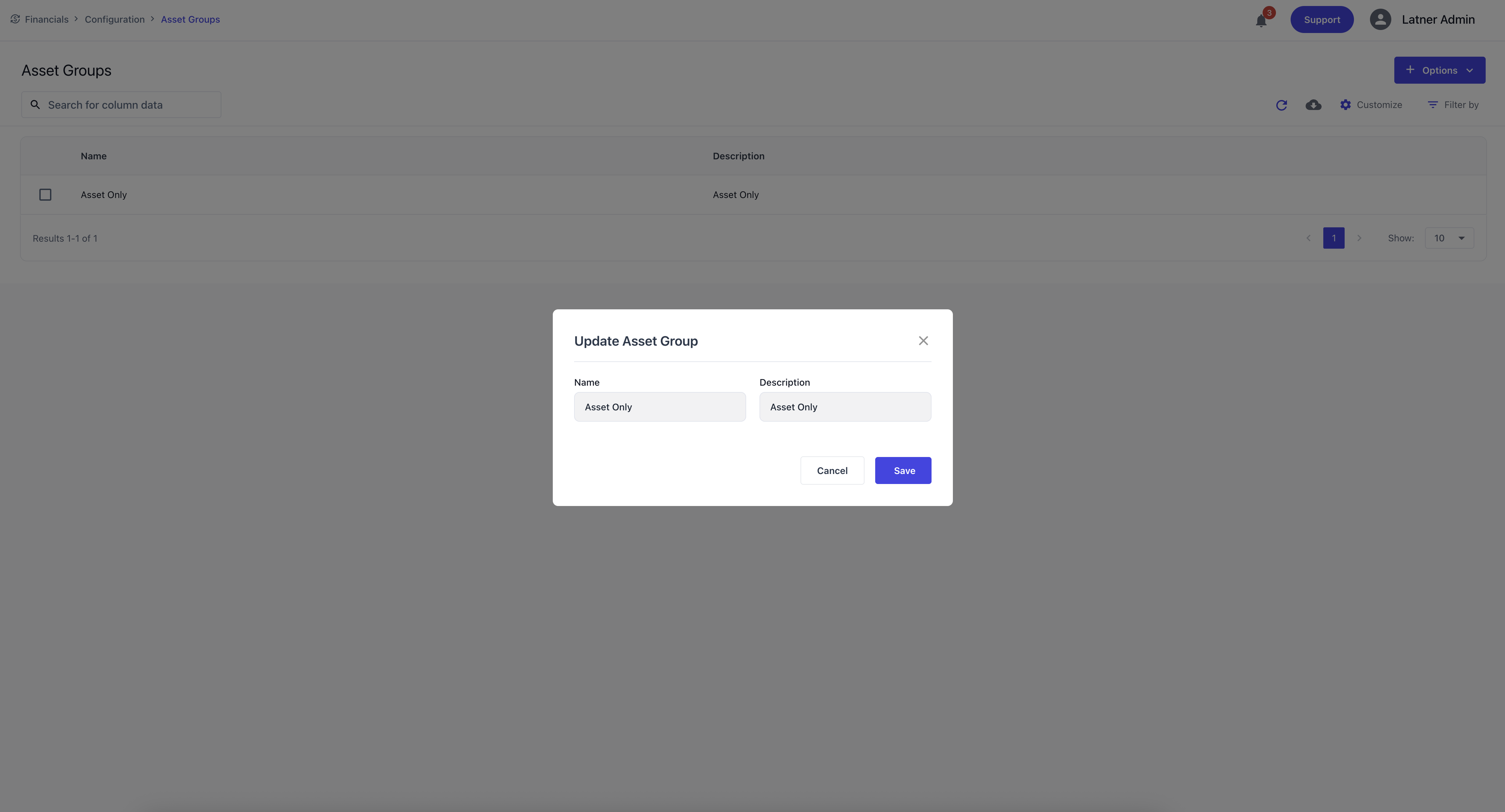
Asset Groups
Asset Groups are used to categorise assets for depreciation and reporting. They ensure that assets are grouped logically for financial and operational analysis. When creating an Asset Group, you specify the name and description.
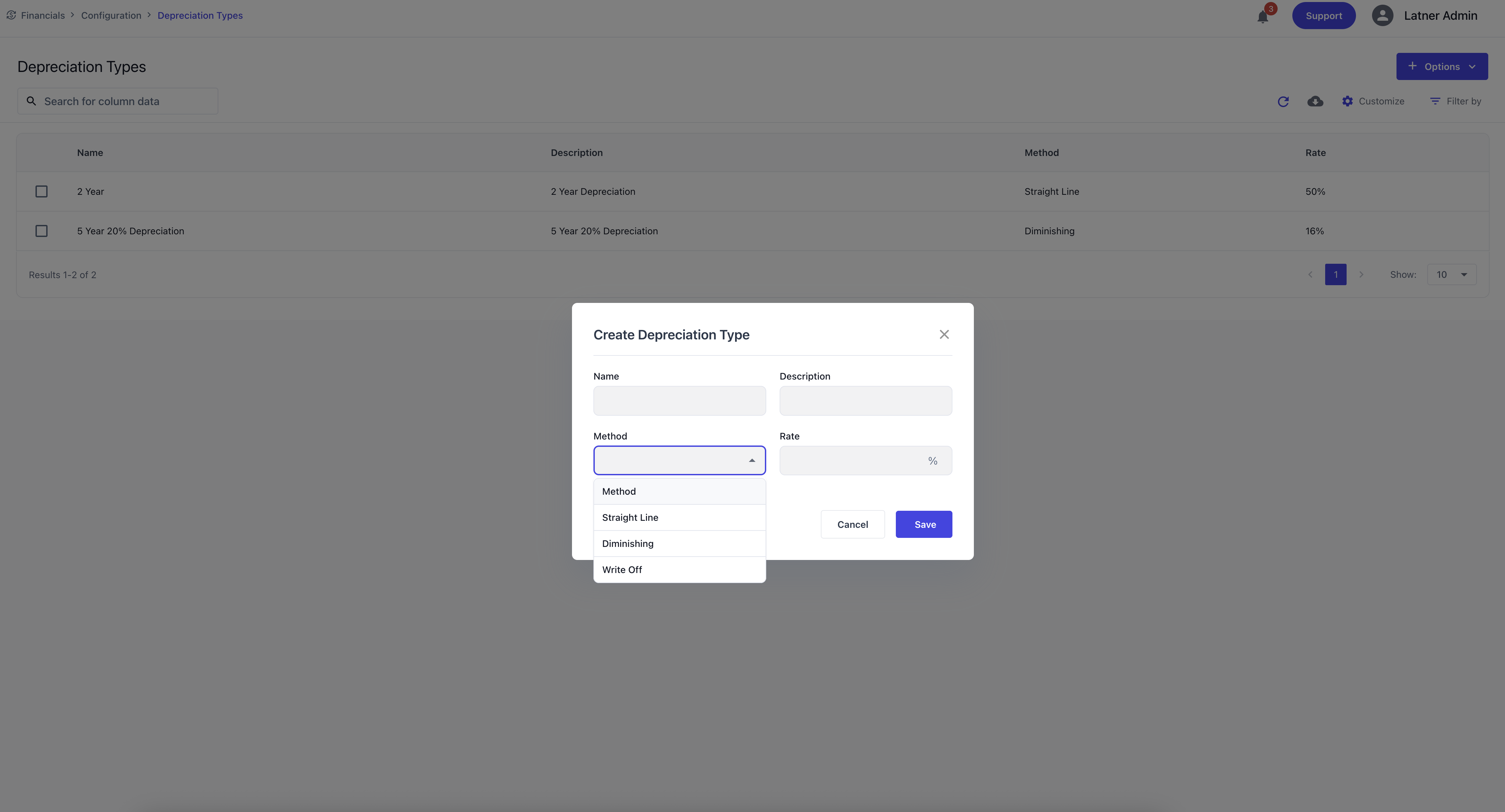
Depreciation Types
Depreciation Types define how assets depreciate over time. They ensure that depreciation is calculated consistently and in accordance with financial policy.
When creating a Depreciation Type, you specify:
Name: the identifier for the depreciation method.
Description: the purpose or context.
Method: the depreciation approach (straight line, diminishing, write‑off).
Rate Percentage: the rate applied to the asset value.
Accounting Integration
An Integration Screen that …
Payment Gateway Integration
An Integration Screen that …
Rouse Integration
An Integration Screen that …
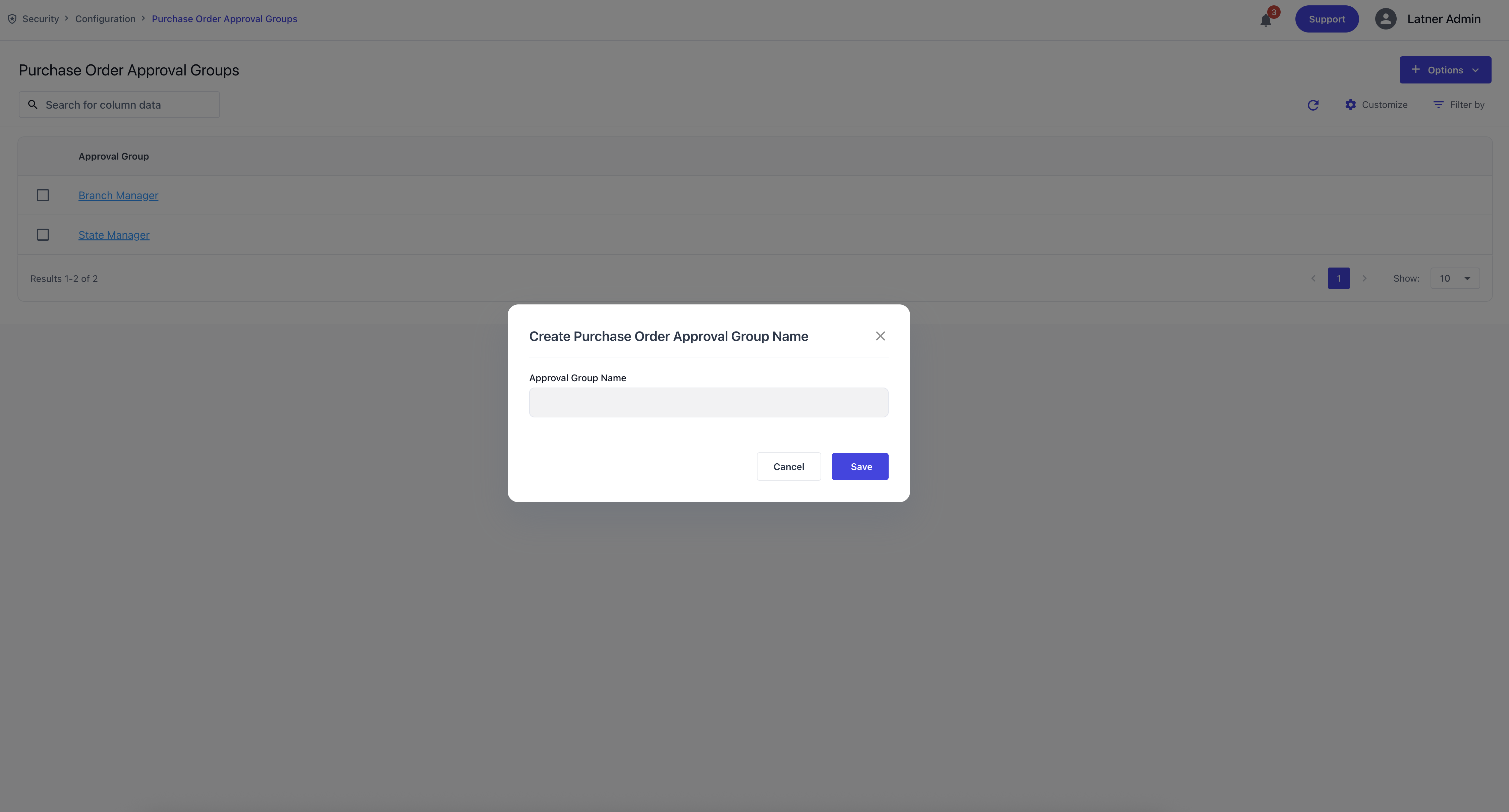
Purchase Order Approval Groups
Purchase Order Approval Groups are used to control who can authorise purchase orders and up to what value. These groups ensure purchasing is governed by clear financial controls.
Approval groups are enforced when the global setting Enforce Purchase Order Approval Limits is enabled.

When creating a Purchase Order Approval Group, you specify:
Approval Group Name: the identifier for the group.
Description (if applicable): the purpose or context.
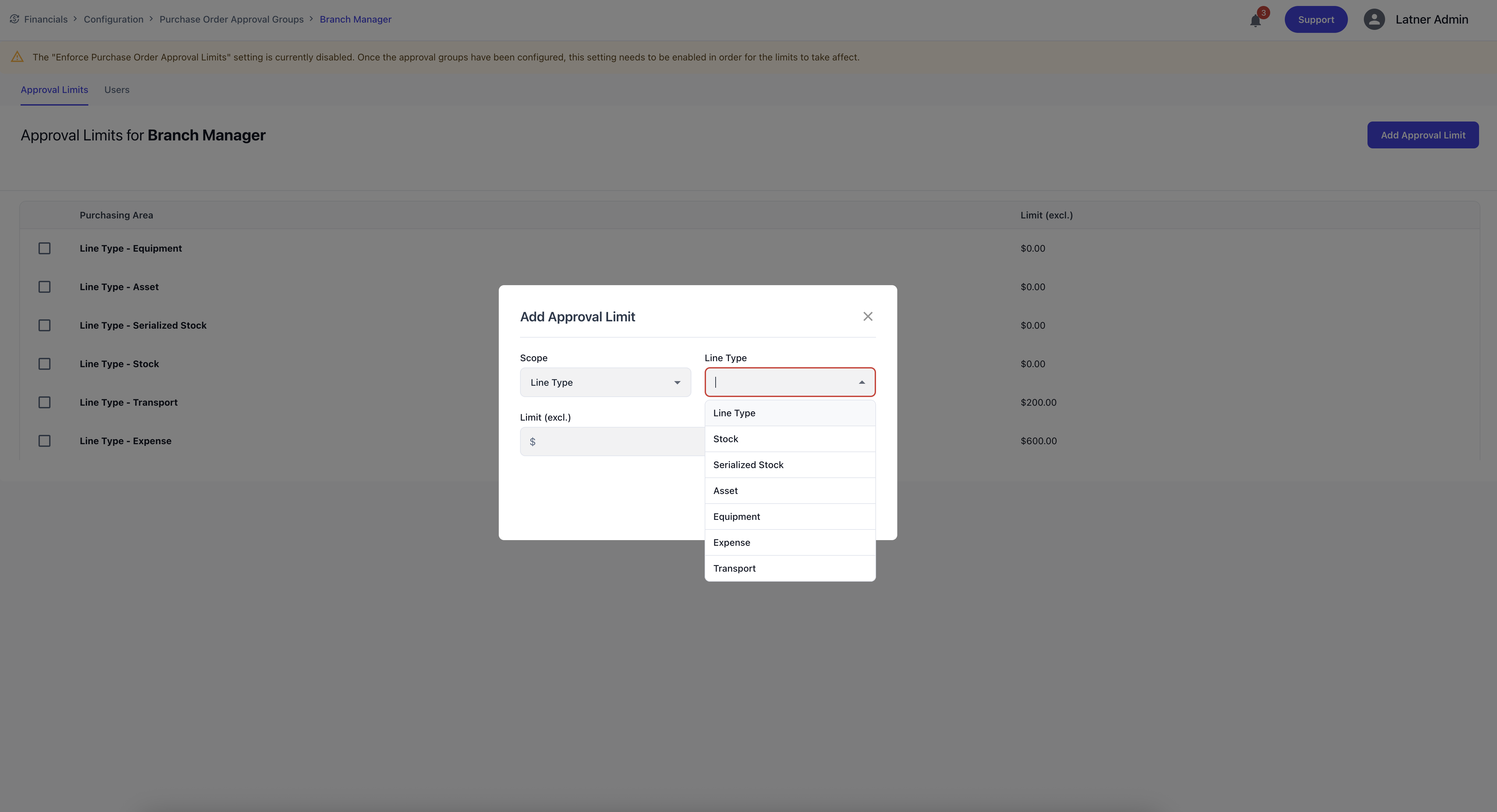
Once created, you can add one or more approval limits. Each approval limit defines:
Scope: either a configurable expense or an system-set line type.
Line/Expense Type: the type of item being purchased.
Approval Limit (excl. GST): the maximum amount the user can approve for that line type.
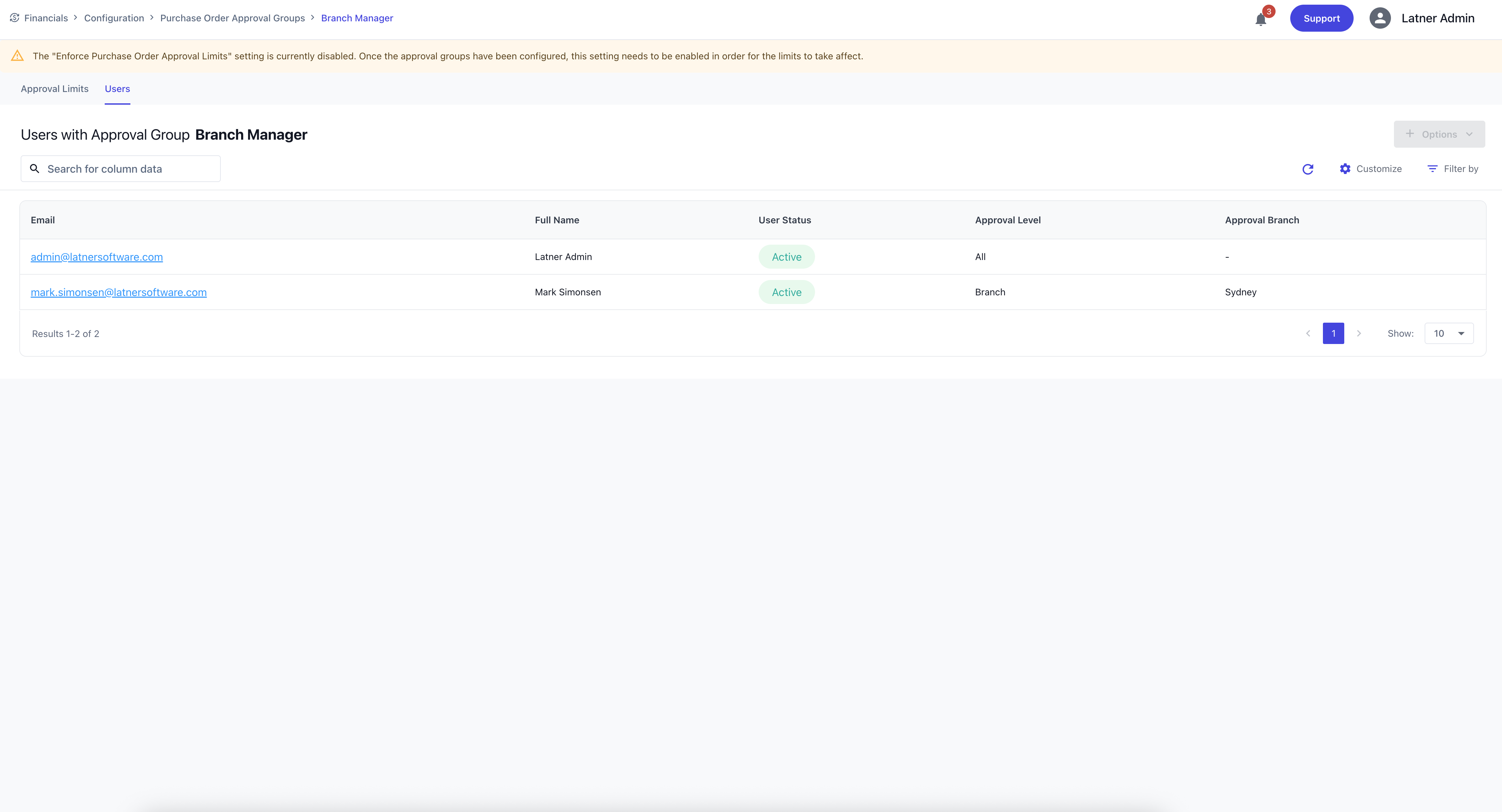
Approval groups are later assigned to Users through their user settings, determining the credit limits they are authorised to approve. See this section on Users on how to assign Approval Groups. You could also see the Users that are currently assigned on this group on the top tab.
Financials Report Config
Purchase Order PDF Templates
Security Module
Permission Groups
Permissions are organised into groups that typically align with departments permissions. When creating a Permission Group, you define the name.
Inside the Permission Group, you’ll see a list of modules, each containing the specific permissions you can enable or disable for that group, all outlined below:
After creating the Permission Group, assign it to the user using the process outlined in the linked Users page. You could also see the Users that are currently assigned on this group on the top tab.
Notification Groups
Similar to Permissions, Notifications are also organised into groups that typically align with department notifications. When creating a Notification Group, you define the name and description.
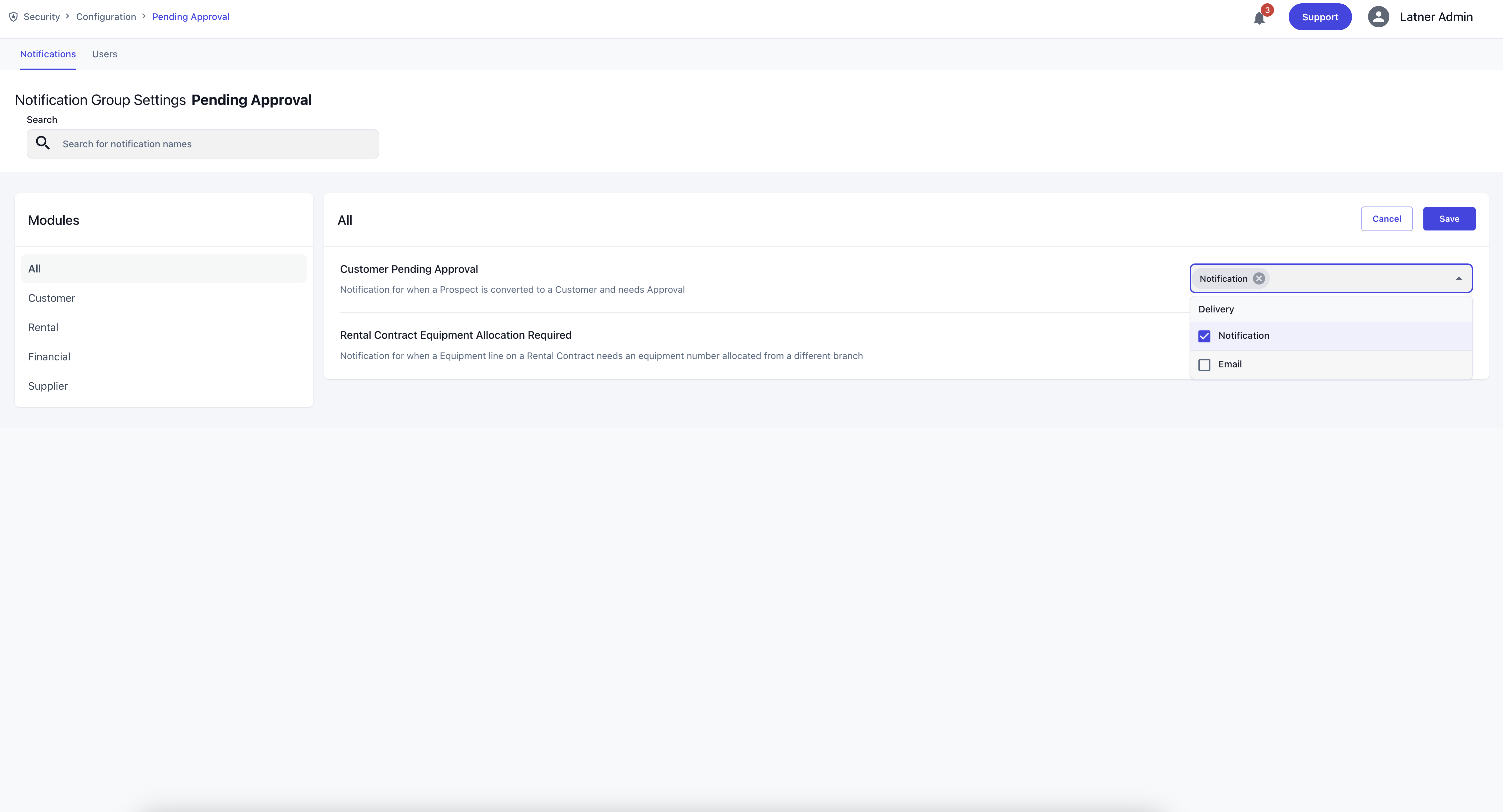
Inside the Notification Group, you’ll see a list of modules, each containing specific notification settings. For each setting, you can choose whether the group should receive an in‑system notification, an email, or none at all.
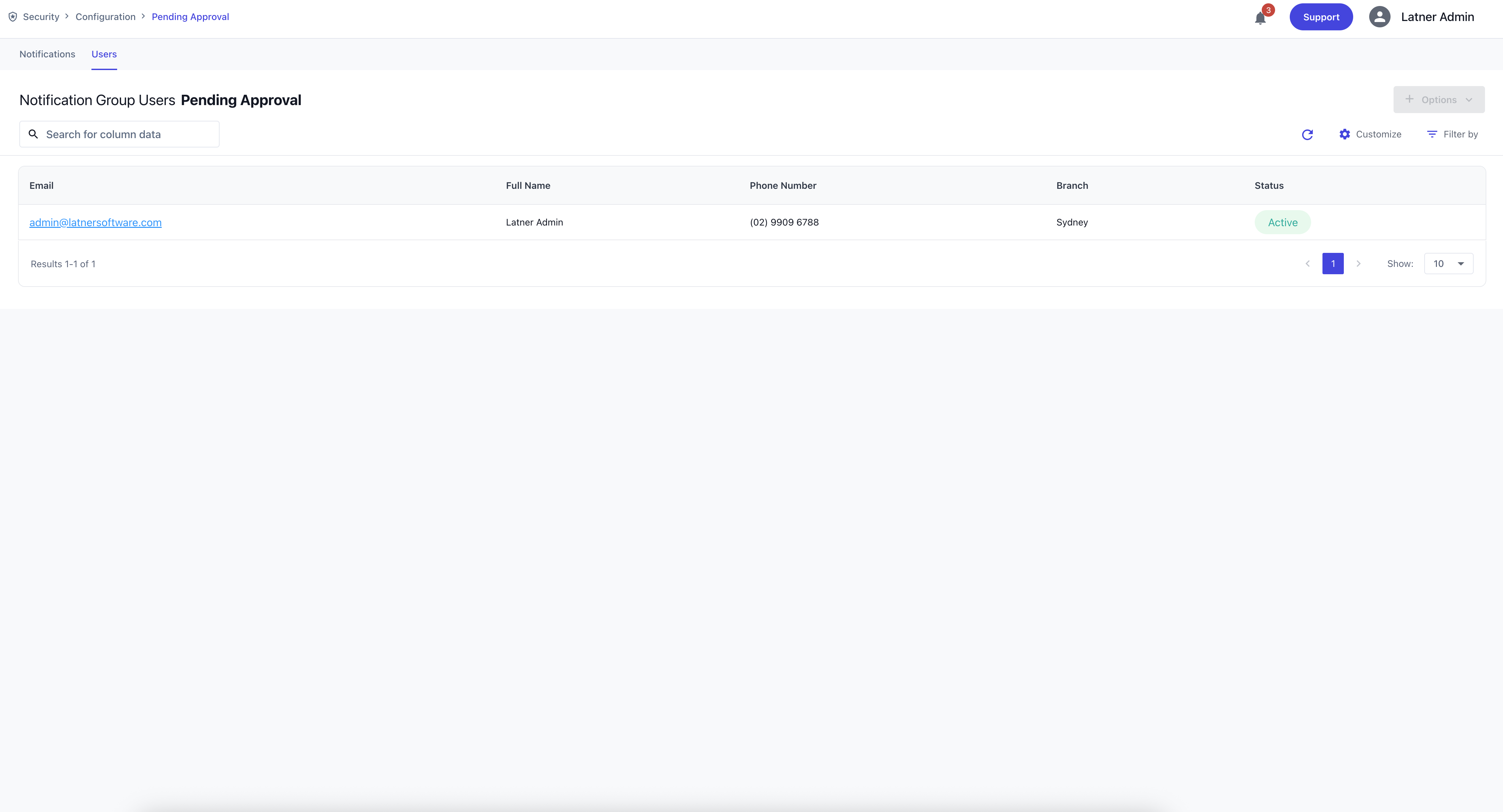
After creating the Notification Group, assign it to the user using the process outlined in the linked Users page. You could also see the Users that are currently assigned on this group on the top tab.
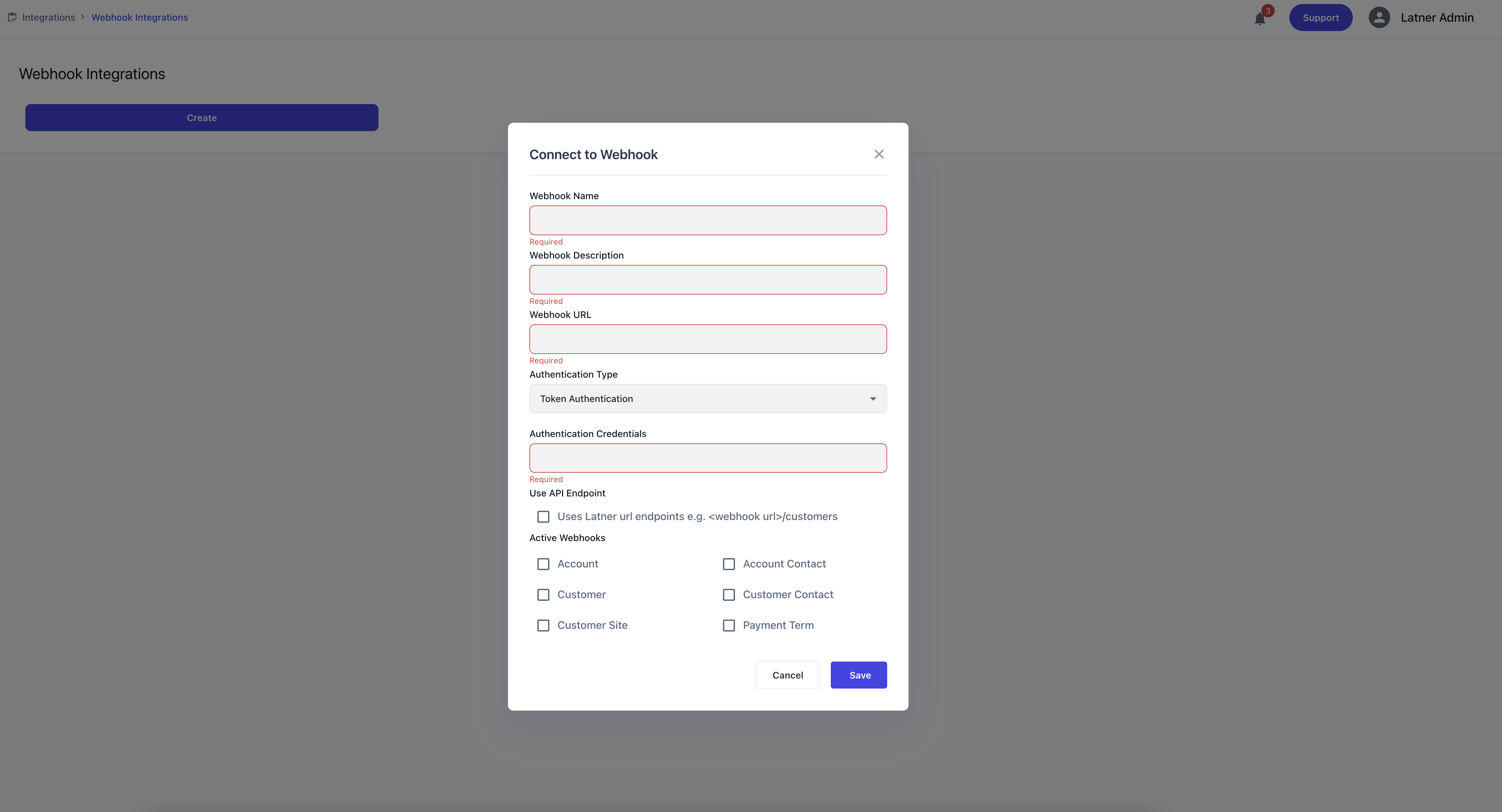
Webhook Integrations
An Integration Screen that …